Abstract
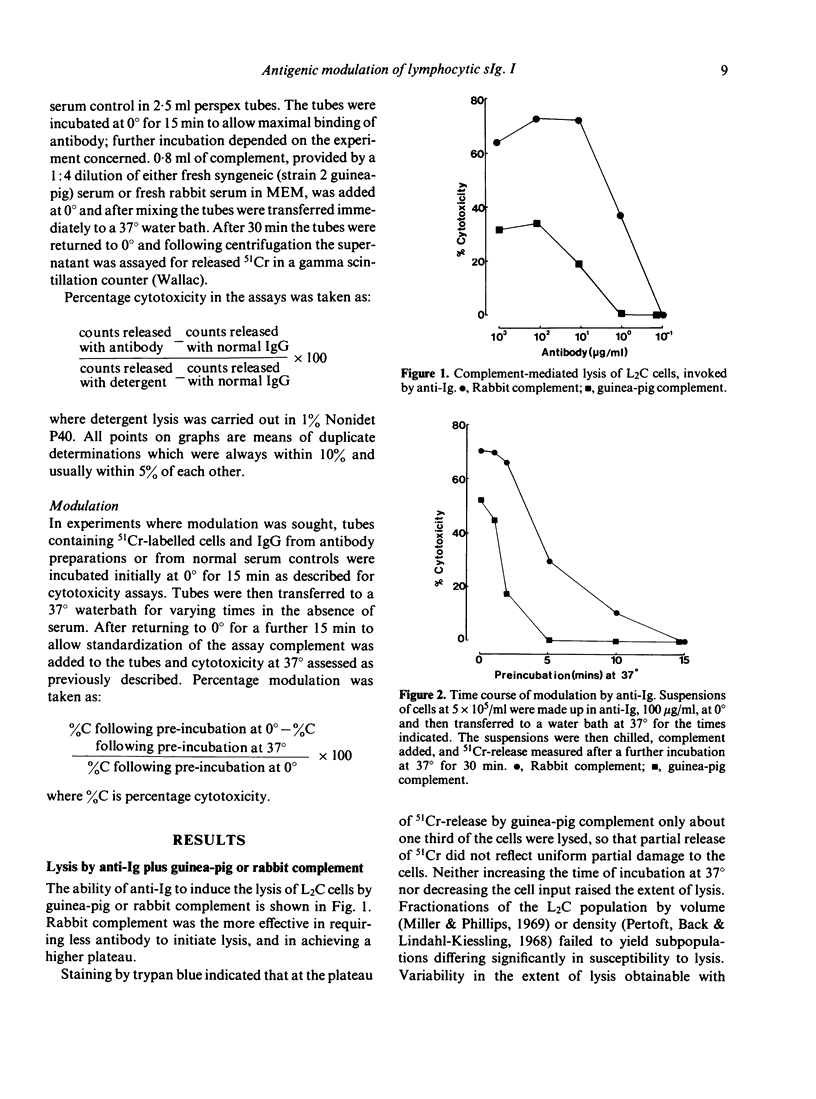
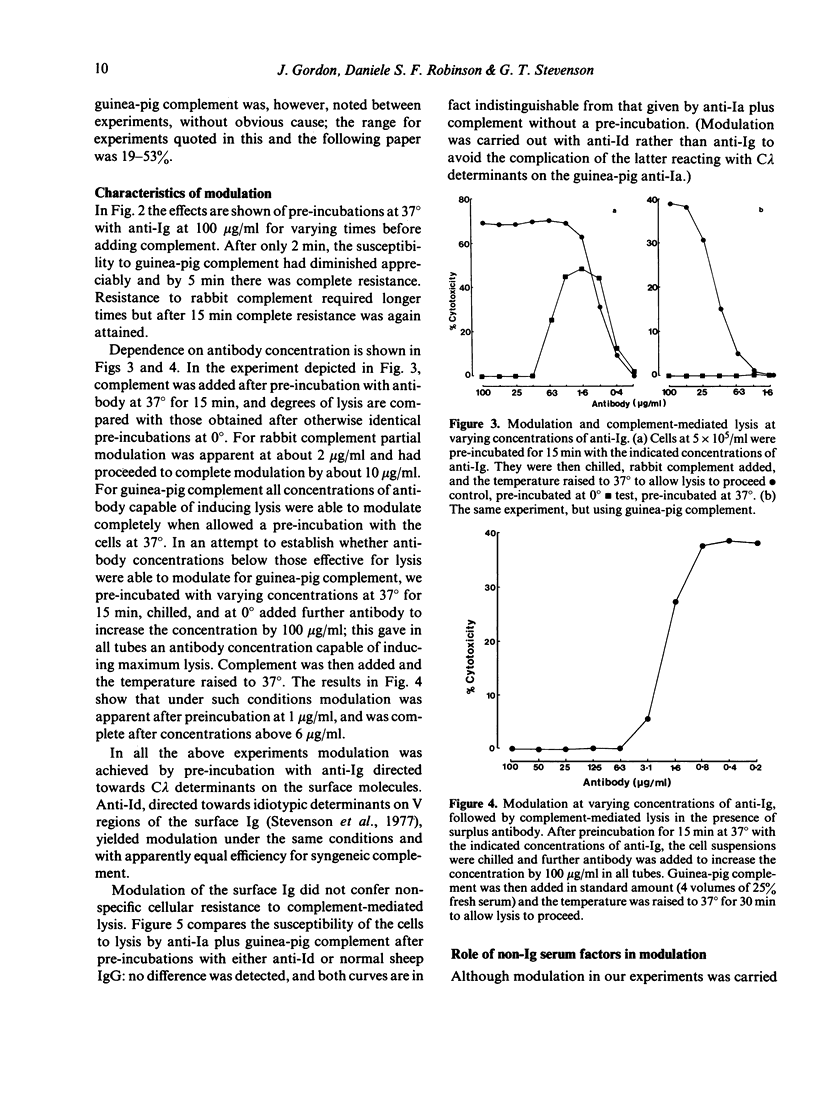
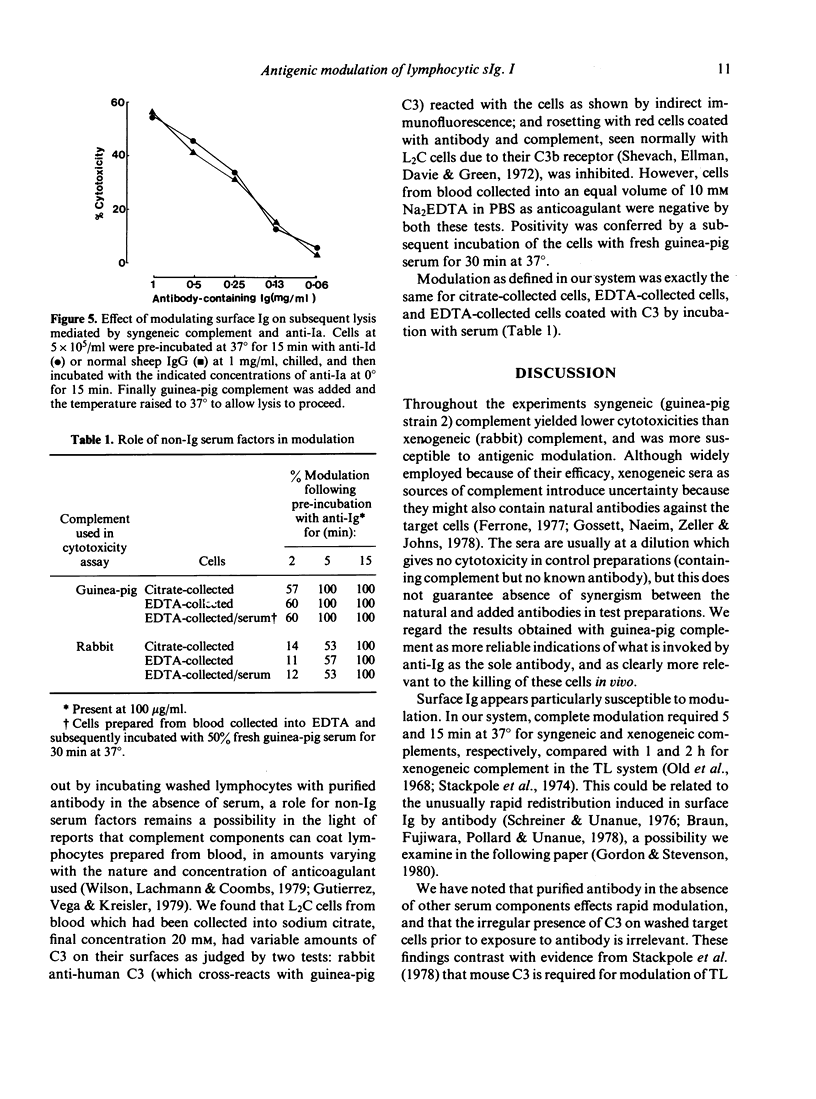
Following previous authors, the term antigenic modulation is used to describe the induction, by antibody, of resistance to lysis by antibody plus complement. A report is given of the rapid antigenic modulation in vitro of surface immunoglobulin (Ig) on guinea-pig L2C leukaemic lymphocytes: incubation of the cells for 2 min or longer at 37 degrees with anti-Ig diminished or removed completely the lysis occurring during subsequent incubation with anti-Ig plus complement. The modulation was effective for both xenogeneic (rabbit) and syngeneic (guinea-pig strain 2) complements, but more rapid for the latter. It appeared simply to require the action of antibody on a metabolically active cell: no requirement could be demonstrated for any serum component other than antibody, and there was a need to raise the temperature to 37 degrees after attachment of the antibody. There was molecular specificity inasmuch as modulation with anti-Ig failed to confer any resistance to lysis by another antibody (anti-Ia) plus complement.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Braun J., Fujiwara K., Pollard T. D., Unanue E. R. Two distinct mechanisms for redistribution of lymphocyte surface macromolecules. I. Relationship to cytoplasmic myosin. J Cell Biol. 1978 Nov;79(2 Pt 1):409–418. doi: 10.1083/jcb.79.2.409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cikes M. Antigenic changes in cultured murine lymphomas after retransplantation into syngeneic hosts. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Apr;54(4):903–906. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.4.903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doig D., Chesebro B. Antibody-induced loss of Friend virus leukemia cell surface antigens occurs during progression of erythroleukemia in F1 mice. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1109–1121. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon N. L., Little J. R. Different mechanisms for the modulation of TL antigens on murine lymphoid cells. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):919–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrone S. Rabbit complement in the lymphocytotoxicity test. Tissue Antigens. 