Abstract
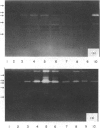
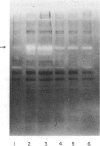
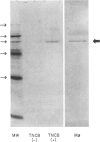
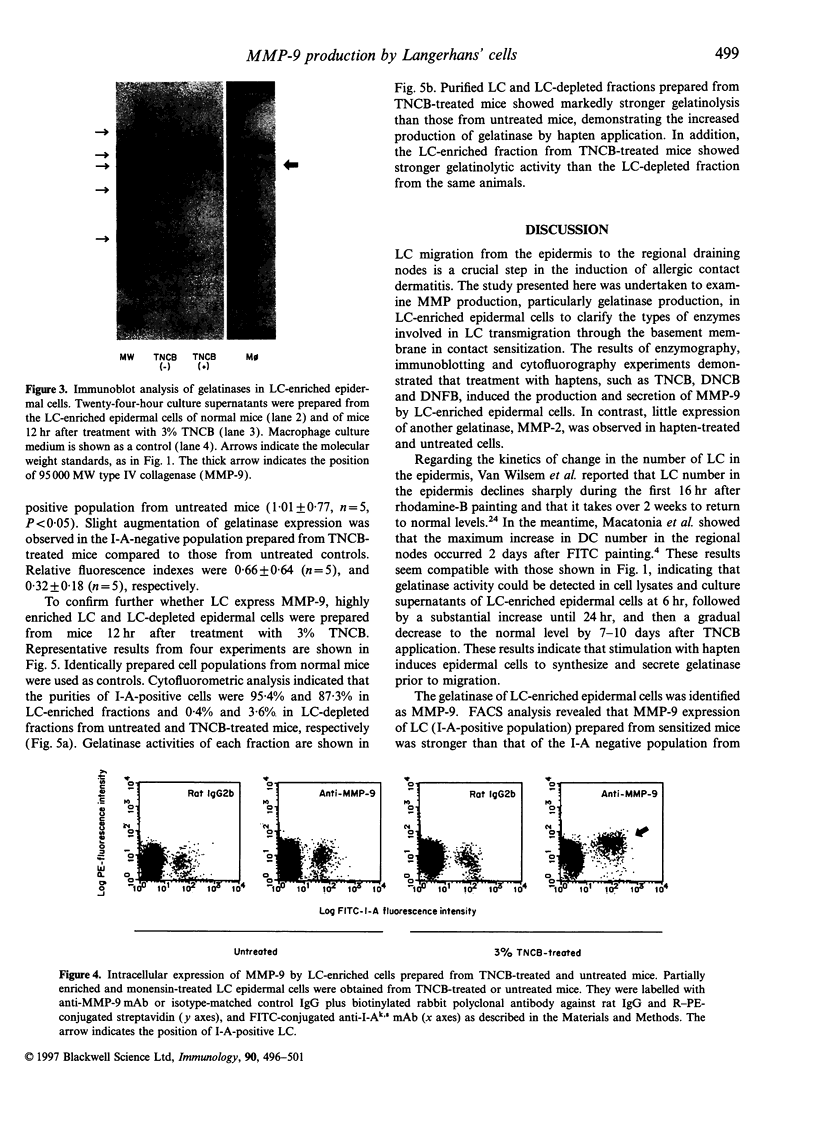
For initiation of the contact hypersensitivity response, epidermal Langerhans' cells (LC) migrate from the epidermis to draining nodes via afferent lymphatics by passing through the basement membrane. In this study, we examined production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in LC-enriched epidermal cells to clarify the type of enzymes involved in LC transmigration through the basement membrane. Using gelatine enzymography and immunoblotting analysis, 95,000 MW type IV collagenase (MMP-9) was found to be produced by LC-enriched epidermal cells. Analysis of the kinetics of MMP-9 expression showed that its production was induced within 6 hr after application of 2,4,6-trinitrochlorobenzene (TNCB), substantially increased between 12 hr and 24 hr, and then decreased to the normal level by 7 to 10 days. Other haptens, such as 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene and 2,4-dinitrofluorobenzene, also induced MMP-9 expression. Fluoroescence-activated cell sorter analysis revealed that LC were one of the major cell types to express MMP-9 in response to TNCB. In addition, highly enriched LC from sensitized skin were shown to express strong gelatinolytic activity. These results indicate that LC by themselves, as well as other epidermal cells, are capable of producing MMP-9, and suggest that MMP-9 may contribute to proteolysis associated with transmigration of LC in the induction phase of contact dermatitis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aiba S., Katz S. I. Phenotypic and functional characteristics of in vivo-activated Langerhans cells. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2791–2796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alcalay J., Craig J. N., Kripke M. L. Alterations in Langerhans cells and Thy-1+ dendritic epidermal cells in murine epidermis during the evolution of ultraviolet radiation-induced skin cancers. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 15;49(16):4591–4596. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baxter C. S., Andringa A., Chalfin K., Miller M. L. Effect of tumor-promoting agents on density and morphometric parameters of mouse epidermal Langerhans and Thy-1+ cells. Carcinogenesis. 1991 Jun;12(6):1017–1021. doi: 10.1093/carcin/12.6.1017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornelius L. A., Nehring L. C., Roby J. D., Parks W. C., Welgus H. G. Human dermal microvascular endothelial cells produce matrix metalloproteinases in response to angiogenic factors and migration. J Invest Dermatol. 1995 Aug;105(2):170–176. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12317080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowen K. S., Sakamoto M., Sakamoto S. Monensin inhibits collagenase production in osteoblastic cell cultures and also inhibits both collagenase release and bone resorption in mouse calvaria cultures. Biochem Int. 1985 Sep;11(3):273–280. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch M., Fielding I., Kimber I. Modulation of epidermal Langerhans' cell frequency by tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Immunology. 1994 Mar;81(3):395–401. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumberbatch M., Kimber I. Dermal tumour necrosis factor-alpha induces dendritic cell migration to draining lymph nodes, and possibly provides one stimulus for Langerhans' cell migration. Immunology. 1992 Feb;75(2):257–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emonard H., Grimaud J. A. Matrix metalloproteinases. A review. Cell Mol Biol. 1990;36(2):131–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the secreted forms of human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2493–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyuga S., Nishikawa Y., Sakata K., Tanaka H., Yamagata S., Sugita K., Saga S., Matsuyama M., Shimizu S. Autocrine factor enhancing the secretion of M(r) 95,000 gelatinase (matrix metalloproteinase 9) in serum-free medium conditioned with murine metastatic colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1994 Jul 1;54(13):3611–3616. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinnaird A., Peters S. W., Foster J. R., Kimber I. Dendritic cell accumulation in draining lymph nodes during the induction phase of contact allergy in mice. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1989;89(2-3):202–210. doi: 10.1159/000234947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Staquet M. J., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D. Development of motility of Langerhans cell through extracellular matrix by in vitro hapten contact. Eur J Immunol. 1994 Sep;24(9):2254–2257. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830240948. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi Y., Staquet M. J., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Schmitt D. In vitro migration capacity of epidermal Langerhans cells. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1995;378:169–171. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-1971-3_37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kripke M. L., Munn C. G., Jeevan A., Tang J. M., Bucana C. Evidence that cutaneous antigen-presenting cells migrate to regional lymph nodes during contact sensitization. