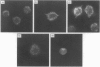
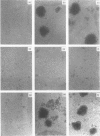
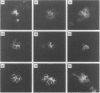
Abstract
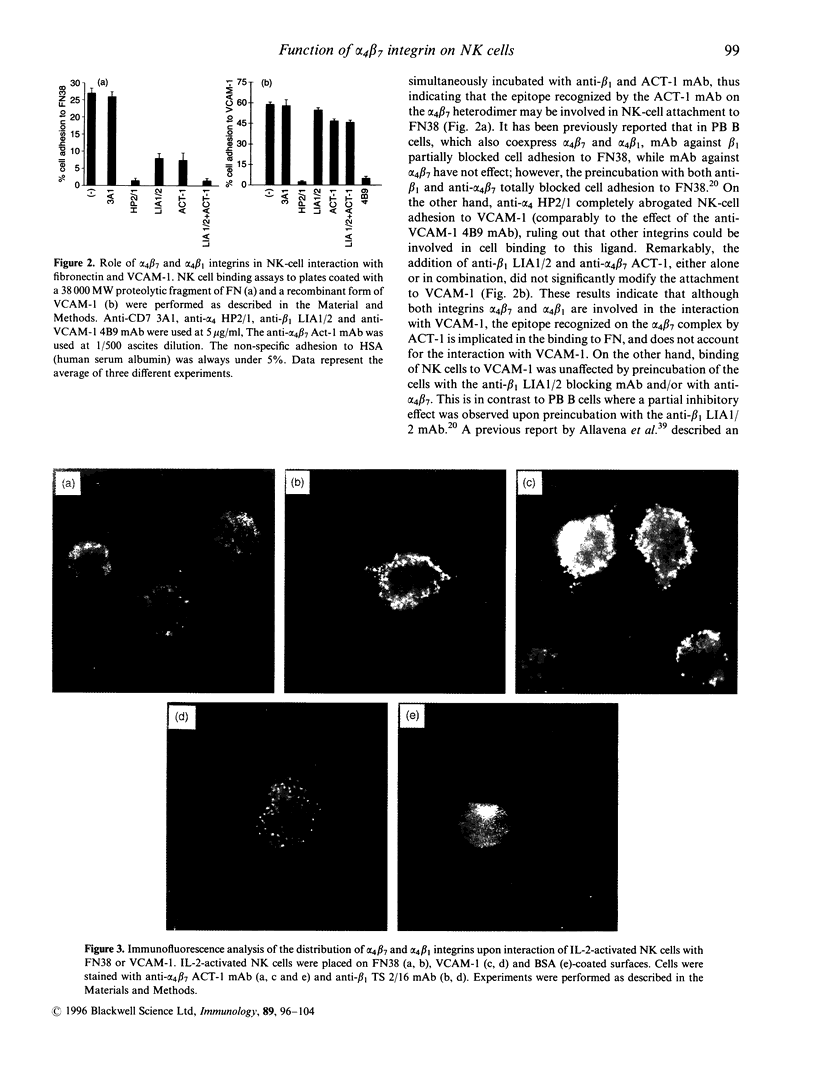
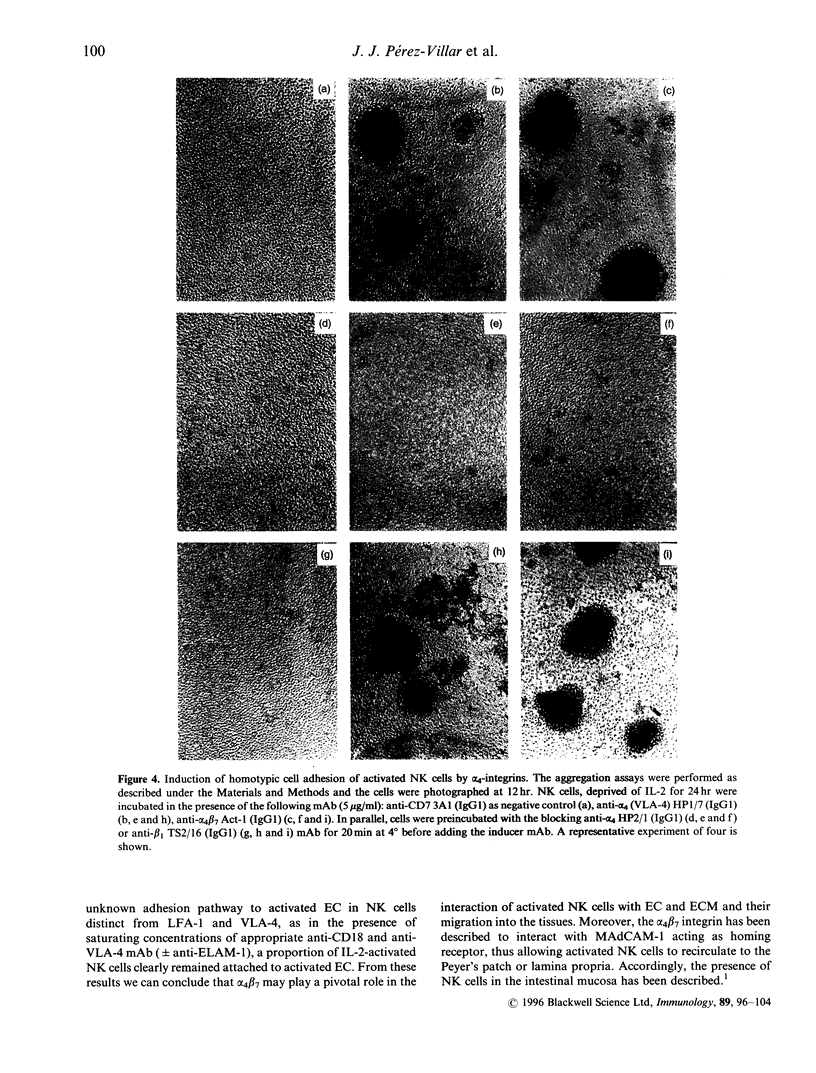
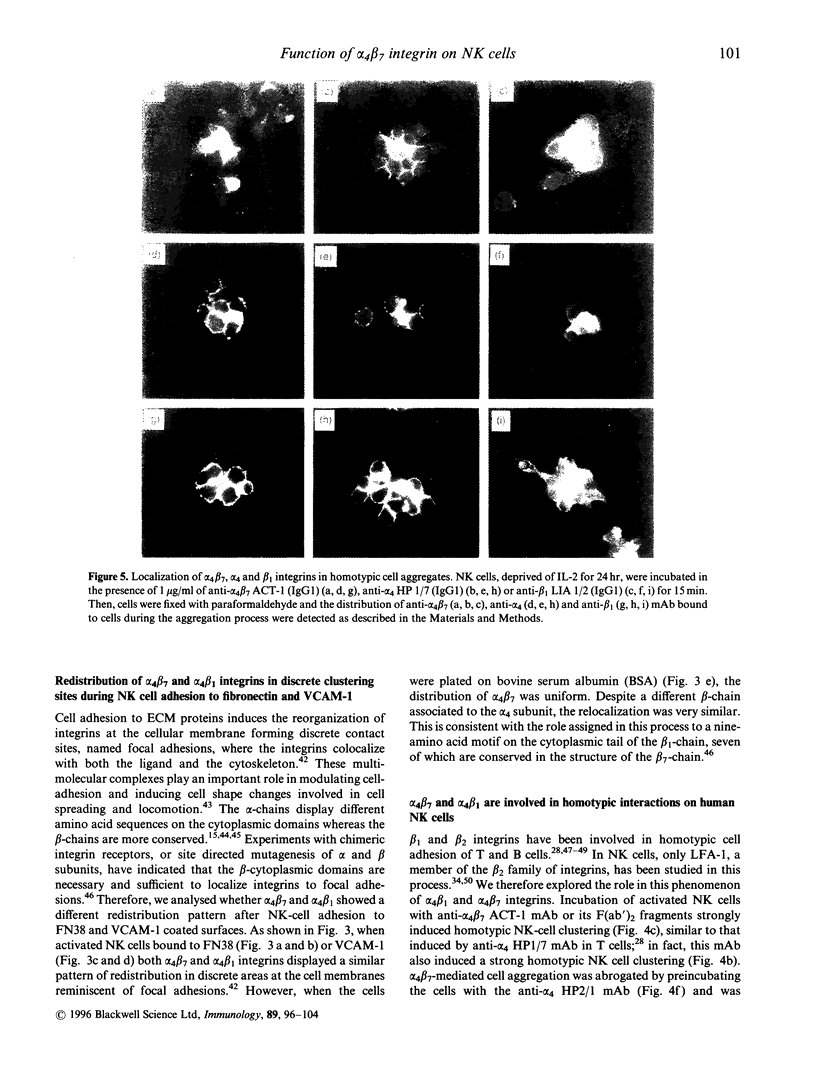
In this report we have analysed the expression and function of the alpha 4/beta 7 heterodimer in human natural killer (NK) cells. The expression of alpha 4 beta 7 is induced in NK cells upon activation as the anti alpha 4 beta 2 ACT-1 monoclonal antibody (mAb) family stained a minority of peripheral blood NK cells, whereas it strongly reacted with in vitro long-term interleukin-2 (IL-2)-activated NK cells. Incubation with ACT-1 on its F(ab) fragments induced a strong homotypic adhesion of NK cells, comparable to than stimulated by the anti-alpha 4 HPI 7 mAb. Cell cell interaction induced by the ACT-1 mAb was only prevented by another anti-alpha 4 mAb (HP2.1) that recognizes a different epitope. In alpha 4 beta 7-mediated cell aggregation the alpha 4 beta 7 heterodimer was redistributed to intercellular contact sites thus, suggesting a direct involvement of this integrin in the formation of cell clusters. In NK cells attached to Fibronectin (FN38) or vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1), both alpha 4 beta 7 and alpha 4 beta 7 integrins were redistributed at the ventral cellular membrane forming discrete contact sites. The ACT-1 mAb only partially blocked NK cell binding to FN38, but in combination with the anti-beta 7 mAb LIAI 2, NK cell binding to FN38 was completely inhibited. In contrast. ACT-1 did not modify NK cell adhesion to VCAM-1 thus supporting the theory that the alpha 4 beta 7 binding sites for both ligands appear to be different. Our results indicate that upon IL-2-activation, expression of functional alpha 4 beta-integrin is induced on NK cells potentially participating in their interaction with both extracellular matrix and endothelial cells.
Full text
PDF

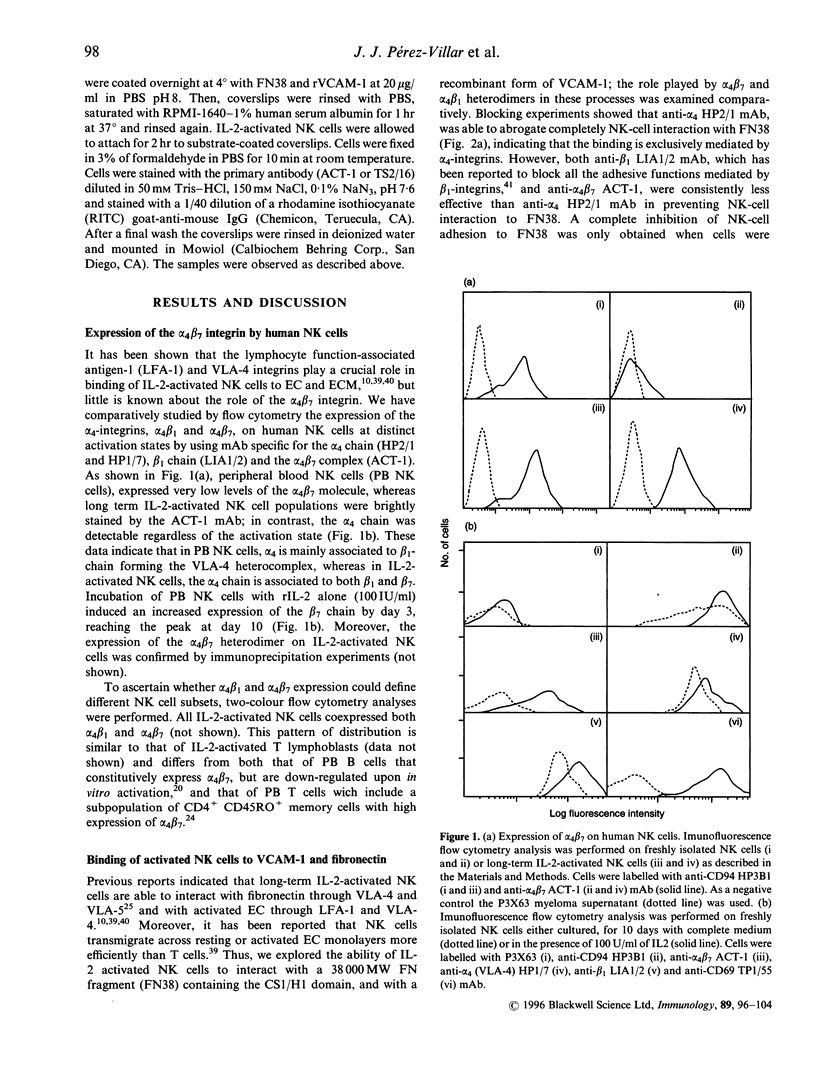



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acevedo A., Aramburu J., López J., Fernández-Herrera J., Fernández-Rañada J. M., López-Botet M. Identification of natural killer (NK) cells in lesions of human cutaneous graft-versus-host disease: expression of a novel NK-associated surface antigen (Kp43) in mononuclear infiltrates. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Oct;97(4):659–666. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12483724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allavena P., Paganin C., Martin-Padura I., Peri G., Gaboli M., Dejana E., Marchisio P. C., Mantovani A. Molecules and structures involved in the adhesion of natural killer cells to vascular endothelium. J Exp Med. 1991 Feb 1;173(2):439–448. doi: 10.1084/jem.173.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Altevogt P., Hubbe M., Ruppert M., Lohr J., von Hoegen P., Sammar M., Andrew D. P., McEvoy L., Humphries M. J., Butcher E. C. The alpha 4 integrin chain is a ligand for alpha 4 beta 7 and alpha 4 beta 1. J Exp Med. 1995 Aug 1;182(2):345–355. