Abstract
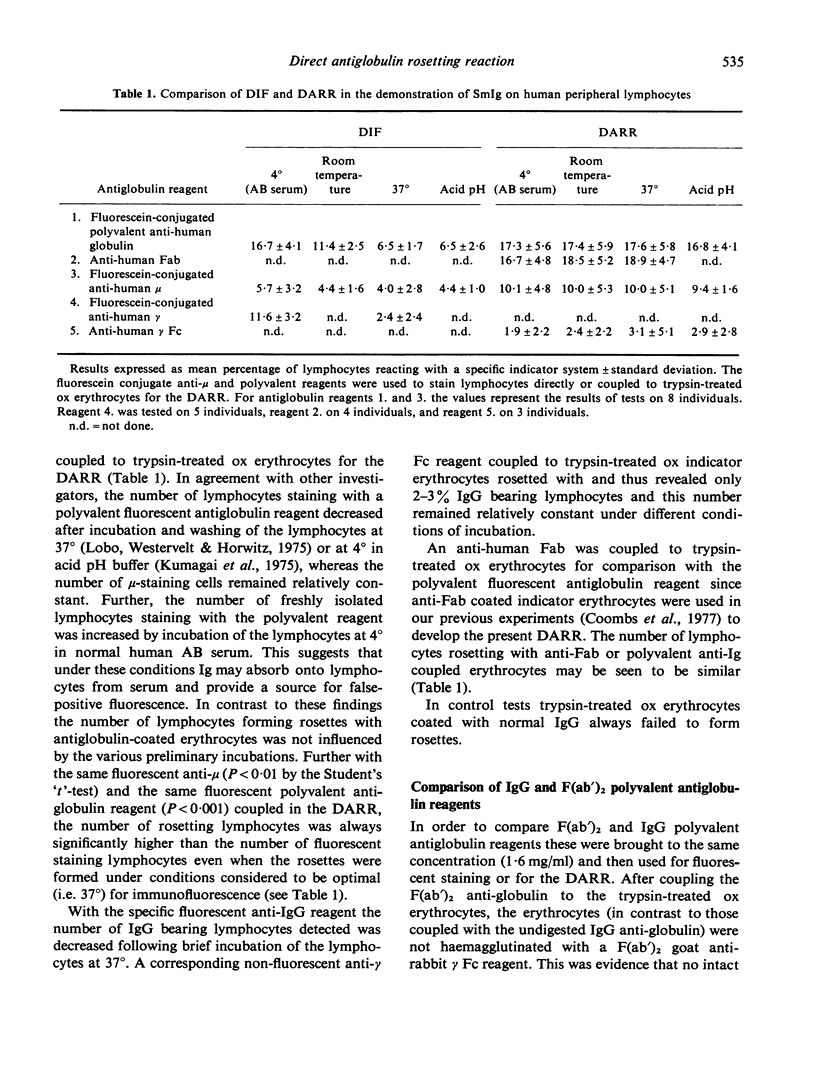
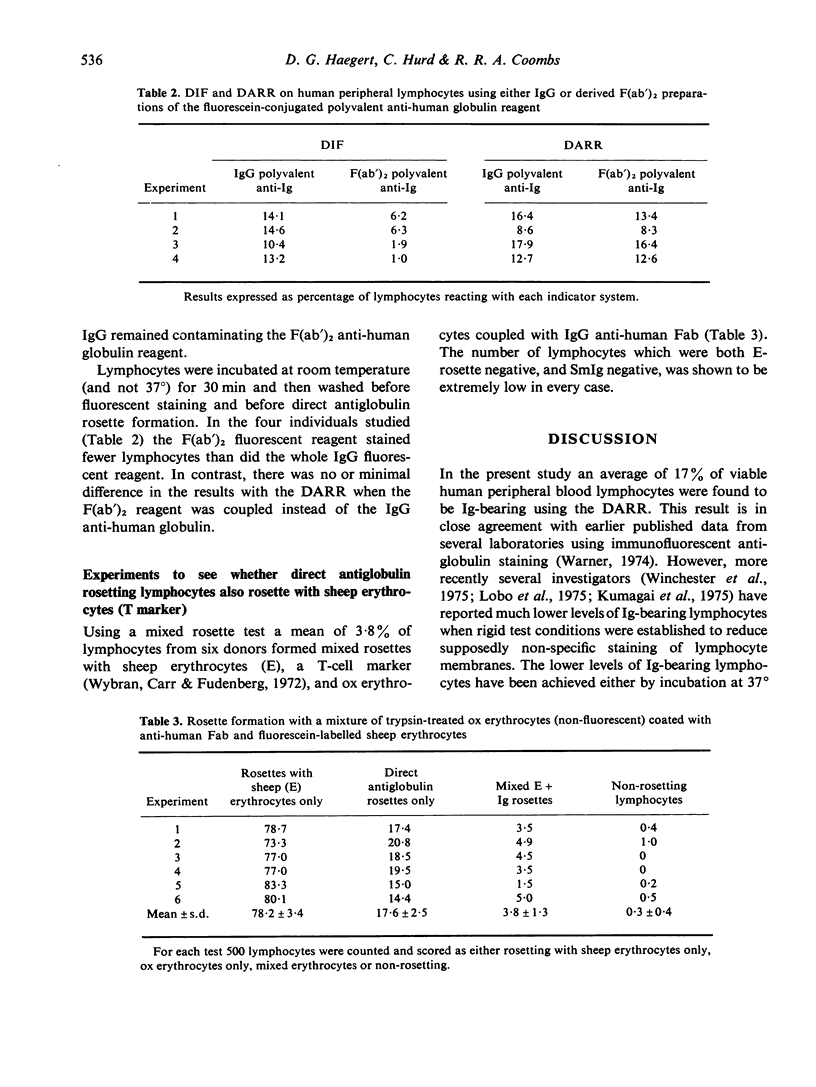
Comparisons were made between the Direct Antiglobulin Rosetting Reaction (DARR) and Direct Immunofluorescence (DIF) in the detection of surface membrane immunoglobulin of human peripheral lymphocytes. The DARR was more sensitive and the results with this testing procedure (as opposed to those with the DIF) were not influenced by various treatments of the lymphocytes before testing, such as incubation in AB serum at +/- 4 degrees, incubation in serum-free medium at 37 degrees or short exposure to acetate buffer at pH 4.0. Again the DARR (as opposed to the DIF) gave essentially the same results whether the red cell-linked antiglobulin was IgG or the F(ab')2 preparation. With mixed rosetting for both T and SmIg+/- lymphocytes, there was only 1% or less null cells and only 5% or less lymphocytes rosetted with both marker red cells.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bright S., Munro A. J., Lawson Y. A., Joysey V. C., Coombs R. R. An indirect anti-immunoglobulin rosetting reaction to detect alloantibodies to human lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):55–62. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90158-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chess L., Levine H., MacDermott R. P., Schlossman S. F. Immunologic functions of isolated human lymphocyte subpopulations. VI. Further characterization of the surface Ig negative, E rosette negative (null cell) subset. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1483–1487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs R. R., Wilson A. B., Eremin O., Gurner B. W., Haegert D. G., Lawson Y. A., Bright S., Munro A. J. Comparison of the direct antiglobulin rosetting reaction with the mixed antiglobulin rosetting reaction for the detection of immunoglobulin on lymphocytes. J Immunol Methods. 1977;18(1-2):45–54. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eremin O., Plumb D., Coombs R. R. T and B lymphocyte populations in human normal lymph node, regional tumour lymph node and inflammatory lymph node. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;52(1-4):277–290. doi: 10.1159/000231693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuliano V. J., Jasin H. E., Hurd E. R., Ziff M. Enumeration of B-lymphocytes in human peripheral blood by a rosette method for the detection of surface-bound immunoglobulin. J Immunol. 1974 Apr;112(4):1494–1499. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haegert D. G., Coombs R. R. Immunoglobulin-positive mononuclear cells in human peripheral blood: detection by mixed anti-globulin and direct anti-globulin-rosetting reactions. