Abstract
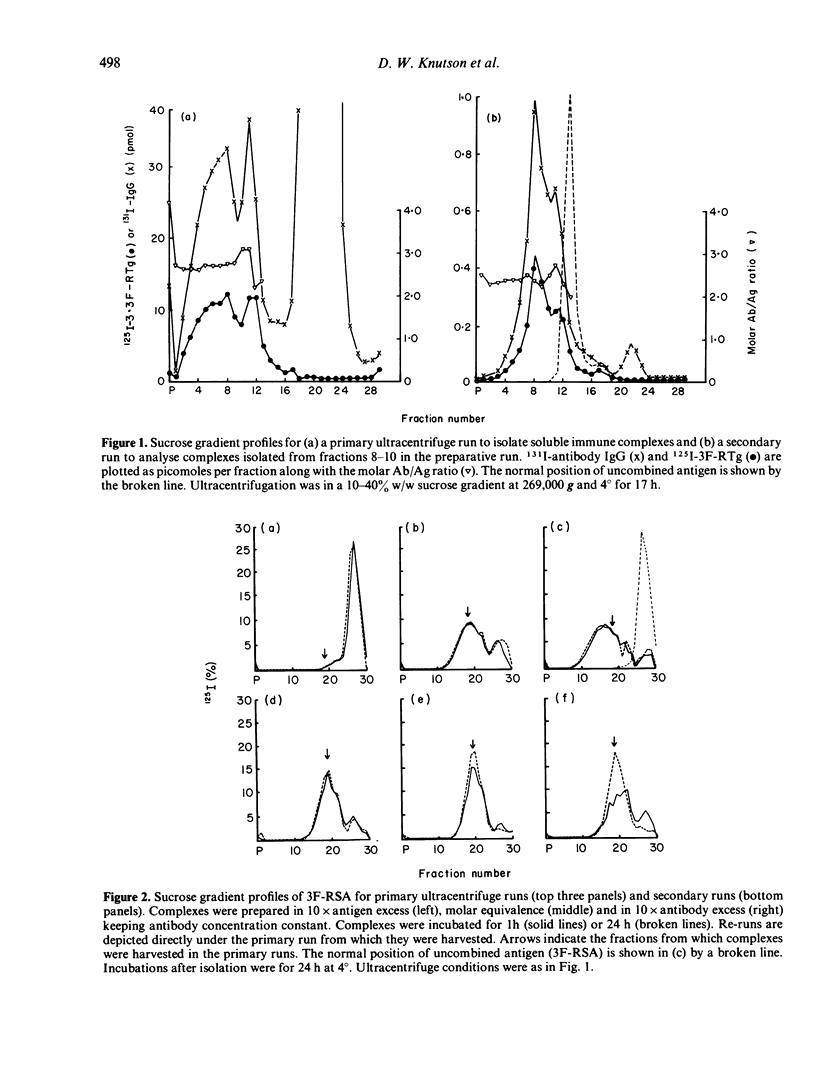
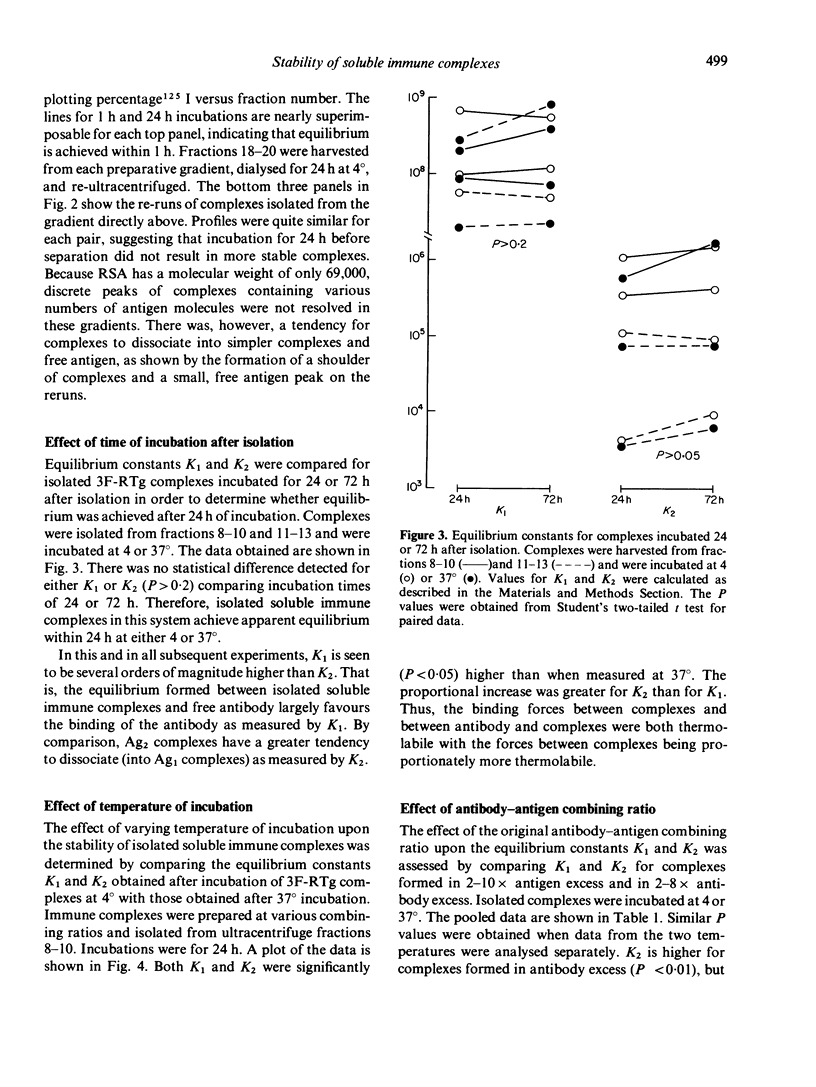
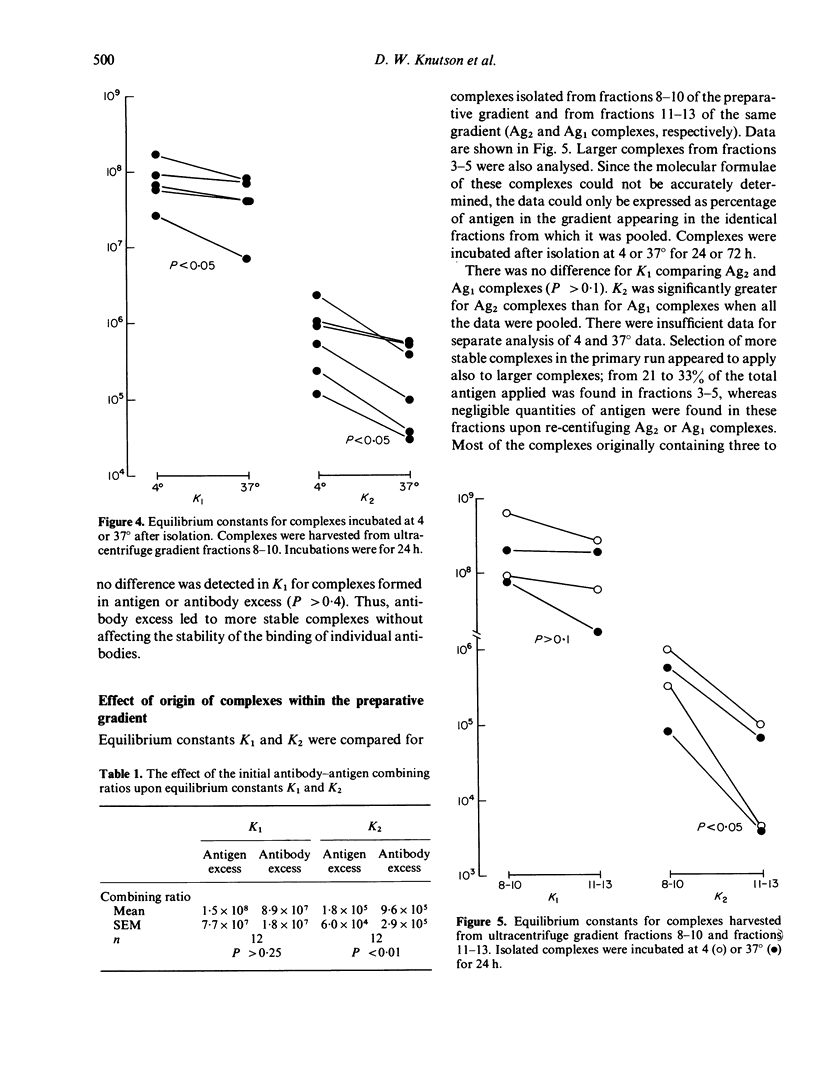
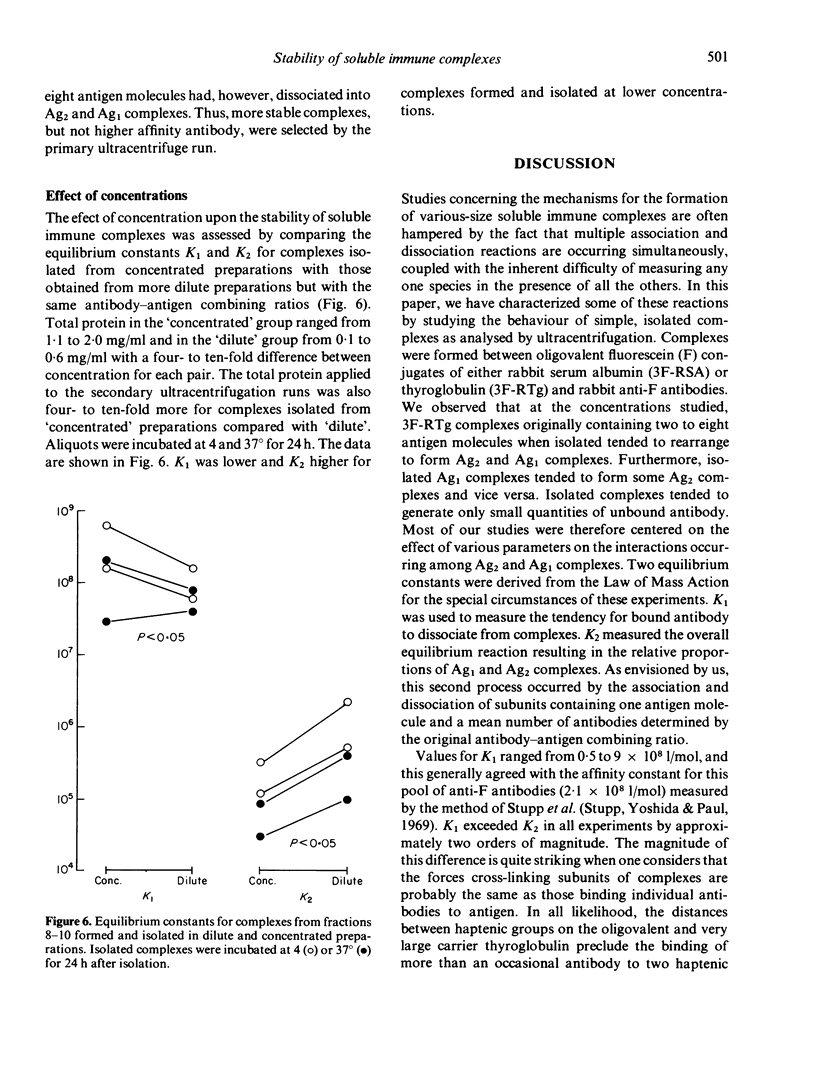
Soluble oligovalent antigen--antibody complexes were isolated and analysed by ultracentrifugation to assess the effect of several forces upon the composition and stability of soluble complexes. Complexes were prepared with fluorescein (F) conjugates of rabbit serum albumin (RSA) or thyroglobulin (RTg) and high affinity rabbit anti-F antibodies. Isolated complexes containing two antigen molecules (Ag2 complexes) tended to dissociate and form an equilibrium with complexes containing one antigen molecule (Ag1 complexes). This equilibrium was thermolabile, concentration dependent and affected by the original combining ratio and the area in the gradient from which complexes were harvested. Small amounts of free antibody dissociated from soluble complexes also to form a dynamic equilibrium; this equilibrium was much less affected by the above parameters. The data support the concept that complexes grow in size by a process analogous to polymerization of simple subunits and that the driving forces for polymerization are of a lower order of magnitude and more affected by physical variables than the primary reaction between antibody and its antigen.