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramburu J., Balboa M. A., Ramírez A., Silva A., Acevedo A., Sánchez-Madrid F., De Landázuri M. O., López-Botet M. A novel functional cell surface dimer (Kp43) expressed by natural killer cells and T cell receptor-gamma/delta+ T lymphocytes. I. Inhibition of the IL-2-dependent proliferation by anti-Kp43 monoclonal antibody. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):3238–3247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aramburu J., Balboa M. A., Rodríguez A., Melero I., Alonso M., Alonso J. L., López-Botet M. Stimulation of IL-2-activated natural killer cells through the Kp43 surface antigen up-regulates TNF-alpha production involving the LFA-1 integrin. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3420–3429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Argraves W. S., Suzuki S., Arai H., Thompson K., Pierschbacher M. D., Ruoslahti E. Amino acid sequence of the human fibronectin receptor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;105(3):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.3.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo A. G., Sánchez-Mateos P., Campanero M. R., Martín-Padura I., Dejana E., Sánchez-Madrid F. Regulation of the VLA integrin-ligand interactions through the beta 1 subunit. J Cell Biol. 1992 May;117(3):659–670. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.3.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bednarczyk J. L., McIntyre B. W. A monoclonal antibody to VLA-4 alpha-chain (CDw49d) induces homotypic lymphocyte aggregation. J Immunol. 1990 Feb 1;144(3):777–784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berlin C., Berg E. L., Briskin M. J., Andrew D. P., Kilshaw P. J., Holzmann B., Weissman I. L., Hamann A., Butcher E. C. Alpha 4 beta 7 integrin mediates lymphocyte binding to the mucosal vascular addressin MAdCAM-1. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):185–195. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90305-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi G., Sironi M., Ghibaudi E., Selvaggini C., Elices M., Allavena P., Mantovani A. Migration of natural killer cells across endothelial cell monolayers. J Immunol. 1993 Nov 15;151(10):5135–5144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burridge K., Fath K., Kelly T., Nuckolls G., Turner C. Focal adhesions: transmembrane junctions between the extracellular matrix and the cytoskeleton. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:487–525. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.002415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanero M. R., Arroyo A. G., Pulido R., Ursa A., de Matías M. S., Sánchez-Mateos P., Kassner P. D., Chan B. M., Hemler M. E., Corbí A. L. Functional role of alpha 2/beta 1 and alpha 4/beta 1 integrins in leukocyte intercellular adhesion induced through the common beta 1 subunit. Eur J Immunol. 1992 Dec;22(12):3111–3119. