Abstract
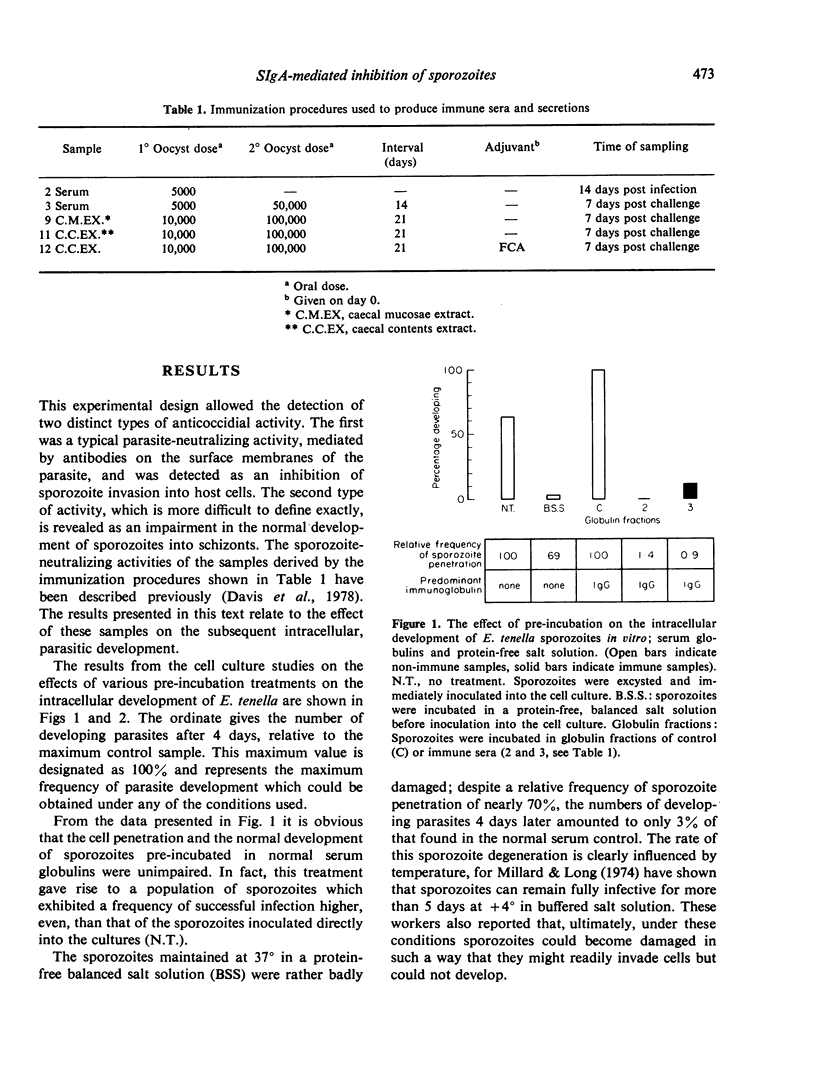
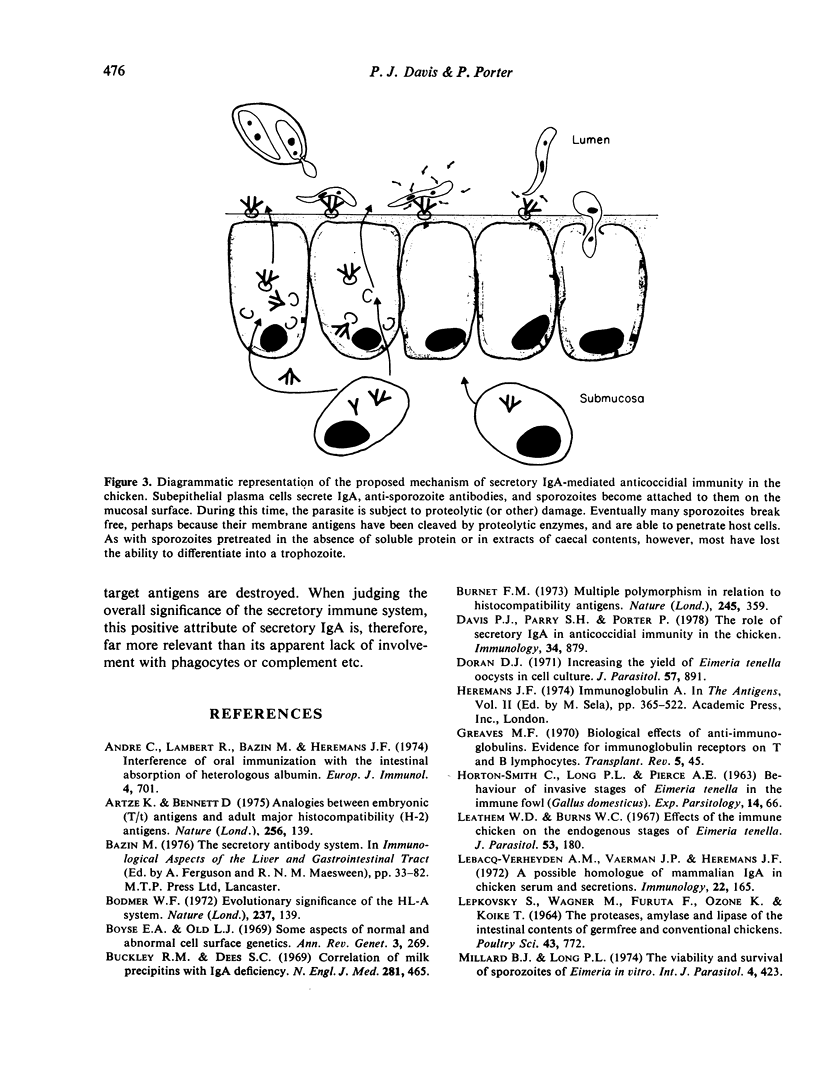
The ability of Eimeria tenella sporozoites to develop normally in cultured chick kidney cells was used as an indicator of the anticoccidial effects of sera and extracts of caecal contents or tissue. Pre-treatment of sporozoites with normal serum globulin enhanced the frequency of intracellular development but pre-treatment in balanced salt solution, without protein, damaged sporozoites so that most had lost the ability to differentiate, even when they were able to invade host cells. The same inhibitory effect was seen when sporozoites were incubated in extracts of caecal contents from non-immunized chickens, although parasitic development was unaffected when sporozoites were pretreated in similar extracts of mucosae. Extracts of immune caecal contents impaired both cell penetration and subsequent development. These results show that sporozoites can lose the ability to differentiate before the ability to penetrate cells and provide evidence of a possible synergism between non-specific factors and secretory antibodies in anticoccidial immunity.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- André C., Lambert R., Bazin H., Heremans J. F. Interference of oral immunization with the intestinal absorption of heterologous albumin. Eur J Immunol. 1974 Oct;4(10):701–704. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830041013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Evolutionary significance of the HL-A system. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):139–passim. doi: 10.1038/237139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley R. H., Dees S. C. Correlation of milk precipitins with IgA deficiency. N Engl J Med. 1969 Aug 28;281(9):465–469. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196908282810903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet F. M. Multiple polymorphism in relation to histocompatibility antigens. Nature. 1973 Oct 19;245(5425):359–361. doi: 10.1038/245359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis P. J., Parry S. H., Porter P. The role of secretory IgA in anti-coccidial immunity in the chicken. Immunology. 1978 May;34(5):879–888. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doran D. J. Increasing the yield of Eimeria tenella oocysts in cell culture. J Parasitol. 