Abstract
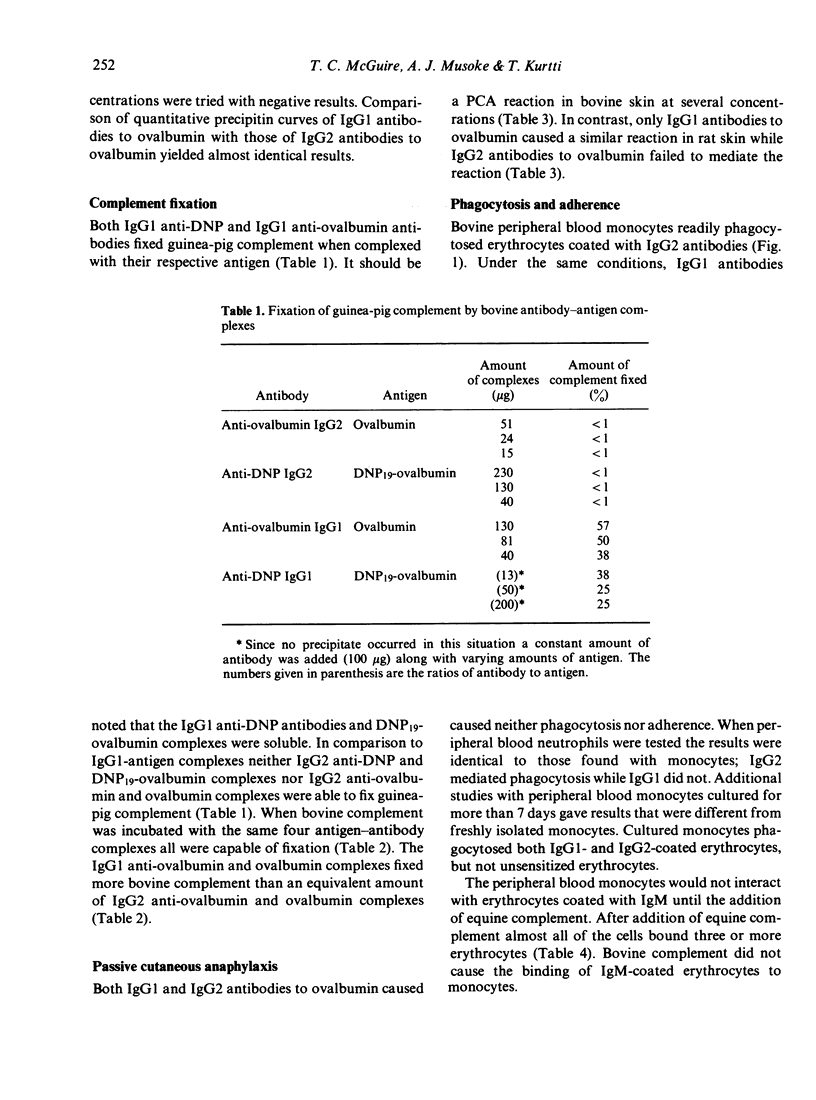
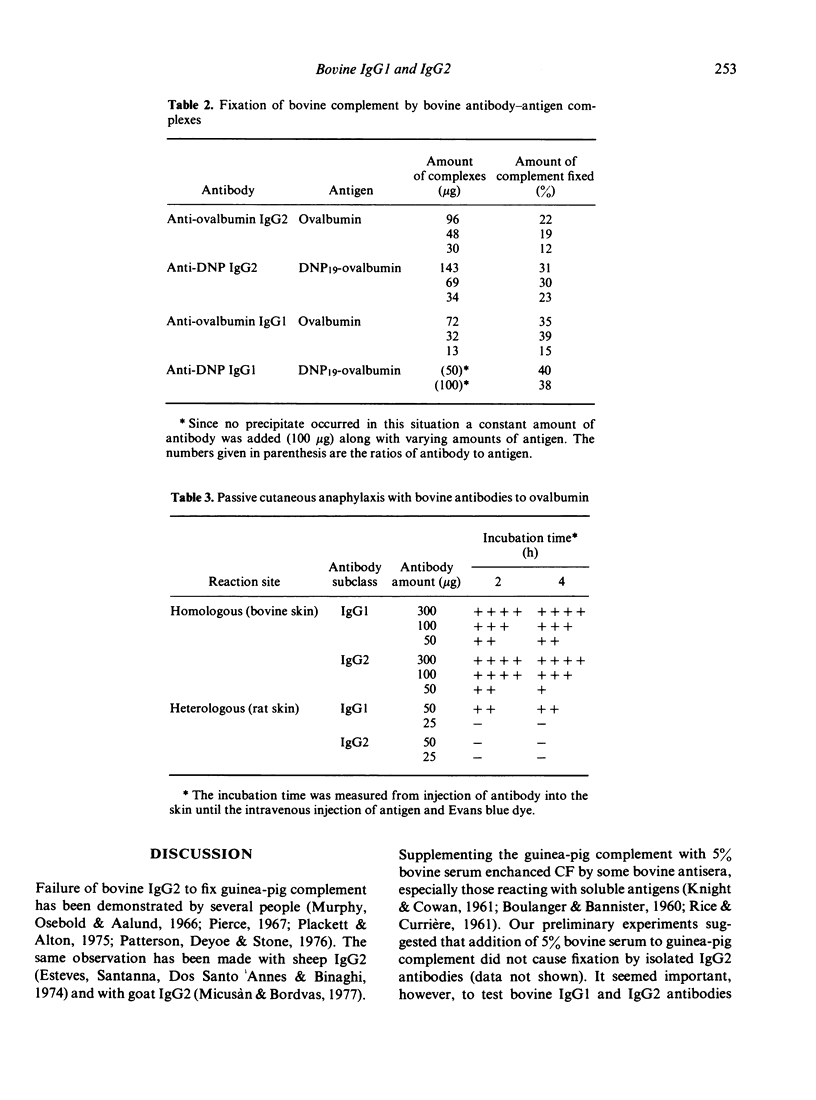
Bovine immunoglobulin G subclass (IgG1 and IgG2) antibodies were found to fix bovine complement while only IgG1 fixed guinea-pig complement in vitro. Similar results were noted when IgG1 and IgG2 antibodies were tested by passive cutaneous anaphylaxis (PCA) in that both IgG1 and IgG2 caused PCA in bovine skin while only IgG1 mediated the reaction in rat skin. In precipitation reactions IgG1 antibodies to DNP failed to cause precipitation of DNP19-ovalbumin while IgG2 antibodies to DNP precipitated DNP19-ovalbumin. Both IgG1 and IgG2 antibodies to ovalbumin precipitated ovalbumin. Surprisingly, IgG2 antibodies to equine erythrocytes caused phagocytosis by bovine neutrophils and peripheral blood monocytes while IgG1 antibodies failed to cause either phagocytosis or adherence. Results with peripheral blood monocytes cultured for 7 days demonstrated that both IgG1 and IgG2 could mediate phagocytosis.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Archer B. G., Krakauer H. Thermodynamics of antibody-antigen reactions. 1. The binding of simple haptens to two classes of antibodies fractionated according to affinity. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):615–617. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer B. G., Krakauer H. Thermodynamics of antibody-antigen reactions. 2. The binding of bivalent synthetic random coil antigens to antibodies having different antigen precipitating properties. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 22;16(4):618–627. doi: 10.1021/bi00623a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks K. L., McGuire T. C. Surface receptors on neutrophils and monocytes from immunodeficient and normal horses. Immunology. 1975 Mar;28(3):581–588. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barbet A. F., McGuire T. C. Crossreacting determinants in variant-specific surface antigens of African trypanosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1989–1993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barta O., Barta V. Haemolytic assay of bovine serum complement. J Immunol Methods. 1972 Aug;1(4):363–374. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(72)90029-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berken A., Benacerraf B. Properties of antibodies cytophilic for macrophages. J Exp Med. 1966 Jan 1;123(1):119–144. doi: 10.1084/jem.123.1.119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esteves M. B., Sant'anna O. A., Annes V. C., Binaghi R. A. Characterization and properties of an anaphylactic 7S antibody in sheep. J Immunol. 1974 Feb;112(2):722–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinstein A., Hobart M. J. Structural relationship and complement fixing activity of sheep and other ruminant immunoglobulin G subclasses. Nature. 1969 Aug 30;223(5209):950–952. doi: 10.1038/223950a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fine D. P., Marney S. R., Jr, Colley D. G., Sergent J. S., Des Prez R. M. C3 shunt activation in human serum chelated with EGTA. J Immunol. 1972 Oct;109(4):807–809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammer D. K., Kickhöfen B., Schmid T. Detection of homocytotropic antibody associated with a unique immunoglobulin class in the bovine species. Eur J Immunol. 1971 Aug;1(4):249–257. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830010407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. L., Allen P. Z. Equine antibodies to human gamma-G-globulin. 3. Immunochemical behavior and specificity of gamma-2- and gamma-1-antibody fractions isolated from equine antisera to human gamma-G-globulin. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):955–963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. L., Allen P. Z. Equine antibodies to human gamma-G-globulin. II. Isolation and antigenic analysis of gamma-2- and gamma-1-antibody fractions from equine antisera to human gamma-G-globulin. J Immunol. 1968 May;100(5):942–954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLIMAN N. R., ROCKEY J. H., KARUSH F. VALENCE AND AFFINITY OF EQUINE NONPRECIPITATING ANTIBODY TO A HAPTENIC GROUP. Science. 1964 Oct 16;146(3642):401–403. doi: 10.1126/science.146.3642.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KNIGHT G. J., COWAN K. M. Studies on allegedly non-complement-fixing immune system. I. A beat labile serum factor requirement for a bovine antibody complement-fixing system. J Immunol. 