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830221213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campanero M. R., Pulido R., Ursa M. A., Rodríguez-Moya M., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. An alternative leukocyte homotypic adhesion mechanism, LFA-1/ICAM-1-independent, triggered through the human VLA-4 integrin. J Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;110(6):2157–2165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.6.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrián M., Yagüe E., Rincón M., López-Botet M., de Landázuri M. O., Sánchez-Madrid F. Triggering of T cell proliferation through AIM, an activation inducer molecule expressed on activated human lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1988 Nov 1;168(5):1621–1637. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.5.1621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dustin M. L., Springer T. A. T-cell receptor cross-linking transiently stimulates adhesiveness through LFA-1. Nature. 1989 Oct 19;341(6243):619–624. doi: 10.1038/341619a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elices M. J., Osborn L., Takada Y., Crouse C., Luhowskyj S., Hemler M. E., Lobb R. R. VCAM-1 on activated endothelium interacts with the leukocyte integrin VLA-4 at a site distinct from the VLA-4/fibronectin binding site. Cell. 1990 Feb 23;60(4):577–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90661-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Pardo A., Wayner E. A., Carter W. G., Ferreira O. C., Jr Human B lymphocytes define an alternative mechanism of adhesion to fibronectin. The interaction of the alpha 4 beta 1 integrin with the LHGPEILDVPST sequence of the type III connecting segment is sufficient to promote cell attachment. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3361–3366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gismondi A., Mainiero F., Morrone S., Palmieri G., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. Triggering through CD16 or phorbol esters enhances adhesion of NK cells to laminin via very late antigen 6. J Exp Med. 1992 Nov 1;176(5):1251–1257. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.5.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gismondi A., Morrone S., Humphries M. J., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. Human natural killer cells express VLA-4 and VLA-5, which mediate their adhesion to fibronectin. J Immunol. 1991 Jan 1;146(1):384–392. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemler M. E. VLA proteins in the integrin family: structures, functions, and their role on leukocytes. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:365–400. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Crowe D. T., Weissman I. L., Holzmann B. Cloning and expression of mouse integrin beta p(beta 7): a functional role in Peyer's patch-specific lymphocyte homing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):8254–8258. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.8254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes R. O. Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90115-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inverardi L., Samaja M., Motterlini R., Mangili F., Bender J. R., Pardi R. Early recognition of a discordant xenogeneic organ by human circulating lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1416–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kansas G. S., Tedder T. F. Transmembrane signals generated through MHC class II, CD19, CD20, CD39, and CD40 antigens induce LFA-1-dependent and independent adhesion in human B cells through a tyrosine kinase-dependent pathway. J Immunol. 1991 Dec 15;147(12):4094–4102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keizer G. D., Visser W., Vliem M., Figdor C. G. A monoclonal antibody (NKI-L16) directed against a unique epitope on the alpha-chain of human leukocyte function-associated antigen 1 induces homotypic cell-cell interactions. J Immunol. 1988 Mar 1;140(5):1393–1400. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilshaw P. J., Murant S. J. Expression and regulation of beta 7(beta p) integrins on mouse lymphocytes: relevance to the mucosal immune system. Eur J Immunol. 1991 Oct;21(10):2591–2597. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830211041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitayama J., Juji T., Atomi Y., Kuroda A., Muto T., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Minami M. Transendothelial migration activity of lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cells. J Immunol. 1993 Aug 1;151(3):1663–1672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarovits A. I., Moscicki R. A., Kurnick J. T., Camerini D., Bhan A. K., Baird L. G., Erikson M., Colvin R. B. Lymphocyte activation antigens. I. A monoclonal antibody, anti-Act I, defines a new late lymphocyte activation antigen. J Immunol. 1984 Oct;133(4):1857–1862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mainiero F., Gismondi A., Milella M., Morrone S., Palmieri G., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. Long term activation of natural killer cells results in modulation of beta 1-integrin expression and function. J Immunol. 1994 Jan 15;152(2):446–454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre K. W., Welsh R. M. Accumulation of natural killer and cytotoxic T large granular lymphocytes in the liver during virus infection. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1667–1681. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melero I., Balboa M. A., Alonso J. L., Yagüe E., Pivel J. P., Sanchez-Madrid F., López-Botet M. Signaling through the LFA-1 leucocyte integrin actively regulates intercellular adhesion and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Aug;23(8):1859–1865. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830230819. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mentzer S. J., Gromkowski S. H., Krensky A. M., Burakoff S. J., Martz E. LFA-1 membrane molecule in the regulation of homotypic adhesions of human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):9–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naume B., Espevik T. Effects of IL-7 and IL-2 on highly enriched CD56+ natural killer cells. A comparative study. J Immunol. 