Abstract
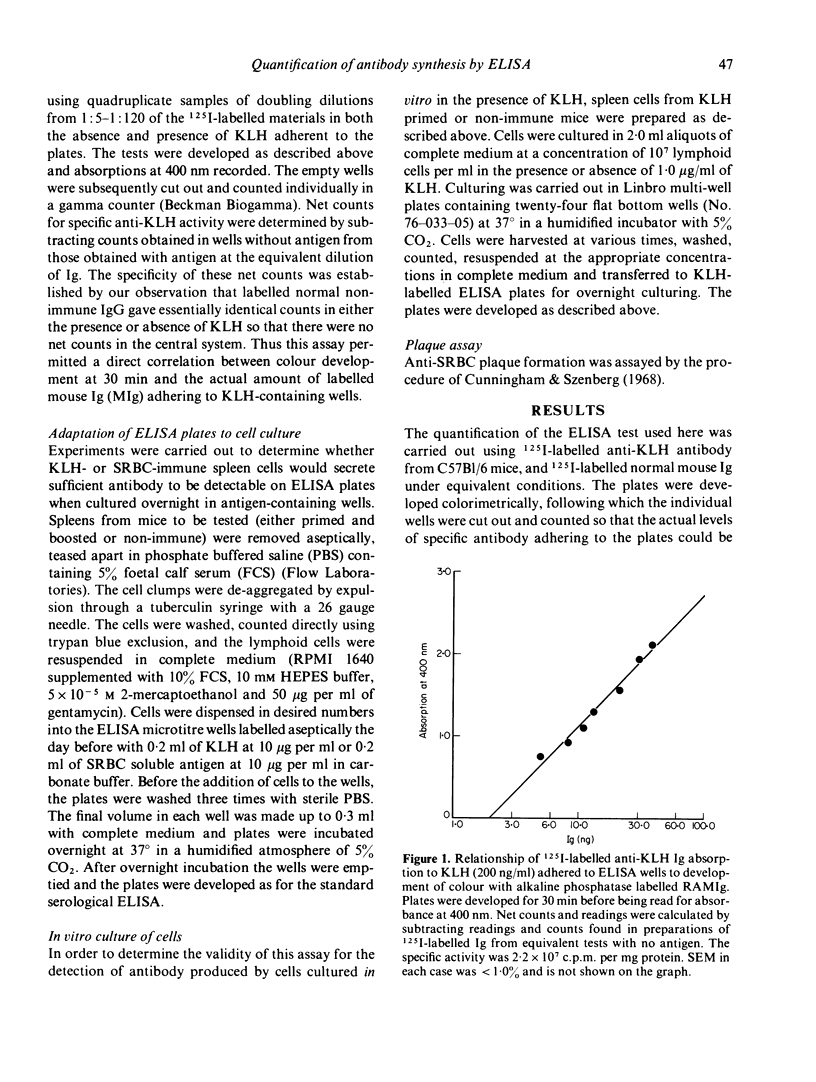
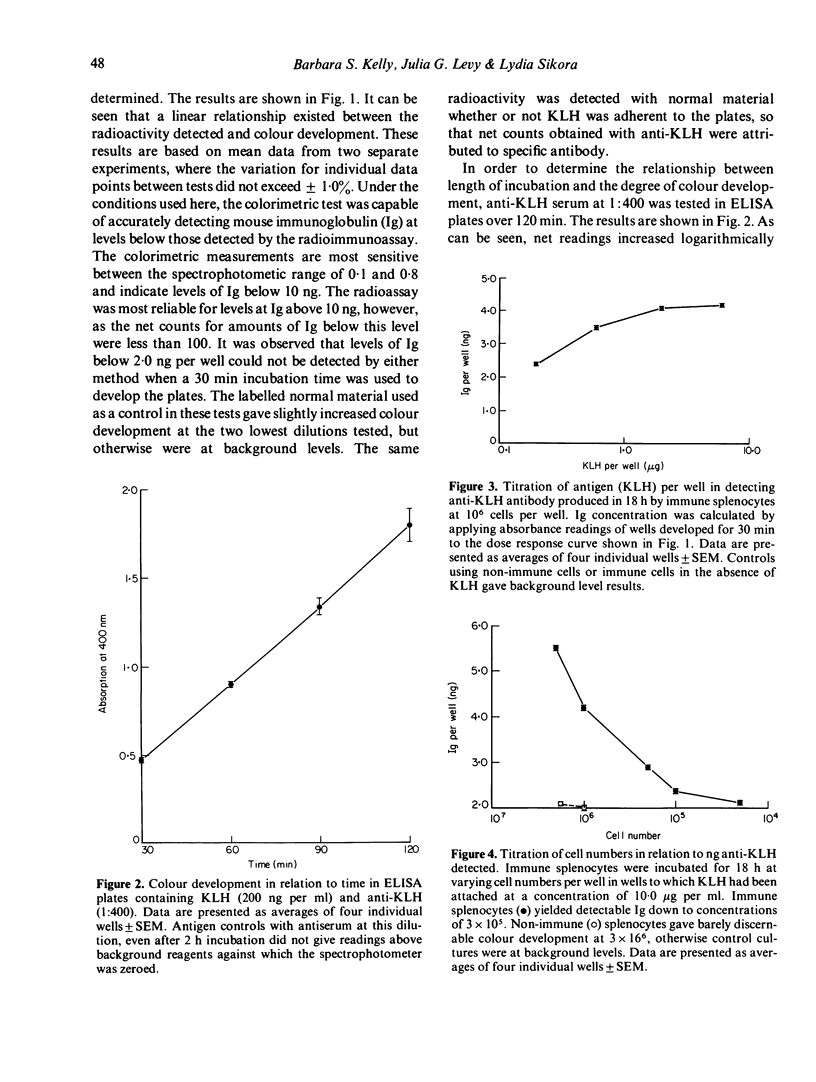
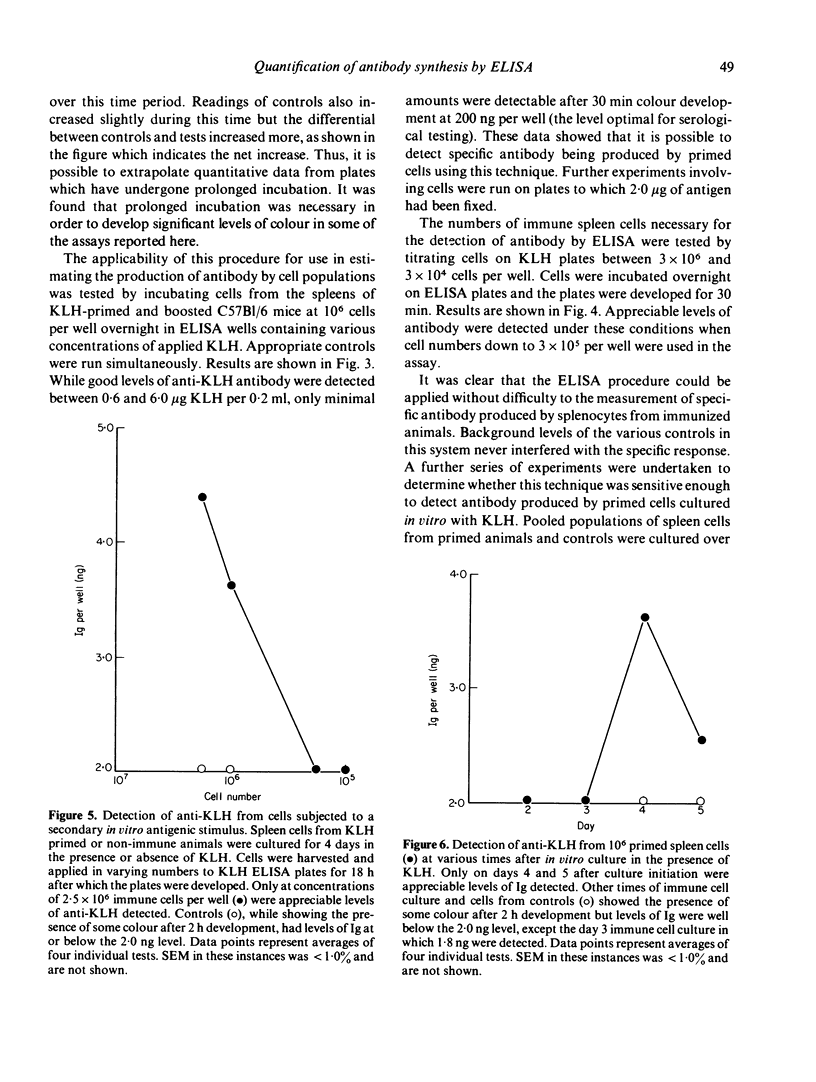
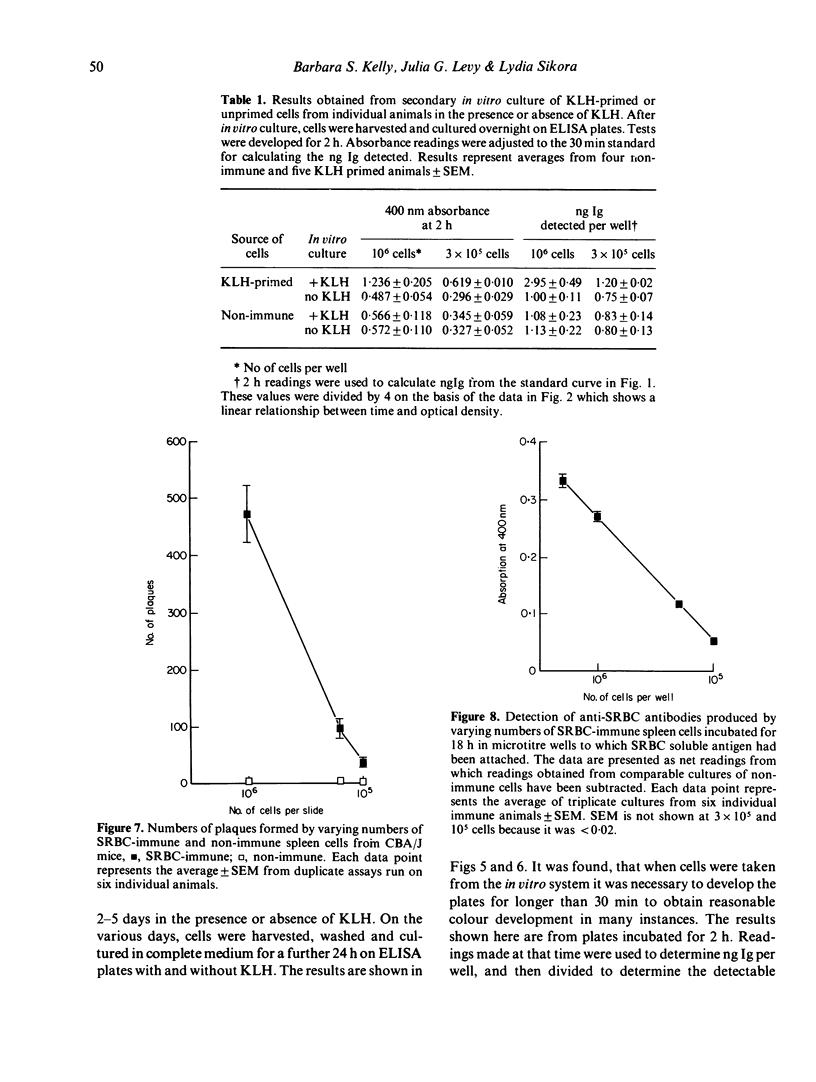
The solid phase enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) has been used to quantify anti-keyhole limpet haemocyanin (anti-KLH) antibody in the serum of KLH-immune C57Bl/6 mice. When spleen cells from immune mice were cultured overnight in ELISA microtitre wells to which KLH had been adsorbed it was found that easily quantifiable amounts of anti-KLH antibody were synthesized and were detectable. It was found further that spleen cells from KLH-primed mice, when cultured in vitro in the presence of KLH, transferred to KLH-labelled ELISA plates, and cultured overnight, also produced detectable levels of antibody. Levels of antibody were detectable only after 4 and 5 days of in vitro stimulation. A comparison was made between detectable numbers of plaque forming cells to sheep red