1971 Aug;57(4):891–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F. Biological effects of anti-immunoglobulins: evidence for immunoglobulin receptors on 'T' and 'B' lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1970;5:45–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1970.tb00356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leathem W. D., Burns W. C. Effects of the immune chicken on the endogenous stages of Eimeria tenella. J Parasitol. 1967 Feb;53(1):180–185. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebacq-Verheyden A. M., Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F. A possible homologue of mammalian IgA in chicken serum and secretions. Immunology. 1972 Jan;22(1):165–175. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millard B. J., Long P. L. The viability and survival of sporozoites of Eimeria in vitro. Int J Parasitol. 1974 Aug;4(4):423–432. doi: 10.1016/0020-7519(74)90052-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orlans E., Rose M. E. An IgA-like immunoglobulin in the fowl. Immunochemistry. 1972 Aug;9(8):833–838. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90262-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parry S. H., Porter P. Characterization and localization of secretory component in the chicken. Immunology. 1978 Mar;34(3):471–478. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter P., Parry S. H. Further characterization of IgA in chicken serum and secretions with evidence of a possible analogue of mammalian secretory component. Immunology. 1976 Sep;31(3):407–415. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. D., Nathenson S. G. Regeneration of transplantation antigens on mouse cells. Transplant Proc. 1971 Mar;3(1):180–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules: effect of oral immunization. Science. 1972 Aug 18;177(4049):608–610. doi: 10.1126/science.177.4049.608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker W. A., Wu M., Isselbacher K. J., Bloch K. J. Intestinal uptake of macromolecules. III. Studies on the mechanism by which immunization interferes with antigen uptake. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):854–861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weksler M. E., Birnbasum G. Lymphocyte transformation induced by autologous cells: stimulation by cultured lymphoblast lines. J Clin Invest. 1972 Dec;51(12):3124–3132. doi: 10.1172/JCI107139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