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arend W. P., Teller D. C., Mannik M. Molecular composition and sedimentation characteristics of soluble antigen-antibody complexes. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 24;11(22):4063–4072. doi: 10.1021/bi00772a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler V. P., Jr, Beiser S. M. Antibodies to small molecules: biological and clinical applications. Adv Immunol. 1973;17:255–310. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60734-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DANDLIKER W. B., SCHAPIRO H. C., MEDUSKI J. W., ALONSO R., FEIGEN G. A., HAMRICK J. R., Jr APPLICATION OF FLUORESCENCE POLARIZATION TO THE ANTIGEN-ANTIBODY REACTION. THEORY AND EXPERIMENTAL METHOD. Immunochemistry. 1964 Oct;1:165–191. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(64)90041-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandliker W. B., De Saussure V. A. Fluorescence polarization in immunochemistry. Immunochemistry. 1970 Sep;7(9):799–828. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(70)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dandliker W. B., Levison S. A. Investigation of antigen-antibody kinetics by fluorescence polarization. Immunochemistry. 1968 Mar;5(2):171–183. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90101-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLisi C. A theory of precipitation and agglutination reactions in immunological systems. J Theor Biol. 1974 Jun;45(2):555–575. doi: 10.1016/0022-5193(74)90130-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froese A. Kinetic and equilibrium studies on 2,4-Dinitrophenyl hapten-antibody systems. Immunochemistry. 1968 May;5(3):253–264. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(68)90070-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyslop N. E., Jr, Dourmashkin R. R., Green N. M., Porter R. R. The fixation of complement and the activated first component (C1) of complement by complexes formed between antibody and divalent hapten. J Exp Med. 1970 Apr 1;131(4):783–802. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.4.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kijlstra A., Knutson D. W., van der Lelij A., van Es L. A. Characteristics of soluble immune complexes prepared from oligovalent DNP conjugates and anti-DNP antibodies. J Immunol Methods. 1977;17(3-4):263–277. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90109-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Effect of antigen binding on the properties of antibody. Adv Immunol. 1974;18:169–207. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schumaker V. N., Green G., Wilder R. L. A theory of bivalent antibody-bivalent hapten interactions. Immunochemistry. 1973 Aug;10(8):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(73)90224-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steensgaard J., Funding L. On the formulation of a reaction scheme for the interaction between an antigen and its antibody. Immunology. 1974 Feb;26(2):299–302. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steward M. W., Petty R. E. The antigen-binding characteristics of antibody pools of different relative affinity. Immunology. 1972 Dec;23(6):881–887. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stupp Y., Yoshida T., Paul W. E. Determination of antibody-hapten equilibrium constants by an ammonium sulfate precipitation technique. J Immunol. 1969 Sep;103(3):625–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TALMAGE D. W. The kinetics of the reaction between antibody and bovine serum albumin using the Farr method. J Infect Dis. 1960 Jul-Aug;107:115–132. doi: 10.1093/infdis/107.1.115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valentine R. C., Green N. M. Electron microscopy of an antibody-hapten complex. J Mol Biol. 1967 Aug 14;27(3):615–617. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90063-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Es L. A., Knutson D. W., Kayser B. S., Glassock R. J. Soluble oligovalent antigen-antibody complexes. I. The effect of antigen valence and combining ratio on the composition of fluorescein-carrier anti-fluorescein complexes. Immunology. 1979 Jun;37(2):485–493. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


