Abstract
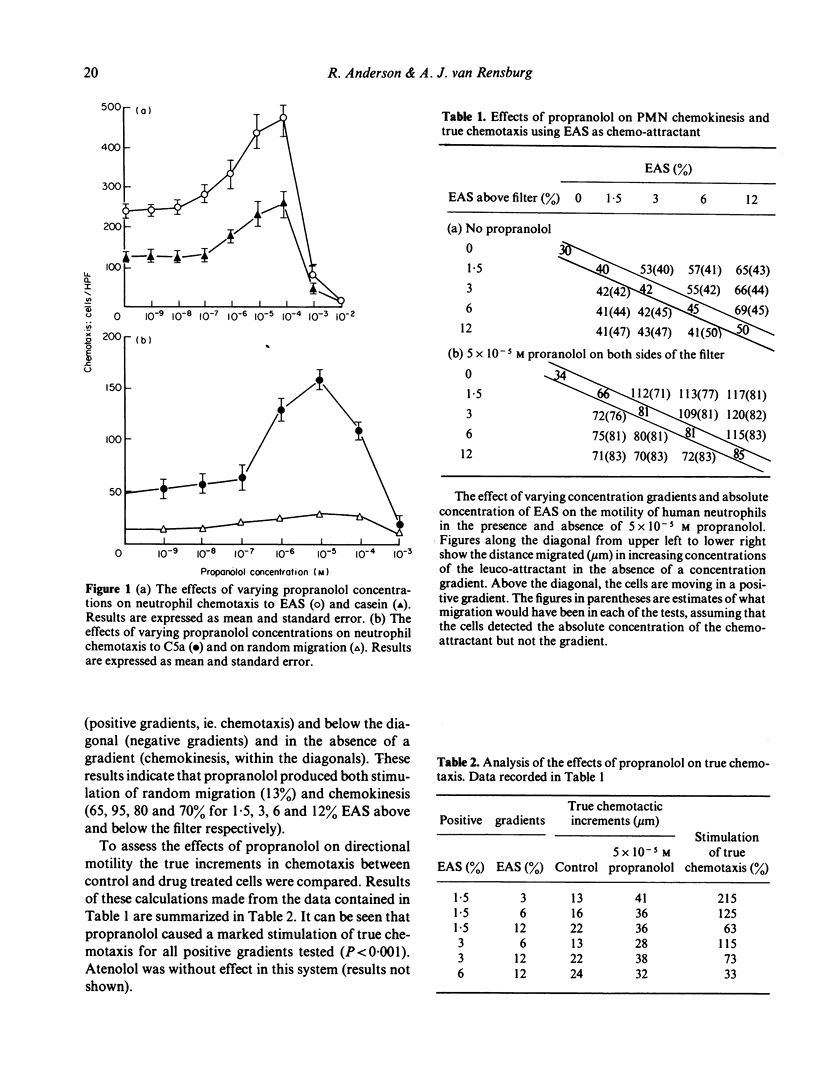
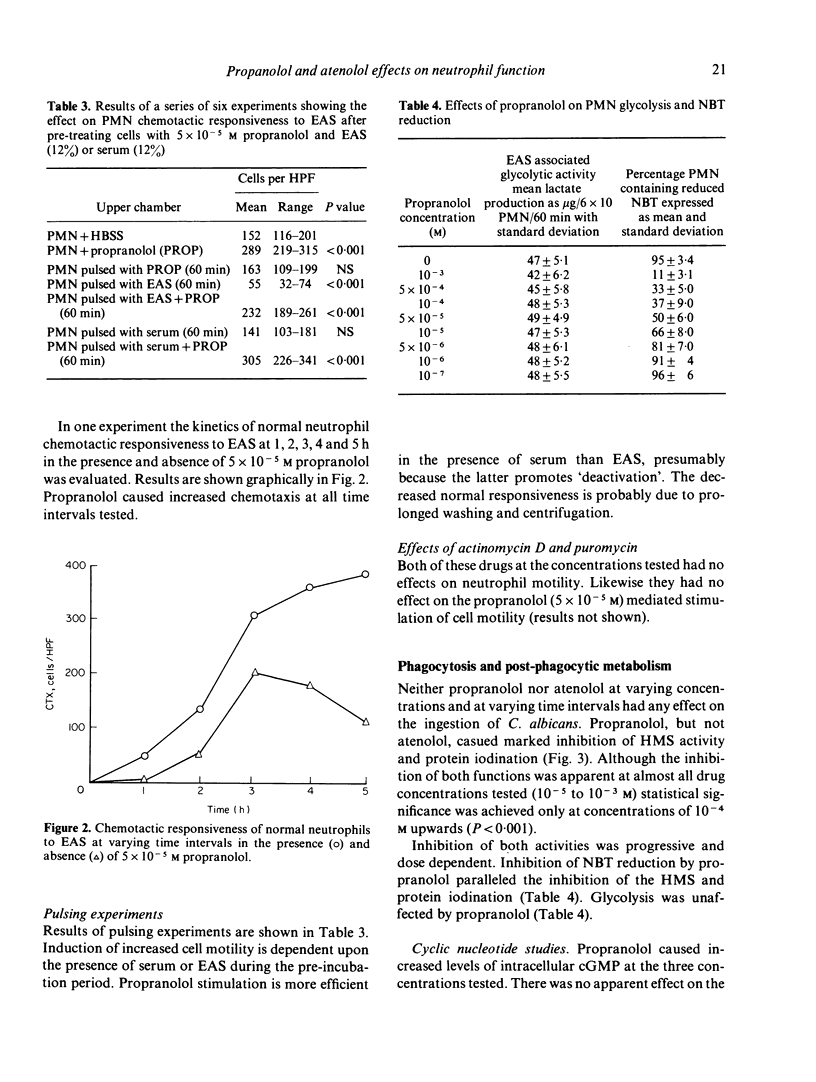
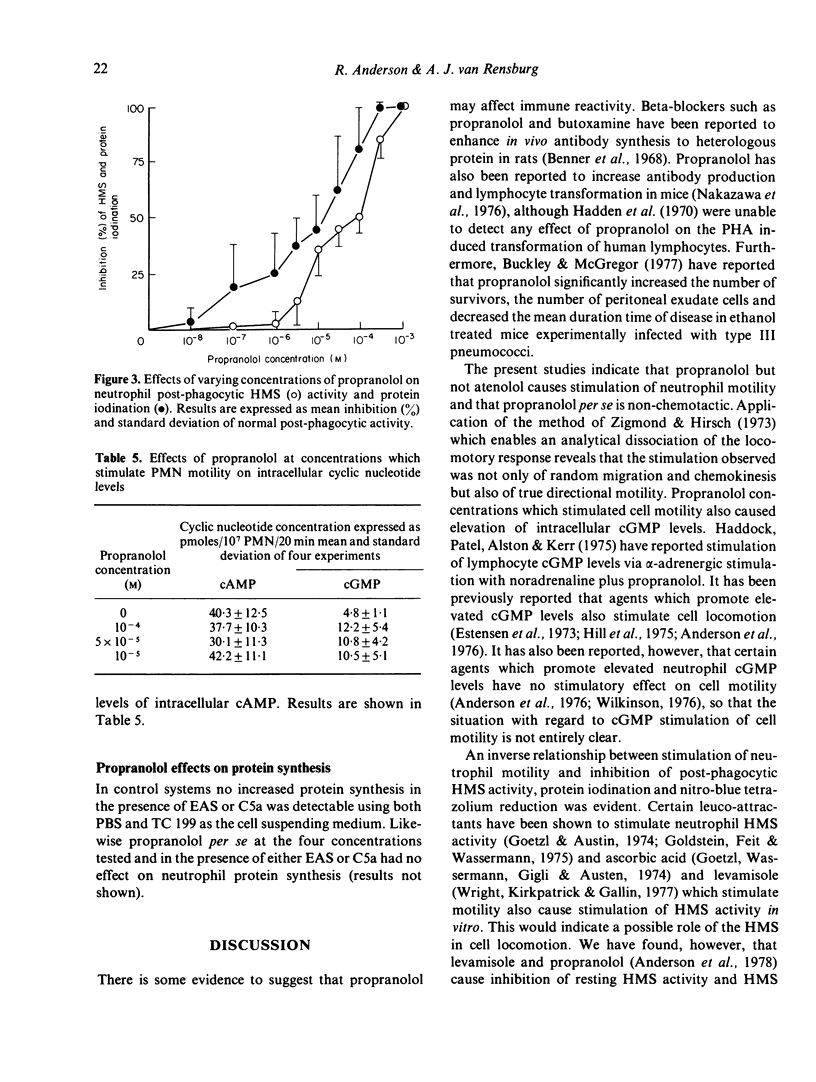
Propranolol at concentrations of 1 x 10(-6) to 1 x 10(-4) M consistently increased neutrophil motility as measured in Boyden chambers. The effects were not due solely to stimulation of random migration and chemokinesis but also of directional motility. Propranolol, over a similar concentration range, caused inhibition of post-phagocytic cell metabolic activity (hexose monophosphate shunt, nitro-blue tetrazolium reduction and protein iodination) without any detectable effect on the ingestion rate of Candida albicans. Atenolol had no effect on any of these neutrophil functions. Both drugs were without effect on glycolysis and intracellular cyclic AMP levels. Propranolol however, at concentrations which stimulated cell motility, caused increased intracellular cyclic GMP levels. It is suggested that propranolol may stimulate neutrophil motility by promoting increased intracellular cyclic GMP levels or by decreasing neutrophil superoxide production.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson R., Glover A., Koornhof H. J., Rabson A. R. In vitro stimulation of neutrophil motility by levamisole: maintenance of cgmp levels in chemotactically stimulated levamisole-treated neutrophils. J Immunol. 1976 Aug;117(2):428–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R., Glover A., Rabson A. R. The effect of chemotactic factors and agents which influence neutrophil movement on anaerobic glycolysis and hexose monophosphate shunt activity. Immunology. 1978 Jul;35(1):141–149. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson R., Glover A., Rabson A. R. The in vitro effects of histamine and metiamide on neutrophil motility and their relationship to intracellular cyclic nucleotide levels. J Immunol. 1977 May;118(5):1690–1696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYDEN S. The chemotactic effect of mixtures of antibody and antigen on polymorphonuclear leucocytes. J Exp Med. 1962 Mar 1;115:453–466. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.3.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estensen R. D., Hill H. R., Quie P. G., Gogan N., Goldberg N. D. Cyclic GMP and cell movement. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):458–460. doi: 10.1038/245458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flyer R. H., Finch S. C. The effects of prostaglandin E1 on human granulocyte metabolism during phagocytosis. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1973 Oct;14(4):325–331. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Austen K. F. Stimulation of human neutrophil leukocyte aerobic glucose metabolism by purified chemotactic factors. