Abstract
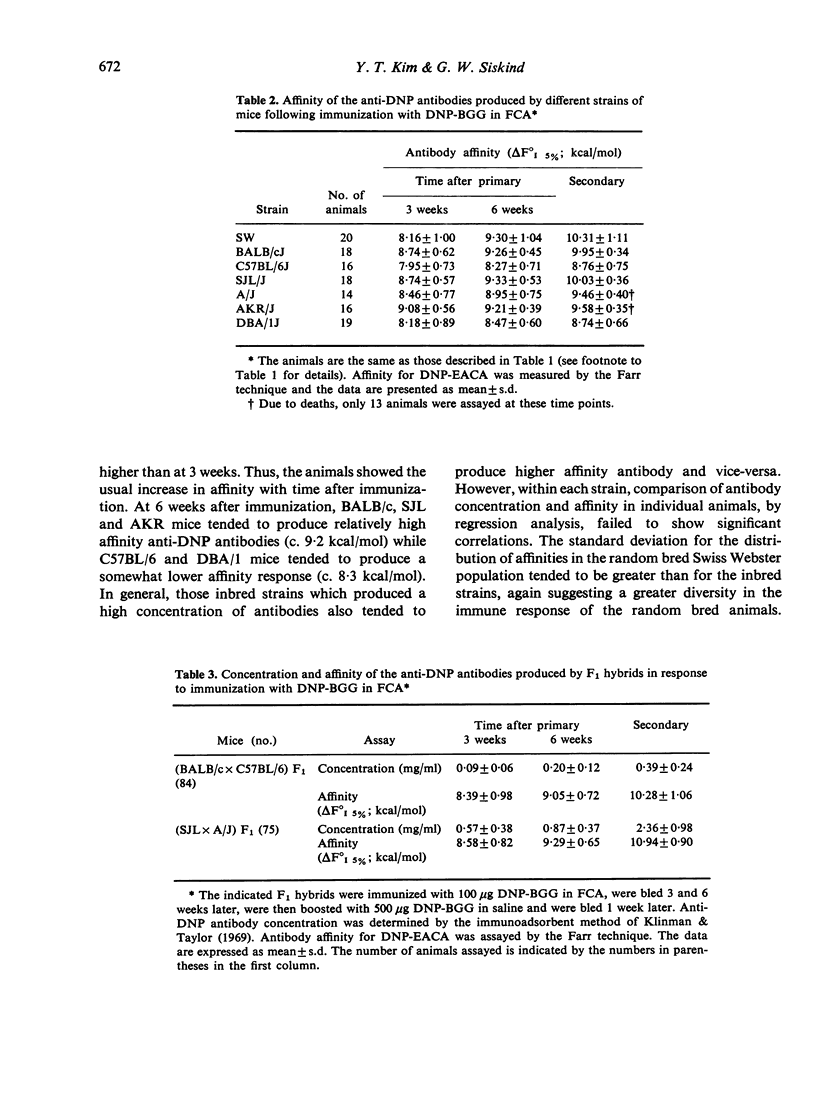
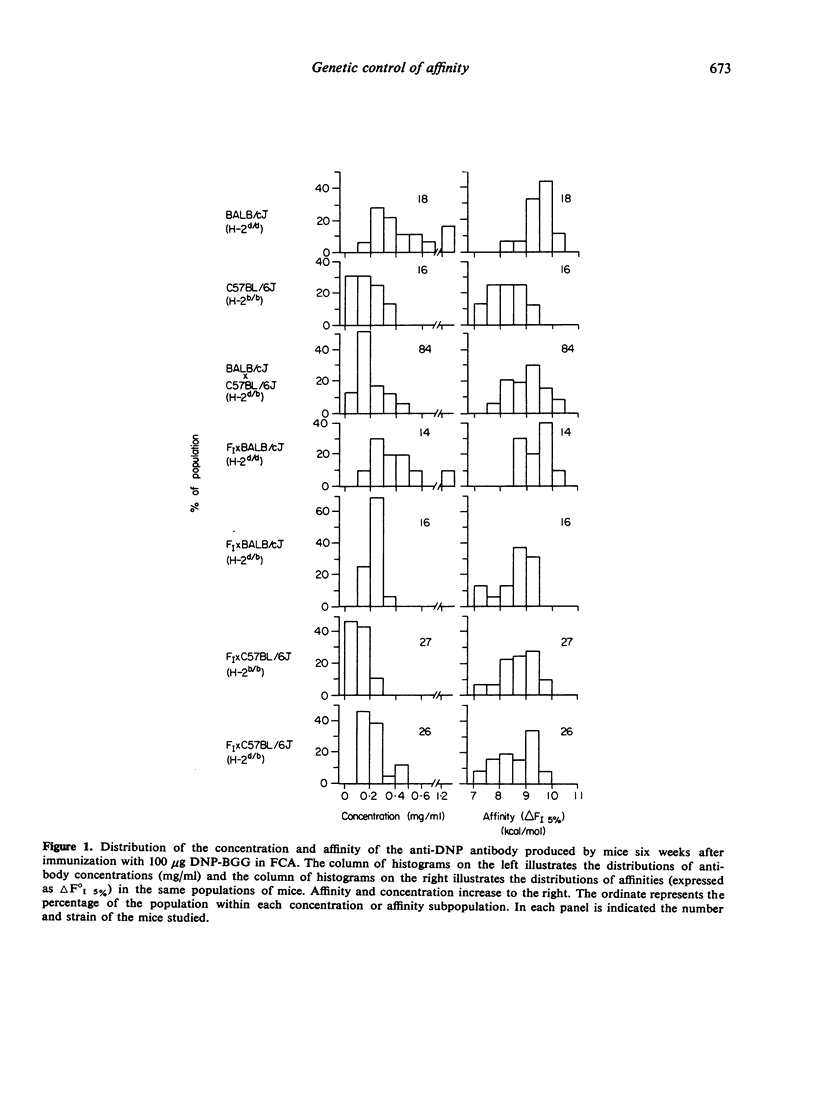
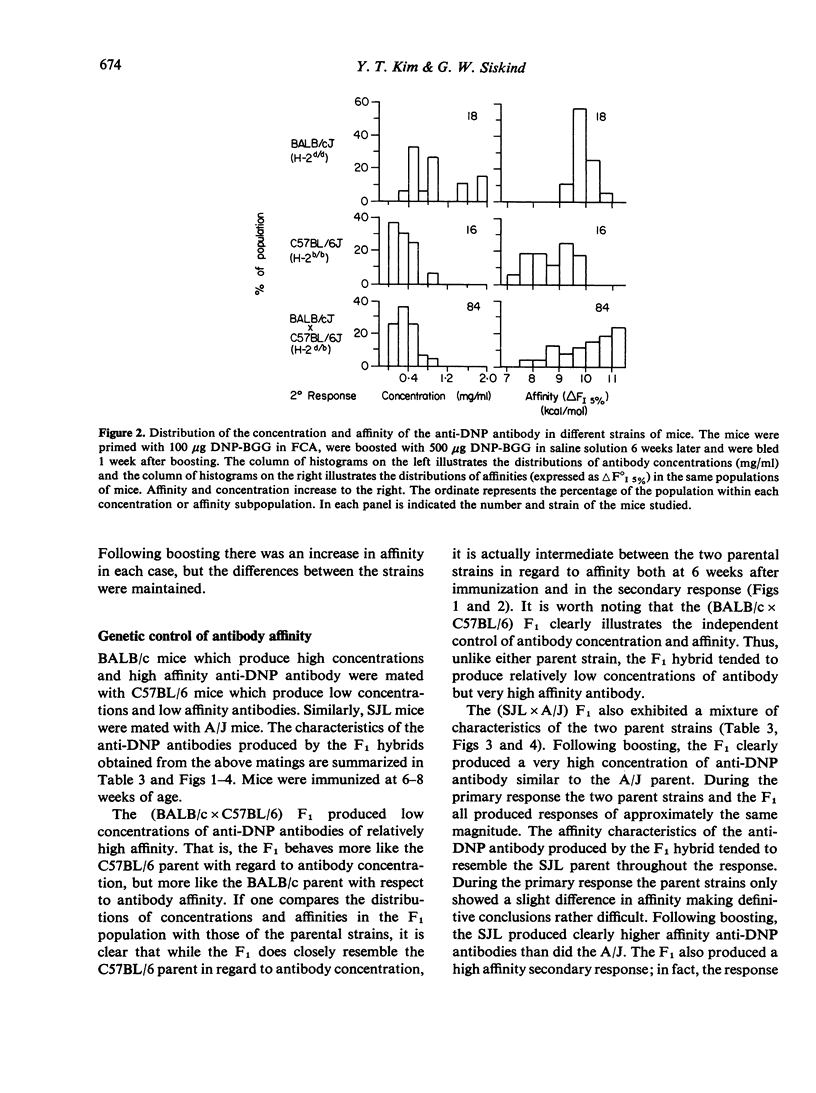
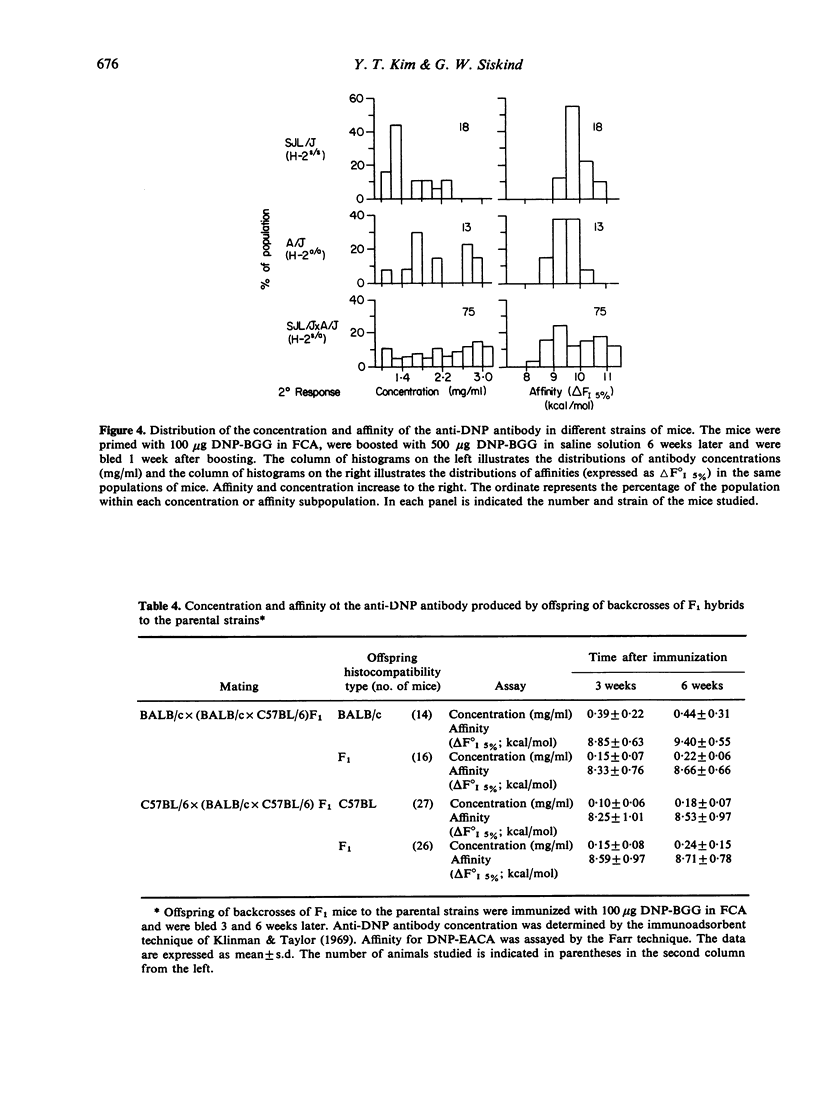
Genetic controls on the concentration and affinity of the anti-dinitrophenyl antibodies produced by different inbred strains of mice in response to immunization with dinitrophenylated bovine gamma globulin in Freund's complete adjuvant were demonstrated. Based upon data on F1 hybrids and backcrosses, it can be concluded that there are genetic controls on antibody affinity which are not linked to the major histocompatibility complex. In addition, the genetic controls on affinity which were studied here appear to be inherited independently of genetic controls on antibody concentration.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benacerraf B., McDevitt H. O. Histocompatibility-linked immune response genes. Science. 1972 Jan 21;175(4019):273–279. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4019.273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EISEN H. N., SISKIND G. W. VARIATIONS IN AFFINITIES OF ANTIBODIES DURING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE. Biochemistry. 1964 Jul;3:996–1008. doi: 10.1021/bi00895a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goidl E. A., Barondess J. J., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. VII. Change in affinity of direct and indirect plaque-forming cells with time after immunization in the mouse: loss of high affinity plaques late after immunization. Immunology. 