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1426–1430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hjelm H., Hjelm K., Sjöquist J. Protein A from Staphylococcus aureus. Its isolation by affinity chromatography and its use as an immunosorbent for isolation of immunoglobulins. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):73–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80680-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai K., Abo T., Sekizawa T., Sasaki M. Studies of surface immunoglobulins on human B lymphocytes. I. Dissociation of cell-bound immunoglobulins with acid pH or at 37 degrees C. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):982–987. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N. R., Bishop S., Jefferis Use of antibody-coated red cells for the sensitive detection of antigen and in rosette tests for cells bearing surface immunoglobulins. J Immunol Methods. 1977;15(3):279–289. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(77)90065-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo P. I., Westervelt F. B., Horwitz D. A. Identification of two populations of immunoglobulin-bearing lymphocytes in man. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):116–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner N. L. Membrane immunoglobulins and antigen receptors on B and T lymphocytes. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):67–216. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60252-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Fu S. M., Hoffman T., Kunkel H. G. IgG on lymphocyte surfaces; technical problems and the significance of a third cell population. J Immunol. 1975 Apr;114(4):1210–1212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Fu S. M. Lymphocyte surface membrane immunoglobulin. Scand J Immunol. 1976 Jun;Suppl 5:77–82. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb03858.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winchester R. J., Winfield J. B., Siegal F., Wernet P., Bentwich Z., Kunkel H. G. Analyses of lymphocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Occurrence of interfering cold-reactive antilymphocyte antibodies. J Clin Invest. 1974 Nov;54(5):1082–1092. doi: 10.1172/JCI107852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wybran J., Carr M. C., Fudenberg H. H. The human rosette-forming cell as a marker of a population of thymus-derived cells. J Clin Invest. 1972 Oct;51(10):2537–2543. doi: 10.1172/JCI107069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweerink H. J. Multiple forms of SS leads to DS RNA polymerase activity in reovirus-infected cells. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):313–315. doi: 10.1038/247313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