1991 Oct 1;147(7):2208–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nemlander A., Saksela E., Häyry P. Are "natural killer" cells involved in allograft rejection? Eur J Immunol. 1983 Apr;13(4):348–350. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830130415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmieri G., Serra A., De Maria R., Gismondi A., Milella M., Piccoli M., Frati L., Santoni A. Cross-linking of alpha 4 beta 1 and alpha 5 beta 1 fibronectin receptors enhances natural killer cell cytotoxic activity. J Immunol. 1995 Dec 1;155(11):5314–5322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. M., Cepek K. L., Russell G. J., Shaw S. K., Posnett D. N., Schwarting R., Brenner M. B. A family of beta 7 integrins on human mucosal lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1924–1928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pavalko F. M., Otey C. A. Role of adhesion molecule cytoplasmic domains in mediating interactions with the cytoskeleton. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1994 Apr;205(4):282–293. doi: 10.3181/00379727-205-43709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B. Lymphokine-activated killer cells, natural killer cells and cytokines. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):49–55. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90076-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perussia B., Ramoni C., Anegon I., Cuturi M. C., Faust J., Trinchieri G. Preferential proliferation of natural killer cells among peripheral blood mononuclear cells cocultured with B lymphoblastoid cell lines. Nat Immun Cell Growth Regul. 1987;6(4):171–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postigo A. A., Sánchez-Mateos P., Lazarovits A. I., Sánchez-Madrid F., de Landázuri M. O. Alpha 4 beta 7 integrin mediates B cell binding to fibronectin and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Expression and function of alpha 4 integrins on human B lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1993 Sep 1;151(5):2471–2483. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reszka A. A., Hayashi Y., Horwitz A. F. Identification of amino acid sequences in the integrin beta 1 cytoplasmic domain implicated in cytoskeletal association. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüegg C., Postigo A. A., Sikorski E. E., Butcher E. C., Pytela R., Erle D. J. Role of integrin alpha 4 beta 7/alpha 4 beta P in lymphocyte adherence to fibronectin and VCAM-1 and in homotypic cell clustering. J Cell Biol. 1992 Apr;117(1):179–189. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.1.179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Tachibana K., Nojima Y., D'Avirro N., Morimoto C. Role of the VLA-4 molecule in T cell costimulation. Identification of the tyrosine phosphorylation pattern induced by the ligation of VLA-4. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 15;155(6):2938–2947. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweighoffer T., Tanaka Y., Tidswell M., Erle D. J., Horgan K. J., Luce G. E., Lazarovits A. I., Buck D., Shaw S. Selective expression of integrin alpha 4 beta 7 on a subset of human CD4+ memory T cells with Hallmarks of gut-trophism. J Immunol. 1993 Jul 15;151(2):717–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu Y., Shaw S. Lymphocyte interactions with extracellular matrix. FASEB J. 1991 Jun;5(9):2292–2299. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.9.1860621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Adhesion receptors of the immune system. Nature. 1990 Aug 2;346(6283):425–434. doi: 10.1038/346425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Mateos P., Campanero M. R., Balboa M. A., Sánchez-Madrid F. Co-clustering of beta 1 integrins, cytoskeletal proteins, and tyrosine-phosphorylated substrates during integrin-mediated leukocyte aggregation. J Immunol. 1993 Oct 1;151(7):3817–3828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G. Biology of natural killer cells. Adv Immunol. 1989;47:187–376. doi: 10.1016/S0065-2776(08)60664-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wayner E. A., Garcia-Pardo A., Humphries M. J., McDonald J. A., Carter W. G. Identification and characterization of the T lymphocyte adhesion receptor for an alternative cell attachment domain (CS-1) in plasma fibronectin. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1321–1330. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whiteside T. L., Herberman R. B. The role of natural killer cells in immune surveillance of cancer. Curr Opin Immunol. 1995 Oct;7(5):704–710. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(95)80080-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiltrout R. H., Mathieson B. J., Talmadge J. E., Reynolds C. W., Zhang S. R., Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Augmentation of organ-associated natural killer activity by biological response modifiers. Isolation and characterization of large granular lymphocytes from the liver. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1431–1449. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuan Q., Jiang W. M., Leung E., Hollander D., Watson J. D., Krissansen G. W. Molecular cloning of the mouse integrin beta 7 subunit. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7352–7358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zapata J. M., Campanero M. R., Marazuela M., Sánchez-Madrid F., de Landázuri M. O. B-cell homotypic adhesion through exon-A restricted epitopes of CD45 involves LFA-1/ICAM-1, ICAM-3 interactions, and induces coclustering of CD45 and LFA-1. Blood. 1995 Sep 1;86(5):1861–1872. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- del Pozo M. A., Sánchez-Mateos P., Nieto M., Sánchez-Madrid F. Chemokines regulate cellular polarization and adhesion receptor redistribution during lymphocyte interaction with endothelium and extracellular matrix. Involvement of cAMP signaling pathway. J Cell Biol. 1995 Oct;131(2):495–508. doi: 10.1083/jcb.131.2.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]