Abstract
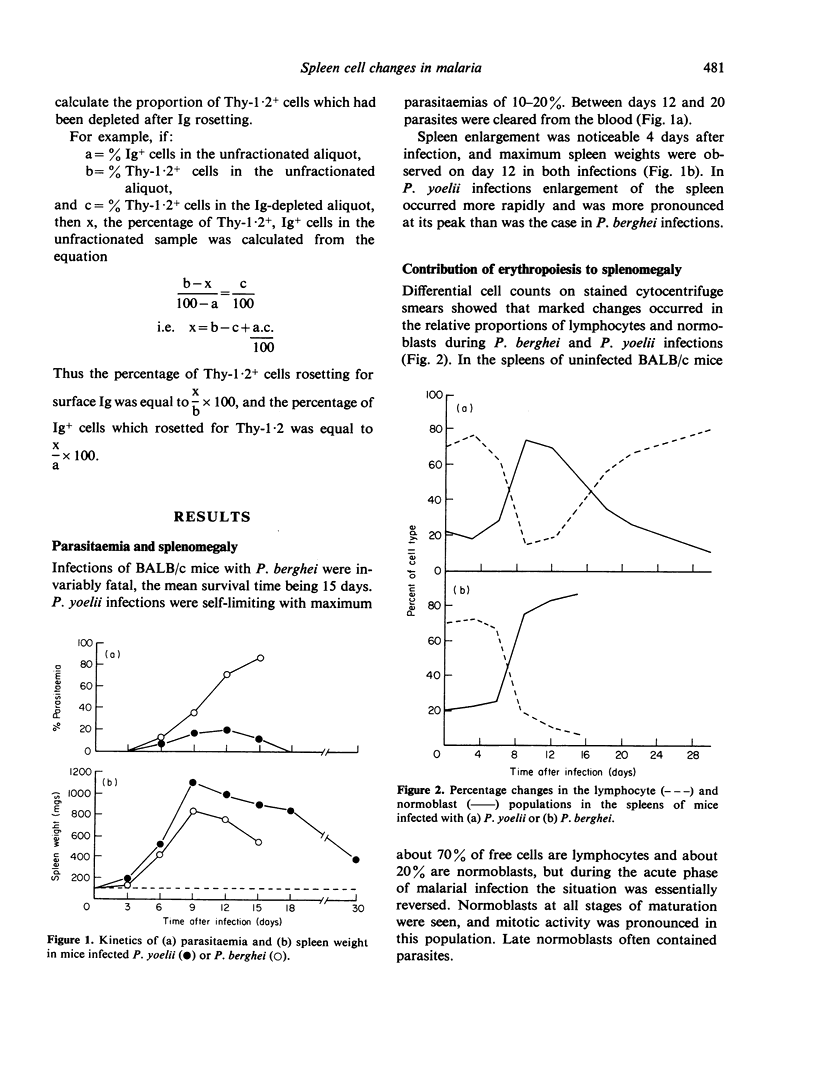
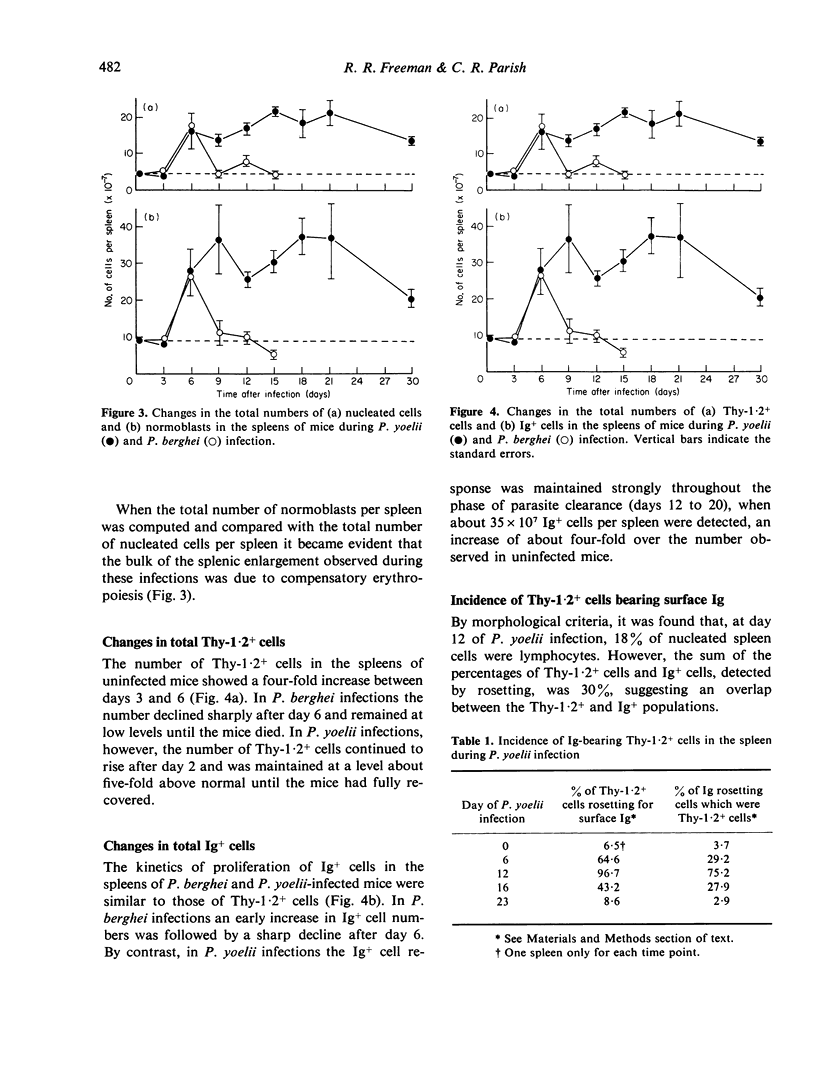
Changes in the proportions and total numbers of splenic Thy-1.2+ cells, Ig+ cells and normoblasts were analysed during fatal Plasmodium berghei and non-fatal P. yoelii infections in mice. Thy-1.2+ and Ig+ cells were identified by rosetting techniques, and normoblasts by morphological criteria. The splenomegaly observed during these infections was found to be caused mainly by proliferation of normoblasts. An early increase in the numbers of Thy-1.2+ and Ig+ cells was detected in both infections, but in P. berghei infections these responses were subsequently suppressed. In P. yoelii infections Thy-1.2+ and Ig+ cell numbers were maintained at four to five-fold above normal levels until the mice had completely recovered. During the acute phase of P. yoelii infection it appeared that most splenic T-cells expressed surface immunoglobulin.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basten A., Miller J. F., Warner N. L., Abraham R., Chia E., Gamble J. A subpopulation of T cells bearing Fc receptors. J Immunol. 1975 Oct;115(4):1159–1165. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown I. N., Phillips R. S. Immunity to Plasmodium berghei in rats: passive serum transfer and role of the spleen. Infect Immun. 1974 Dec;10(6):1213–1218. doi: 10.1128/iai.10.6.1213-1218.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark I. A., Allison A. C. Babesia microti and Plasmodium berghei yoelii infections in nude mice. Nature. 1974 Nov 22;252(5481):328–329. doi: 10.1038/252328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diggs C. L., Osler A. G. Humoral immunity in rodent malaria. II. Inhibition of parasitemia by serum antibody. J Immunol. 1969 Feb;102(2):298–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gravely S. M., Hamburger J., Kreier J. P. T and B cell population changes in young and in adult rats infected with Plasmodium berghei. Infect Immun. 1976 Jul;14(1):178–183. doi: 10.1128/iai.14.1.178-183.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Targett G. A., Carter R. L., Leuchars E., Davies A. J. The immunological response of CBA mice to P. yoelii. I. General characteristics, the effects of T-cell deprivation and reconstitution with thymus grafts. Immunology. 1977 Jun;32(6):849–859. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Targett G. A., Davies A. J., Leuchars E., Carter R. Proceedings: The passive transfer of immunity to Plasmodium berghei yoelii. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1975;69(4):426–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayawardena A. N., Targett G. A., Leuchars E., Carter R. L., Doenhoff M. J., Davies A. J. T-cell activation in murine malaria. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):149–151. doi: 10.1038/258149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Möller G. Effect of B-cell mitogens on lymphocyte subpopulations possesing C'3 and Fc receptors. J Exp Med. 1974 Apr 1;139(4):969–982. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.4.969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parish C. R. Separation and functional analysis of subpopulations of lymphocytes bearing complement and Fc receptors. Transplant Rev. 1975;25:98–120. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb00727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Playfair J. H. The role of antibody in T-cell responses. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 May;17(1):1–18. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramshaw I. A., Parish C. R. Surface properties of cells involved in antibody-dependent cytotoxicity. Cell Immunol. 1976 Feb;21(2):226–235. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salaman M. H., Wedderburn N., Bruce-Chwatt L. J. The immunodepressive effect of a murine plasmodium and its interaction with murine oncogenic viruses. J Gen Microbiol. 1969 Dec;59(3):383–391. doi: 10.1099/00221287-59-3-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soteriades-Vlachos C., Gyöngyössy M. I., Playfair J. H. Rosette formation by mouse lymphocytes. III. Receptors for immunoglobulin on normal and activated T cells. Clin Exp Immunol. 1974 Oct;18(2):187–192. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stout R. D., Herzenberg L. A. The Fc receptor on thymus-derived lymphocytes: II. Mitogen responsiveness of T lymphocytes bearing the Fc receptor. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1041–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topley E., Bruce-Chwatt L. J., Dorrell J. Haematological study of a rodent malaria model. J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Jan;73(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren H. S., Weidanz W. P. Malarial immunodepression in vitro: adherent spleen cells are functionally defective as accessory cells in the response to horse erythrocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Nov;6(11):816–819. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830061112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wedderburn N., Dracott B. N. The immune reponse to type III pneumococcal polysaccharide in mice with malaria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1977 Apr;28(1):130–137. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinbaum F. I., Evans C. B., Tigelaar R. E. Immunity to Plasmodium Berghei yoelii in mice. I. The course of infection in T cell and B cell deficient mice. J Immunol. 1976 Nov;117(5 PT2):1999–2005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyler D. J., Gallin J. I. Spleen-derived mononuclear cell chemotactic factor in malaria infections: a possible mechanism for splenic macrophage accumulation. J Immunol. 1977 Feb;118(2):478–484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


