Abstract
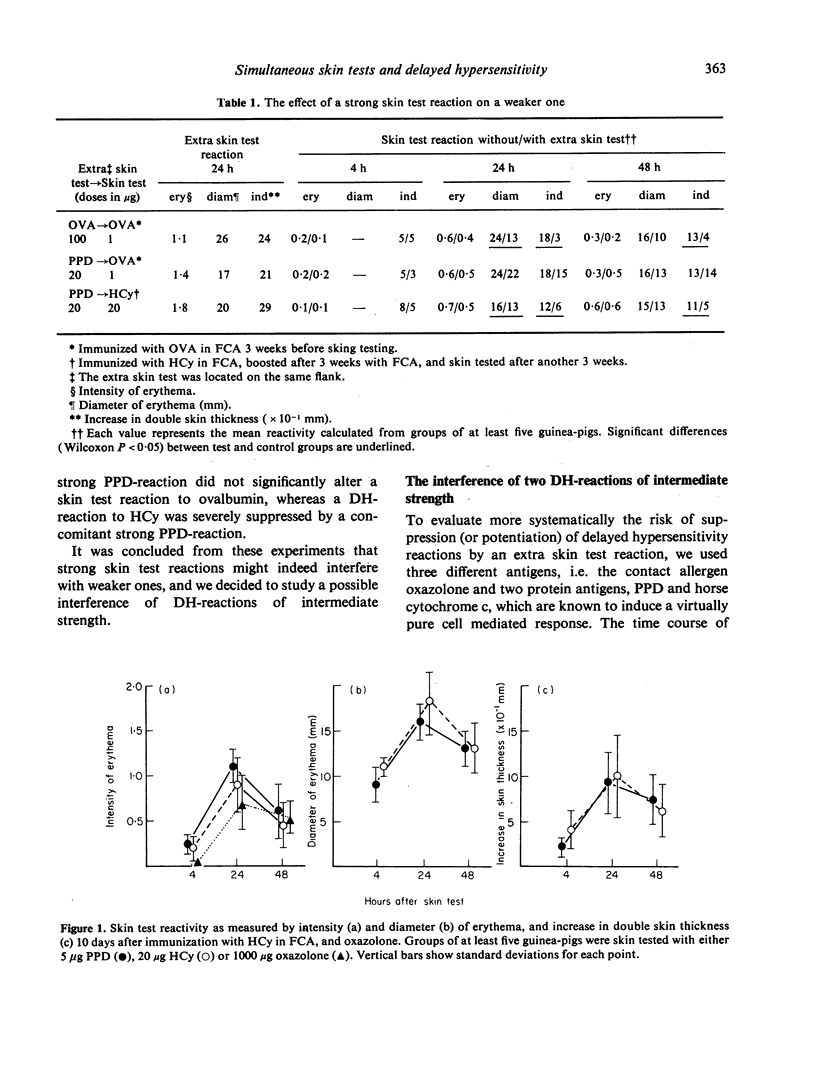
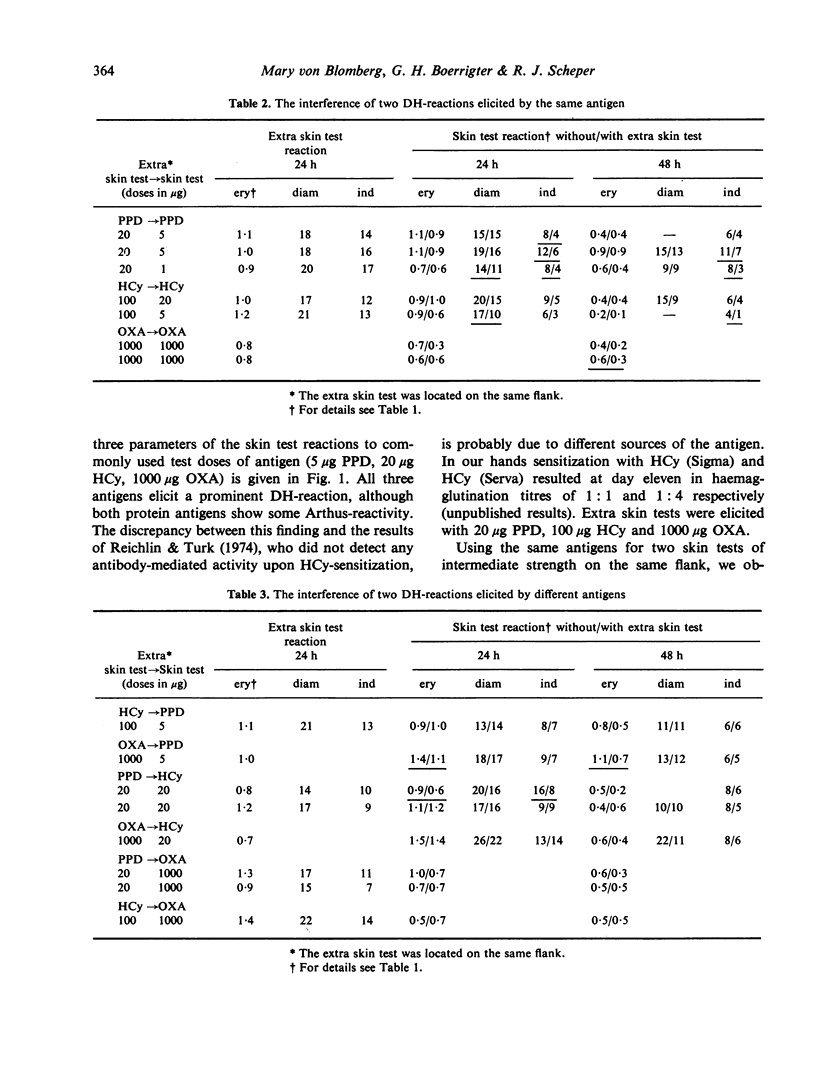
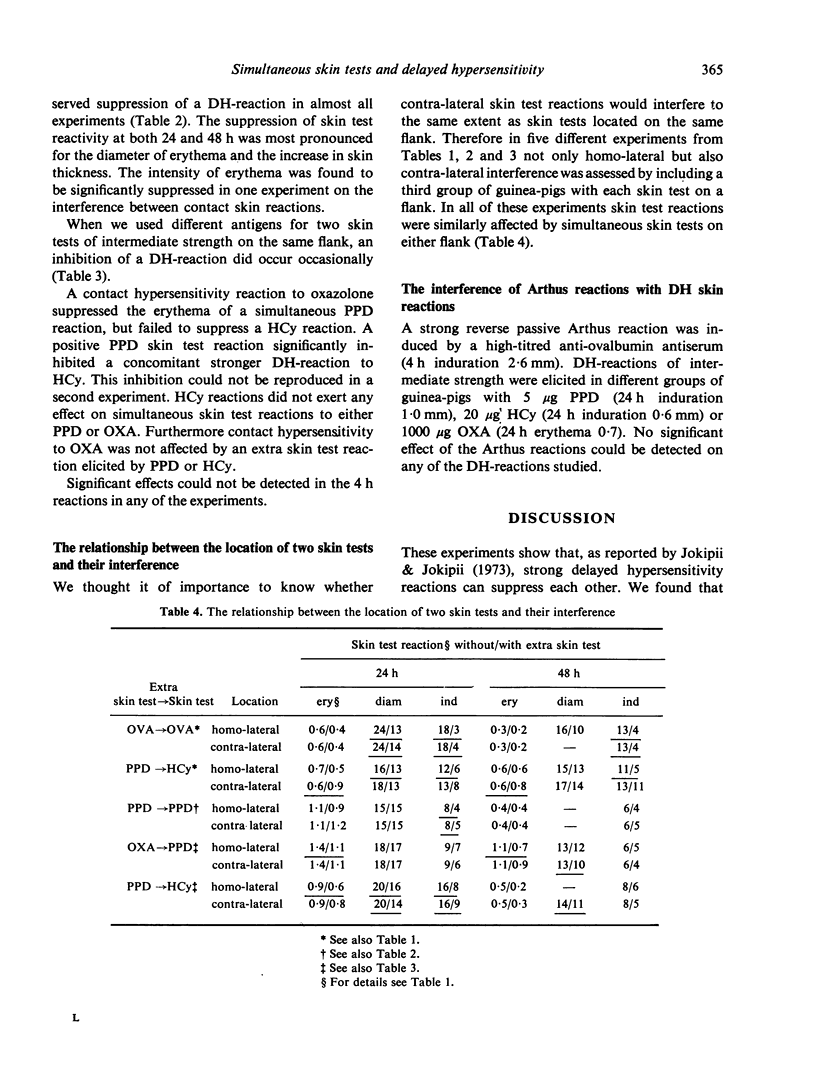
The interference of two simultaneous skin test reactions of intermediate strength has been studied in the guinea-pig, using four different antigens, i.e. ovalbumin, horse cytochrome c, PPD and oxazolone. Skin test reactions were evaluated at 4, 24 and 48 h by measuring three parameters: increase in skin thickness, diameter of erythema and intensity of erythema. When an Arthus reaction was elicited simultaneously with a delayed hypersensitivity (DH) reaction, no effect on the DH reaction was observed. When two simultaneous DH reactions were elicited with different antigens, the risk of interference appeared to be rather small. When, however, the same antigen was used for both skin tests, suppression of at least one parameter of a DH-reaction was found in almost all experiments. Suppression of one skin test by another one could not be reduced by introducing a large distance between the two skin tests. As complete inhibition of either of the parameters never occurred, multiple skin testing may allow one to obtain a qualitative impression of the state of delayed hypersensitivity; when, however, reliable quantitative data are needed, the performance of more than one skin test at a time should be avoided.