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 1;145(9):2833–2838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurie G. W., Leblond C. P., Martin G. R. Localization of type IV collagen, laminin, heparan sulfate proteoglycan, and fibronectin to the basal lamina of basement membranes. J Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;95(1):340–344. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.1.340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Varlet B., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Staquet M. J., Delorme P., Schmitt D. Human epidermal Langerhans cells express integrins of the beta 1 subfamily. J Invest Dermatol. 1991 Apr;96(4):518–522. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12470229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Varlet B., Staquet M. J., Dezutter-Dambuyant C., Delorme P., Schmitt D. In vitro adhesion of human epidermal Langerhans cells to laminin and fibronectin occurs through beta 1 integrin receptors. J Leukoc Biol. 1992 Apr;51(4):415–420. doi: 10.1002/jlb.51.4.415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Rao C. N., Wewer U. M. Biochemical interactions of tumor cells with the basement membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1037–1057. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macatonia S. E., Edwards A. J., Knight S. C. Dendritic cells and the initiation of contact sensitivity to fluorescein isothiocyanate. Immunology. 1986 Dec;59(4):509–514. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macatonia S. E., Knight S. C., Edwards A. J., Griffiths S., Fryer P. Localization of antigen on lymph node dendritic cells after exposure to the contact sensitizer fluorescein isothiocyanate. Functional and morphological studies. J Exp Med. 1987 Dec 1;166(6):1654–1667. doi: 10.1084/jem.166.6.1654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada Y., Tsuchiya H., Shimizu H., Tomita K., Nakanishi I., Sato H., Seiki M., Yamashita K., Hayakawa T. Induction and stimulation of 92-kDa gelatinase/type IV collagenase production in osteosarcoma and fibrosarcoma cell lines by tumor necrosis factor alpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Sep 14;171(2):610–617. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ries C., Kolb H., Petrides P. E. Regulation of 92-kD gelatinase release in HL-60 leukemia cells: tumor necrosis factor-alpha as an autocrine stimulus for basal- and phorbol ester-induced secretion. Blood. 1994 Jun 15;83(12):3638–3646. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinman R. M. The dendritic cell system and its role in immunogenicity. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:271–296. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.001415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terranova V. P., Hujanen E. S., Martin G. R. Basement membrane and the invasive activity of metastatic tumor cells. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1986 Aug;77(2):311–316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryggvason K., Höyhtyä M., Pyke C. Type IV collagenases in invasive tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 1993;24(3):209–218. doi: 10.1007/BF01833261. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda Y., Imai K., Tsuchiya H., Fujimoto N., Nakanishi I., Katsuda S., Seiki M., Okada Y. Matrix metalloproteinase 9 (gelatinase B) is expressed in multinucleated giant cells of human giant cell tumor of bone and is associated with vascular invasion. Am J Pathol. 1996 Feb;148(2):611–622. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varani J., Perone P., Inman D. R., Burmeister W., Schollenberger S. B., Fligiel S. E., Sitrin R. G., Johnson K. J. Human skin in organ culture. Elaboration of proteolytic enzymes in the presence and absence of exogenous growth factors. Am J Pathol. 1995 Jan;146(1):210–217. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Gordon S. Secretion of a specific collagenase by stimulated macrophages. J Exp Med. 1975 Aug 1;142(2):346–360. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner J. F., Jr Matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors in connective tissue remodeling. FASEB J. 1991 May;5(8):2145–2154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata S., Ito Y., Tanaka R., Shimizu S. Gelatinases of metastatic cell lines of murine colonic carcinoma as detected by substrate-gel electrophoresis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 29;151(1):158–162. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90573-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamagata S., Tanaka R., Ito Y., Shimizu S. Gelatinases of murine metastatic tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jan 16;158(1):228–234. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(89)80202-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Wilsem E. J., Brevé J., Kleijmeer M., Kraal G. Antigen-bearing Langerhans cells in skin draining lymph nodes: phenotype and kinetics of migration. J Invest Dermatol. 1994 Aug;103(2):217–220. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12393088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]