1975 Oct;29(4):629–641. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi T., Makela O. Inheritance of antibody specificity. II. Anti-(4-hydroxy-5-bromo-3-nitrophenyl) acetyl in the mouse. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):840–854. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imanishi T., Mäkelä O. Inheritance of antibody specificity. I. Anti-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrophenyl)acetyl of the mouse primary response. J Exp Med. 1974 Dec 1;140(6):1498–1510. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.6.1498. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz F. E., Steward M. W. Studies on the genetic control of antibody affinity: the independent control of antibody levels and affinity in Biozzi mice. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):477–479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. T., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. VI. Effect of antigen dose and time after immunization on antibody affinity and heterogeneity in the mouse. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Jun;17(2):329–338. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klinman N. R., Taylor R. B. General methods for the study of cells and serum during the immune response: the response to dinitrophenyl in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1969 Apr;4(4):473–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamelin J. P., Paul W. E. Rate of increase of antibody affinity in different rat strains. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1971;40(3):351–360. doi: 10.1159/000230418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O., Benacerraf B. Genetic control of specific immune responses. Adv Immunol. 1969;11:31–74. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60477-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mond J., Kim Y. T., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. V. Effect of nonspecific modification of the magnitude of the immune response on the affinity of the antibody synthesized. J Immunol. 1974 Mar;112(3):1255–1263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petty R. E., Steward M. W., Soothill J. F. The heterogeneity of antibody affinity in inbred mice and its possible immunopathologic significance. Clin Exp Immunol. 1972 Oct;12(2):231–241. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. B., Haimovich J., Sela M. Purification of antibodies with immunoadsorbents prepared using bromoacetyl cellulose. Immunochemistry. 1967 Jan;4(1):11–22. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(67)90192-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S. K., Kunz H. W., Gill T. J., 3rd The genetic control of antibody binding constants and specificities in inbred rats. J Immunol. 1974 Nov;113(5):1468–1476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siskind G. W., Benacerraf B. Cell selection by antigen in the immune response. Adv Immunol. 1969;10:1–50. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60414-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonoda S., Schlamowitz M. Studies of 125I trace labeling of immunoglobulin G by chloramine-T. Immunochemistry. 1970 Nov;7(11):885–898. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90051-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Kim Y. T., Quagliata F., Siskind G. W. Studies on the control of antibody synthesis. 3. Changes in heterogeneity of antibody affinity during the course of the immune response. Immunology. 1973 Mar;24(3):477–492. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Siskind G. W. Distribution of antibody affinities: technique of measurement. Immunochemistry. 1972 Oct;9(10):987–1011. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90110-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werblin T. P., Siskind G. W. Effect of tolerance and immunity on antibody affinity. Transplant Rev. 1972;8:104–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1972.tb01566.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


