Abstract
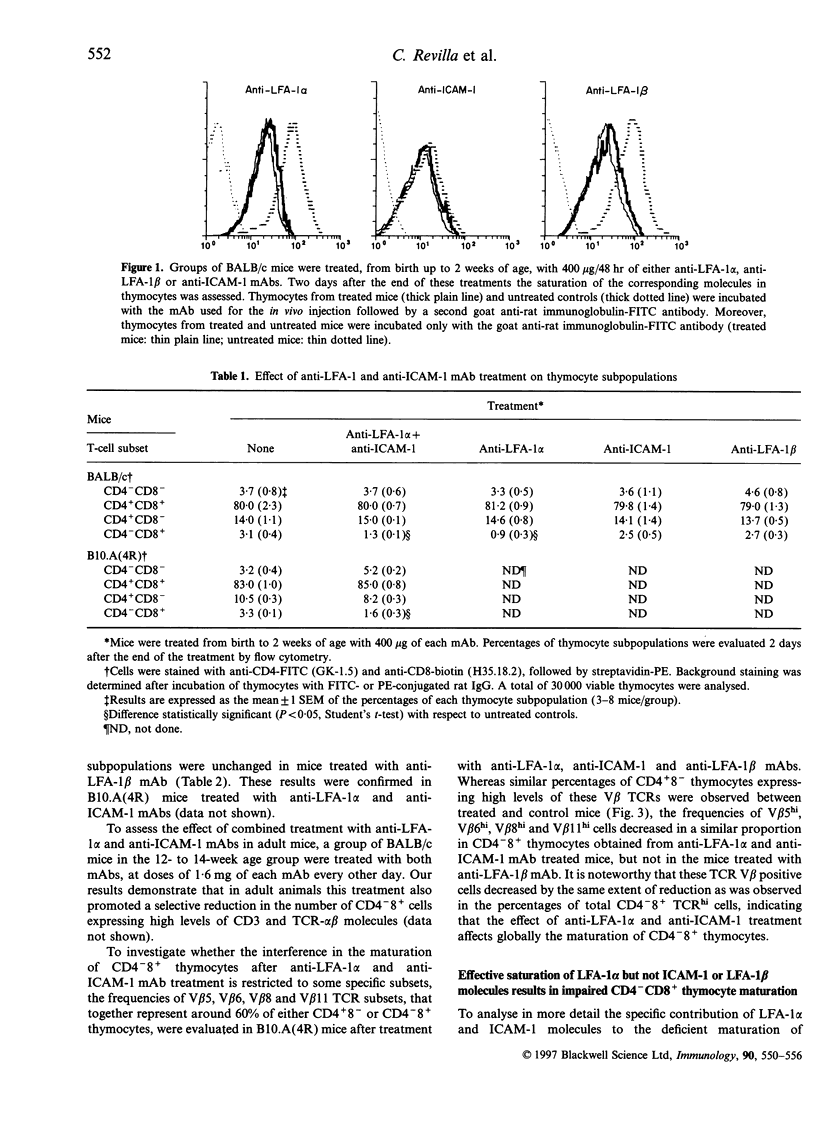
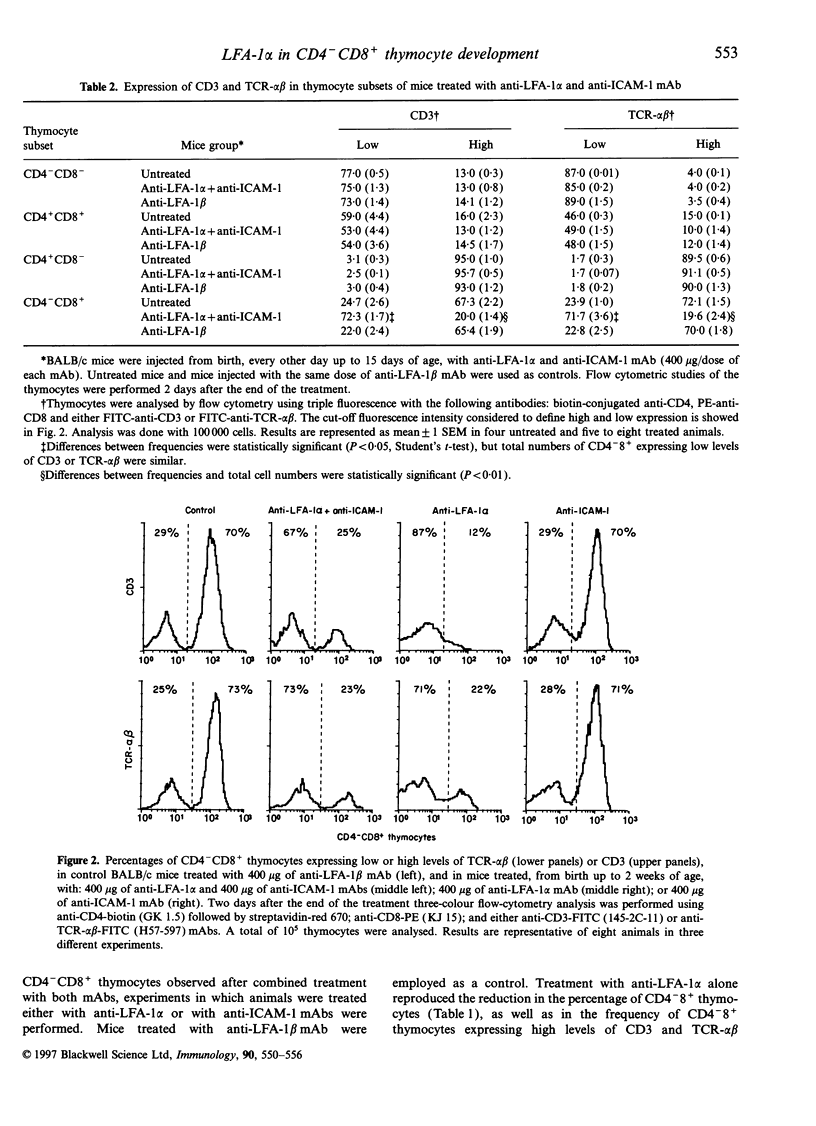
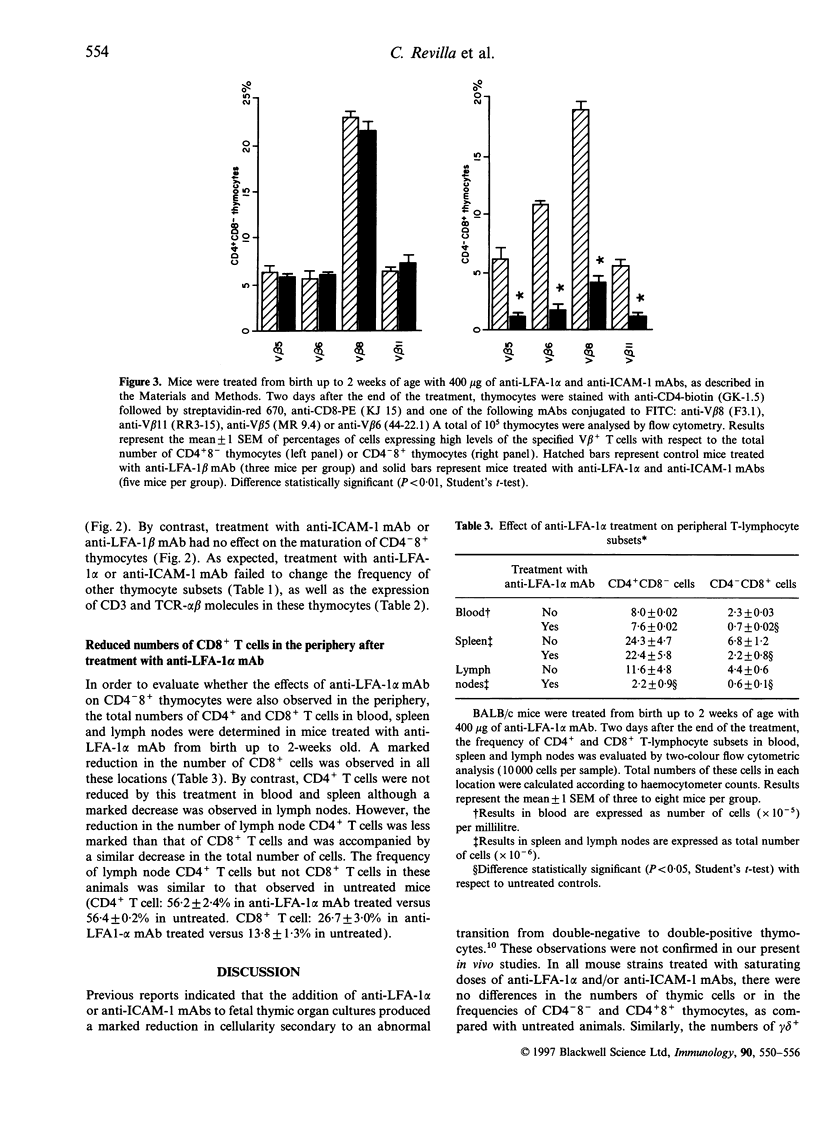
Maturation of T lymphocytes in the thymus is driven by signals provided by soluble factors and by the direct interaction between thymocytes and stromal cells. Although the interaction between T-cell receptor (TCR) and major histocompalibility complex (MHC) molecules on stromal cells is crucial for T-cell development, other accessory molecules seem to play a role in this process. In order to better understand the role of lymphocyte function-associated antigen-1 (LFA-1) and intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) molecules in thymocyte maturation, mice were treated from birth with saturating doses of non-cytolytic-specific monoclonal antibodies. The effect of this treatment on thymocyte subpopulations and the expression of CD3 and TCR-alpha beta by these cells was investigated by flow cytometry. Our data demonstrated that the effective saturation of LFA-1 alpha chain in the thymus, but not ICAM-I or LFA-I beta chain, selectively interfered with the maturation of CD8+ T cells, as manifested by a marked reduction in the frequency of CD4-8+ thymocytes expressing high levels of CD3 and TCR-alpha beta. This selective reduction was also observed in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and spleen cells. The analysis of the frequencies of various V beta TCR showed that CD4-8+ thymocytes were globally affected by the treatment. These results underline the importance of the interaction between LFA-1 and its ligands in the maturation of CD8+ T cells and document the existence of different molecular requirements for the differentiation of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arpaia E., Shahar M., Dadi H., Cohen A., Roifman C. M. Defective T cell receptor signaling and CD8+ thymic selection in humans lacking zap-70 kinase. Cell. 1994 Mar 11;76(5):947–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90368-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bamezai A., Palliser D., Berezovskaya A., McGrew J., Higgins K., Lacy E., Rock K. L. Regulated expression of Ly-6A.2 is important for T cell development. J Immunol. 1995 May 1;154(9):4233–4239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard G., Zoccola D., Ticchioni M., Breittmayer J. P., Aussel C., Bernard A. Engagement of the CD45 molecule induces homotypic adhesion of human thymocytes through a LFA-1/ICAM-3-dependent pathway. J Immunol. 