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baer H., Kolb R. W. Suppression og the tuberculin reaction by high concentrations of tuberculin and the relationship of this phenomenon to the potency assay of tuberculin. J Immunol. 1967 May;98(5):1015–1019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burger D. R., Lilley D. P., Vetto R. M. Lymphocyte suppression associated with alpha globulin. Changes in cellular immunity. Cell Immunol. 1974 Mar 15;10(3):432–441. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(74)90134-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokipii A. M., Jokipii L. Dose response relationships and interference of simultaneous skin tests in delayed hypersensitivity. J Clin Pathol. 1973 Sep;26(9):687–690. doi: 10.1136/jcp.26.9.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter L. W., Turk J. L. Changes in macrophages in vivo induced by desensitization. Cell Immunol. 1976 Apr;23(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90180-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichlin M., Turk J. L. Specificity of antigen receptors for cytochrome c in delayed hypersensitivity. Nature. 1974 Sep 27;251(5473):355–356. doi: 10.1038/251355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson J. H., Naysmith J. D. A comparison of four methods for measuring cutaneous delayed- type hypersensitivity reactions to protein antigens in the mouse. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(3):299–304. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00282.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheper R. J., Noble B., Parker D., Turk J. L. The value of an assessment of erythema and increase in thickness of the skin reaction for a full appreciation of the nature of delayed hypersensitivity in the guinea pig. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1977;54(1):58–66. doi: 10.1159/000231808. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thestrup-Pedersen K. Suppression of tuberculin skin reactivity by prior tuberculin skin testing. Immunology. 1975 Feb;28(2):343–348. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turk J. L., Polák L. A comparison of the effect of anti-lymph node serum and anti-granulocyte serum on local passive transfer of the tuberculin reaction and the normal lymphocyte transfer reaction. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1968;34(2):105–118. doi: 10.1159/000230101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


