Abstract
Phosphatidylcholine-phospholipase D has been proposed to play a key role in the transduction of the proliferative responses of a wide range of mitogens and growth factors. We now report that the antigen receptors on T lymphocytes derived from human tonsillar or murine splenic preparations are coupled to phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho)-phospholipase D (PLD) activation following stimulation of these T cells with anti-CD3 antibodies. However, since we also demonstrate that the antigen receptors on murine thymocytes are coupled to PtdCho-PLD activation, we propose that it is unlikely that this PLD pathway plays a central role in the transduction of T-cell proliferative responses, but rather, may be involved in either driving cells into cycle or maintaining cell cycle progression, processes required both for proliferation and activation-induced cell death. Whilst the molecular mechanisms underlying T-cell receptor (TCR)-coupling to PtdCho-PLD activation in these cells have not been fully defined, kinetics studies and experiments using pharmacological inhibitors of protein tyrosine phosphatases (PTPases) and reconstituting CD3-coupled PtdCho-PLD activity in streptolysin-O permeabilized cells, suggest that the TCR/CD3 complex, under optimal conditions of activation, may be predominantly coupled to PtdCho-PLD activation downstream of tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-gamma (PLC-gamma), phosphatidylinositol (PtdIns)P2 hydrolysis, calcium mobilization and protein kinase C (PKC) activation.
Full text
PDF

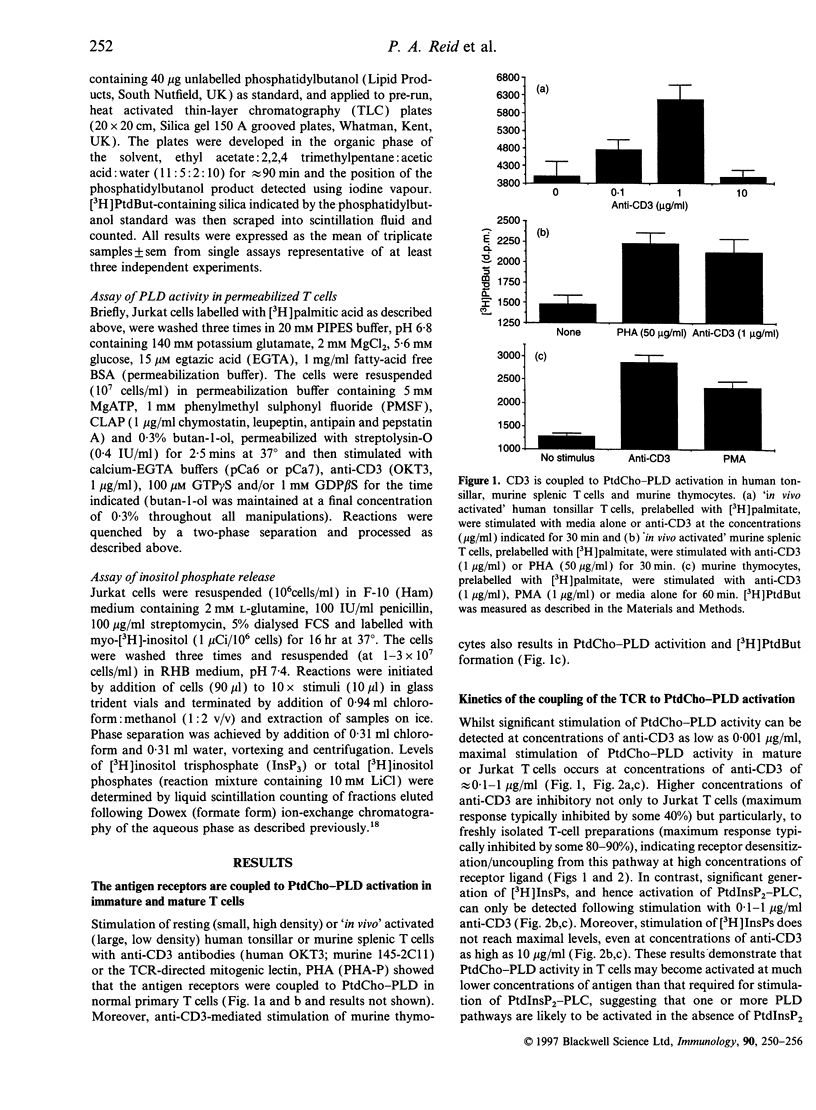
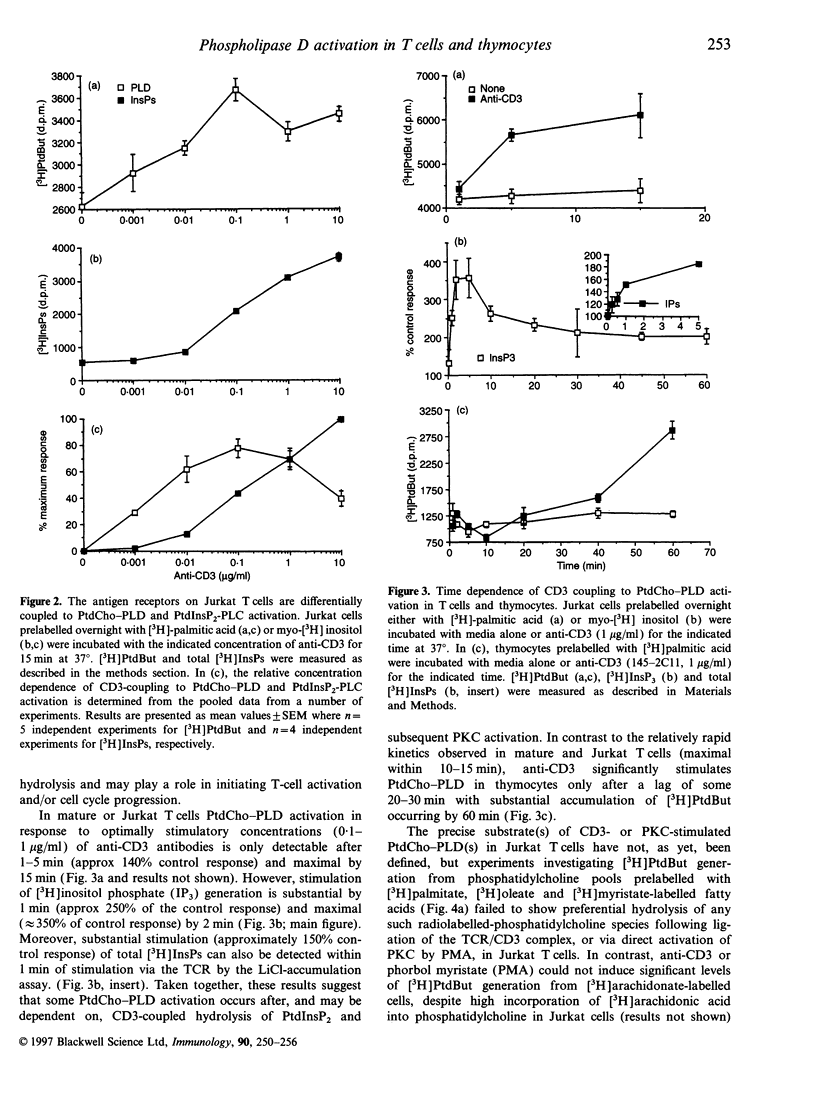



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Biffen M., Shiroo M., Alexander D. R. Selective coupling of the T cell antigen receptor to phosphoinositide-derived diacylglycerol production in HPB-ALL T cells correlates with CD45-regulated p59fyn activity. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Nov;23(11):2980–2987. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billah M. M. Phospholipase D and cell signaling. Curr Opin Immunol. 1993 Feb;5(1):114–123. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(93)90090-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boarder M. R. A role for phospholipase D in control of mitogenesis. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Feb;15(2):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90111-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Exton J. H. Phosphatidylcholine breakdown and signal transduction. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1994 Apr 14;1212(1):26–42. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(94)90186-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe L. R., Weiss A. Multiple kinases mediate T-cell-receptor signaling. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Feb;20(2):59–64. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)88958-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leo O., Foo M., Sachs D. H., Samelson L. E., Bluestone J. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody specific for a murine T3 polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1374–1378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mollinedo F., Gajate C., Flores I. Involvement of phospholipase D in the activation of transcription factor AP-1 in human T lymphoid Jurkat cells. J Immunol. 1994 Sep 15;153(6):2457–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H. LPA: a novel lipid mediator with diverse biological actions. Trends Cell Biol. 1994 Jun;4(6):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(94)90144-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris A. J., Engebrecht J., Frohman M. A. Structure and regulation of phospholipase D. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1996 May;17(5):182–185. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(96)10016-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Rourke A. M., Mescher M. F. T cell receptor-mediated signaling occurs in the absence of inositol phosphate production. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 15;263(35):18594–18597. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips R. J., Harnett M. M., Klaus G. G. Antigen receptor-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in murine T cells is not initiated via G-protein activation. Int Immunol. 1991 Jul;3(7):617–621. doi: 10.1093/intimm/3.7.617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho J., Silverman L. B., Castigli E., Ahern D., Laudano A. P., Terhorst C., Geha R. S., Chatila T. A. Developmental regulation of transmembrane signaling via the T cell antigen receptor/CD3 complex in human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1992 Mar 1;148(5):1315–1321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Cunningham G. R., House F. S. Activation of phospholipase D following perturbation of the human T lymphocyte antigen receptor/CD3 complex is dependent upon protein kinase C. Cell Signal. 1993 May;5(3):315–323. doi: 10.1016/0898-6568(93)90022-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S. J., Cunningham G. R., Strupp J. A., House F. S., Kelley L. L., Henderson G. S., Exton J. H., Bocckino S. B. Activation of phospholipase D: a signaling system set in motion by perturbation of the T lymphocyte antigen receptor/CD3 complex. Cell Regul. 1991 Oct;2(10):841–850. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.10.841. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sussman J. J., Merćep M., Saito T., Germain R. N., Bonvini E., Ashwell J. D. Dissociation of phosphoinositide hydrolysis and Ca2+ fluxes from the biological responses of a T-cell hybridoma. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):625–628. doi: 10.1038/334625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Wauwe J. P., De Mey J. R., Goossens J. G. OKT3: a monoclonal anti-human T lymphocyte antibody with potent mitogenic properties. J Immunol. 1980 Jun;124(6):2708–2713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Pettitt T. R., Kaur P., Briscoe C. P., Stewart A., Paul A., Paterson A., Cross M. J., Gardner S. D., Currie S. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis: a multiple messenger generating system. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res. 1993;28:73–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