1961 Mar;86:354–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linscott W. D., Ranken R., Triglia R. P. Evidence that bovine conglutinin reacts with an early product of C3b degradation, and an improved conglutination assay. J Immunol. 1978 Aug;121(2):658–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mach J. P., Pahud J. J., Isliker H. IgA with "secretory piece" in bovine colostrum and saliva. Nature. 1969 Aug 30;223(5209):952–955. doi: 10.1038/223952a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
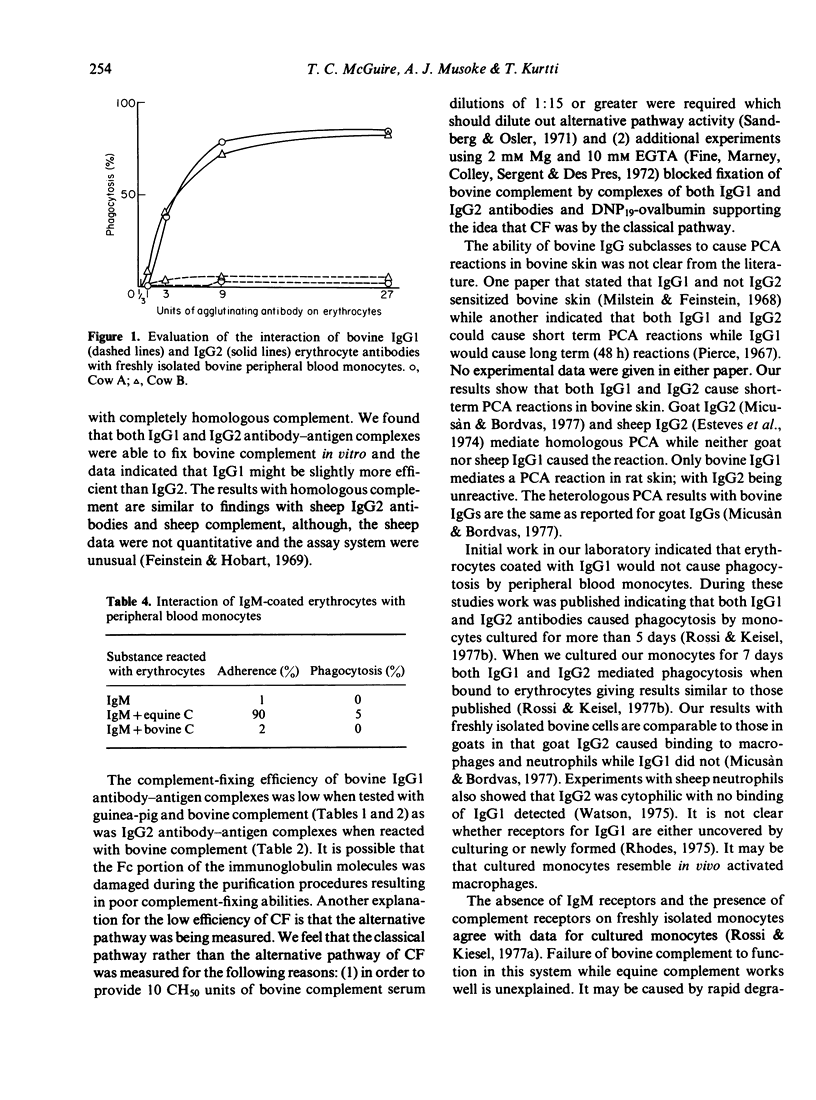
- McGuire T. C., Pfeiffer N. E., Weikel J. M., Bartsch R. C. Failure of colostral immunoglobulin transfer in calves dying from infectious disease. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1976 Oct 1;169(7):713–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire T. C., Van Hoosier G. L., Jr, Henson J. B. The complement-fixation reaction in eguine infectious anemia: demonstration of inhibition by IgG (T). J Immunol. 1971 Dec;107(6):1738–1744. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Micusan V. V., Borduas A. G. Biological properties of goat immunoglobulins G. Immunology. 1977 Apr;32(4):373–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. P., Feinstein A. Comparative studies of two types of bovine immunoglobulin G heavy chains. Biochem J. 1968 Apr;107(4):559–564. doi: 10.1042/bj1070559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy F. A., Osebold J. W., Aalund O. Kinetics of the antibody response to Anaplasma marginale infection. J Infect Dis. 1966 Feb;116(1):99–111. doi: 10.1093/infdis/116.1.99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen K., Holmes W., Wilkie B., Tizard I. Bovine reaginic antibody. I. Rat mast cell degranulation by bovine allergic serum. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1976;51(4):441–450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patterson J. M., Deyoe B. L., Stone S. S. Identification of immunoglobulins associated with complement fixation, agglutination, and low pH buffered antigen tests for brucellosis. Am J Vet Res. 1976 Mar;37(3):319–324. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plackett P., Alton G. G. A mechanism for prozone formation in the complement fixation test for bovine brucellosis. Aust Vet J. 1975 Aug;51(8):374–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1975.tb15598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes J. Macrophage heterogeneity in receptor activity: the activation of macrophage Fc receptor function in vivo and in vitro. J Immunol. 1975 Mar;114(3):976–981. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C. R., Kiesel G. K. Bovine immunoglobulin G subclass receptor sites on bovine macrophages. Am J Vet Res. 1977 Jul;38(7):1023–1025. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi C. R., Kiesel G. K. Bovine peripheral blood monocyte cultures: growth characteristics and cellular receptors for immunoglobulin G and complement. Am J Vet Res. 1977 May;38(5):559–563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandberg A. L., Osler A. G. Dual pathways of complement interaction with guinea pig immunoglobulins. J Immunol. 1971 Nov;107(5):1268–1273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelberg H. L. Biological activities of immunoglobulins of different classes and subclasses. Adv Immunol. 1974;19(0):259–294. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60254-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaerman J. P., Heremans J. F., Van Kerckhoven G. Communications. Identification of IgA in several mammalian species. J Immunol. 1969 Dec;103(6):1421–1423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson D. L. Cytophilic attachment of ovine IgG2 to autologous polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Aust J Exp Biol Med Sci. 1975 Dec;53(6):527–529. doi: 10.1038/icb.1975.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells P. W., Eyre P. Bovine homocytotropic (skin-sensitizing) antibody. Immunol Commun. 1972;1(2):105–111. doi: 10.3109/08820137209022928. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wofsy L., Burr B. The use of affinity chromatography for the specific purification of antibodies and antigens. J Immunol. 1969 Aug;103(2):380–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