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):591–599. doi: 10.1172/JCI107594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goetzl E. J., Wasserman S. I., Gigli I., Austen K. F. Enhancement of random migration and chemotactic response of human leukocytes by ascorbic acid. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):813–818. doi: 10.1172/JCI107620. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein I. M., Feit F., Weissmann G. Enhancement of nitroblue tetrazolium dye reduction by leukocytes exposed to a component of complement in the absence of phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):516–518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadden J. W., Hadden E. M., Middleton E., Jr Lymphocyte blast transformation. I. Demonstration of adrenergic receptors in human peripheral lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1970 Dec;1(6):583–595. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(70)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haddock A. M., Patel K. R., Alston W. C., Kerr J. W. Response of lymphocyte guanyl cyclase to propranolol, noradrenaline, thymoxamine, and acetylcholine in extrinsic bronchial asthma. Br Med J. 1975 May 17;2(5967):357–359. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5967.357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatch G. E., Nichols W. K., Hill H. R. Cyclic nucleotide changes in human neutrophils induced by chemoattractants and chemotactic modulators. J Immunol. 1977 Aug;119(2):450–456. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill H. R., Estensen R. D., Quie P. G., Hogan N. A., Goldberg N. D. Modulation of human neutrophil chemotactic responses by cyclic 3',5'-guanosine monophosphate and cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate. Metabolism. 1975 Mar;24(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(75)90124-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., George W. J. Hormonal control of lysosomal enzyme release from human neutrophils: elevation of cyclic nucleotide levels by autonomic neurohormones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2027–2031. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignarro L. J., Lint T. F., George W. J. Hormonal control of lysosomal enzyme release from human neutrophils. Effects of autonomic agents on enzyme release, phagocytosis, and cylic nucleotide levels. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1395–1414. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomnitzer R., Rabson A. R., Koornhof H. J. The effects of cyclic AMP on leucocyte inhibitory factor (LIF) production and on the inhibition of leucocyte migration. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Apr;24(1):42–48. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCall C. E., DeChatelet L. R., Cooper M. R., Ashburn P. The effects of ascorbic acid on bactericidal mechanisms of neutrophils. J Infect Dis. 1971 Aug;124(2):194–198. doi: 10.1093/infdis/124.2.194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin I., Becker E. L. Effect of exogenous cyclic AMP and other adenine nucleotides on neutrophil chemotaxis and motility. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;50(1):95–102. doi: 10.1159/000231485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivkin I., Rosenblatt J., Becker E. L. The role of cyclic AMP in the chemotactic responsiveness and spontaneous motility of rabbit peritoneal neutrophils. The inhibition of neutrophil movement and the elevation of cyclic AMP levels by catecholamines, prostaglandins, theophylline and cholera toxin. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1126–1134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Root R. K., Stossel T. P. Myeloperoxidase-mediated iodination by granulocytes. Intracellular site of operation and some regulating factors. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1207–1215. doi: 10.1172/JCI107667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sher R., Anderson R., Rabson A. R., Koornhof H. J. Standardisation of the nitro-blue tetrazolium test and factors affecting its clinical application. S Afr Med J. 1974 Feb 9;48(6):209–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tse R. L., Phelps P., Urban D. Polymorphonuclear leukocyte motility in vitro. VI. Effect of purine and pyrimidine analogues: possible role of cyclic AMP. J Lab Clin Med. 1972 Aug;80(2):264–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WOOD H. G., KATZ J., LANDAU B. R. ESTIMATION OF PATHWAYS OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM. Biochem Z. 1963;338:809–847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson P. C. Recognition and response in mononuclear and granular phagocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1976 Sep;25(3):355–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright D. G., Kirkpatrick C. H., Gallin J. I. Effects of levamisole on normal and abnormal leukocyte locomotion. J Clin Invest. 1977 May;59(5):941–950. doi: 10.1172/JCI108716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurier R. B., Weissmann G., Hoffstein S., Kammerman S., Tai H. H. Mechanisms of lysosomal enzyme release from human leukocytes. II. Effects of cAMP and cGMP, autonomic agonists, and agents which affect microtubule function. J Clin Invest. 1974 Jan;53(1):297–309. doi: 10.1172/JCI107550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