blood cells (SRBC) in SRBC primed CBA mice and levels of antibody detected by the ELISA procedure. It was found that the sensitivities of the two tests were comparable. The applications of this technique to the study of in vitro antibody synthesis using soluble antigens are discussed.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butler J. E., Feldbush T. L., McGivern P. L., Stewart N. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA): a measure of antibody concentration or affinity. Immunochemistry. 1978 Feb;15(2):131–136. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(78)90053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A. J., Szenberg A. Further improvements in the plaque technique for detecting single antibody-forming cells. Immunology. 1968 Apr;14(4):599–600. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dissanayake S., Hay F. C. Isolation of pure normal IgG 1 from mouse serum. Immunochemistry. 1975 Jan;12(1):101–103. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(75)90057-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engvall E., Perlmann P. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Quantitative assay of immunoglobulin G. Immunochemistry. 1971 Sep;8(9):871–874. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90454-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gripenberg M., Linder E., Kurki P., Engvall E. A solid phase enzyme-linked immunosurbent assay (ELISA) for the demonstration of antibodies against denatured, single-stranded DNA in patient sera. Scand J Immunol. 1978;7(2):151–157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1978.tb00438.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. G., McMaster R., Kelly B., Whitney R. B., Kilburn D. G. Identity of a T-lymphocyte inhibitor with mouse immunoglobulin in the serum of tumour-bearing mice. Immunology. 1977 Apr;32(4):475–481. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