1994 Jun 1;152(11):5161–5170. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackman M., Kappler J., Marrack P. The role of the T cell receptor in positive and negative selection of developing T cells. Science. 1990 Jun 15;248(4961):1335–1341. doi: 10.1126/science.1972592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlow D. A., van Oers N. S., Teh S. J., Teh H. S. Deletion of antigen-specific immature thymocytes by dendritic cells requires LFA-1/ICAM interactions. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 15;148(6):1595–1603. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosgrove D., Gray D., Dierich A., Kaufman J., Lemeur M., Benoist C., Mathis D. Mice lacking MHC class II molecules. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):1051–1066. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine J. S., Kruisbeek A. M. The role of LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions during murine T lymphocyte development. J Immunol. 1991 Nov 1;147(9):2852–2859. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung-Leung W. P., Schilham M. W., Rahemtulla A., Kündig T. M., Vollenweider M., Potter J., van Ewijk W., Mak T. W. CD8 is needed for development of cytotoxic T cells but not helper T cells. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):443–449. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90462-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galy A. H., Spits H. CD40 is functionally expressed on human thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 1;149(3):775–782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkinson E. J., Anderson G., Owen J. J. Studies on T cell maturation on defined thymic stromal cell populations in vitro. J Exp Med. 1992 Sep 1;176(3):845–853. doi: 10.1084/jem.176.3.845. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lucas B., Vasseur F., Penit C. Stochastic coreceptor shut-off is restricted to the CD4 lineage maturation pathway. J Exp Med. 1995 May 1;181(5):1623–1633. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.5.1623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundberg K., Heath W., Köntgen F., Carbone F. R., Shortman K. Intermediate steps in positive selection: differentiation of CD4+8int TCRint thymocytes into CD4-8+TCRhi thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1995 May 1;181(5):1643–1651. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.5.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuyama T., Kimura T., Kitagawa M., Pfeffer K., Kawakami T., Watanabe N., Kündig T. M., Amakawa R., Kishihara K., Wakeham A. Targeted disruption of IRF-1 or IRF-2 results in abnormal type I IFN gene induction and aberrant lymphocyte development. Cell. 1993 Oct 8;75(1):83–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Negishi I., Motoyama N., Nakayama K., Nakayama K., Senju S., Hatakeyama S., Zhang Q., Chan A. C., Loh D. Y. Essential role for ZAP-70 in both positive and negative selection of thymocytes. Nature. 1995 Aug 3;376(6539):435–438. doi: 10.1038/376435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonoyama S., Nakayama M., Shiohara T., Yata J. Only dull CD3+ thymocytes bind to thymic epithelial cells. The binding is elicited by both CD2/LFA-3 and LFA-1/ICAM-1 interactions. Eur J Immunol. 1989 Sep;19(9):1631–1635. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830190917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres M., Goridis C., Golstein P. Inhibition of murine T cell-mediated cytolysis and T cell proliferation by a rat monoclonal antibody immunoprecipitating two lymphoid cell surface polypeptides of 94 000 and 180 000 molecular weight. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Jan;12(1):60–69. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quddus J., Kaplan A., Richardson B. C. Anti-CD11a prevents deletion of self-reactive T cells in neonatal C57BR mice. Immunology. 1994 Jun;82(2):301–305. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raulet D. H. MHC class I-deficient mice. Adv Immunol. 1994;55:381–421. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60514-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaün J., Calman F., Coltey M., Le Douarin N. M. Construction of chimeric thymuses in the mouse fetus by in utero surgery. Eur J Immunol. 1986 May;16(5):523–530. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830160511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez-Madrid F., Simon P., Thompson S., Springer T. A. Mapping of antigenic and functional epitopes on the alpha- and beta-subunits of two related mouse glycoproteins involved in cell interactions, LFA-1 and Mac-1. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):586–602. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer K. H., Denning S. M., Whichard L. P., Haynes B. F. Thymocyte LFA-1 and thymic epithelial cell ICAM-1 molecules mediate binding of activated human thymocytes to thymic epithelial cells. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 15;144(8):2931–2939. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sligh J. E., Jr, Ballantyne C. M., Rich S. S., Hawkins H. K., Smith C. W., Bradley A., Beaudet A. L. Inflammatory and immune responses are impaired in mice deficient in intercellular adhesion molecule 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Sep 15;90(18):8529–8533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.18.8529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer T. A. Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90337-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki H., Punt J. A., Granger L. G., Singer A. Asymmetric signaling requirements for thymocyte commitment to the CD4+ versus CD8+ T cell lineages: a new perspective on thymic commitment and selection. Immunity. 1995 Apr;2(4):413–425. doi: 10.1016/1074-7613(95)90149-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takei F. Inhibition of mixed lymphocyte response by a rat monoclonal antibody to a novel murine lymphocyte activation antigen (MALA-2). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1403–1407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiest D. L., Yuan L., Jefferson J., Benveniste P., Tsokos M., Klausner R. D., Glimcher L. H., Samelson L. E., Singer A. Regulation of T cell receptor expression in immature CD4+CD8+ thymocytes by p56lck tyrosine kinase: basis for differential signaling by CD4 and CD8 in immature thymocytes expressing both coreceptor molecules. J Exp Med. 1993 Nov 1;178(5):1701–1712. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.5.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Fougerolles A. R., Springer T. A. Intercellular adhesion molecule 3, a third adhesion counter-receptor for lymphocyte function-associated molecule 1 on resting lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):185–190. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Boehmer H. Positive selection of lymphocytes. Cell. 1994 Jan 28;76(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90330-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