1977 Apr;9(4):223–226. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1977.tb01111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett T., Naeim F., Zeller E., Johns S. Activation of classical complement pathway by naturally occurring heteroantibodies in normal rabbit serum. Effect on subpopulations of human lymphoid cells. Tissue Antigens. 1978 Nov;12(5):330–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0039.1978.tb01341.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez C., Vega J., Kreisler M. Antibody-independent activation of complement by human peripheral B lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1979 Jan;9(1):72–76. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830090115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough D. W., Chapple J. C., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T. Further studies of immunoglobulin synthesis by guinea pig leukaemic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1978 May;34(5):889–899. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hough D. W., Eady R. P., Hamblin T. J., Stevenson F. K., Stevenson G. T. Anti-idiotype sera raised against surface immunoglobulin of human neoplastic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):960–969. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioachim H. L., Keller S. E., Dorsett B. H., Pearse A. Induction of partial immunologic tolerance in rats and progressive loss of cellular antigenicity in Gross virus lymphoma. J Exp Med. 1974 Jun 1;139(6):1382–1394. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.6.1382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ioachim H. L., Sabbath M. Redistribution and modulation of Gross murine leukemia virus antigens induced by specific antibodies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jan;62(1):169–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamm M. E., Boyse E. A., Old L. J., Lisowska-Bernstein B., Stockert E. Modulation of TL (thymus-leukemia) antigens by Fab-fragments of TL antibody. J Immunol. 1968 Jul;101(1):99–103. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadel E. M. History and further observations (1954-1976) of the L2C leukemia in the guinea pig. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2249–2254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Stockert E., Boyse E. A., Kim J. H. Antigenic modulation. Loss of TL antigen from cells exposed to TL antibody. Study of the phenomenon in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):523–539. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Ting C. C., Herberman R. B. Modulation of fetal antigen(s) in mouse leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1974 Jun;34(6):1366–1371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porath J., Axen R., Ernback S. Chemical coupling of proteins to agarose. Nature. 1967 Sep 30;215(5109):1491–1492. doi: 10.1038/2151491a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G. F., Unanue E. R. Membrane and cytoplasmic changes in B lymphocytes induced by ligand-surface immunoglobulin interaction. Adv Immunol. 1976;24:37–165. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. D., Kask A. M., Paul W. E., Shevach E. M. Structural characteristics of the alloantigens determined by the major histocompatibility complex of the guinea pig. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):541–558. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackpole C. W., Jacobson J. B., Lardis M. P. Antigenic modulation in vitro. I. Fate of thymus-leukemia (TL) antigen-antibody complexes following modulation of TL antigenicity from the surfaces of mouse leukemia cells and thymocytes. J Exp Med. 1974 Oct 1;140(4):939–953. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.4.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackpole C. W., Jocobson J. B., Galuska S. Antigenic modulation in vitro. II. Modulation of thymus-leukemia (TL) antigenicity requires complement component C3. J Immunol. 1978 Jan;120(1):188–197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stackpole C. W. Serum requirements for in vivo modulation of thymus-leukemia antigens on mouse leukemia cells and thymocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1979 Jun;62(6):1529–1536. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson F. K., Mole L. E., Raymont C. M., Stevenson G. T. A gamma Bence-Jones protein in guinea pigs. Biochem J. 1975 Dec;151(3):751–753. doi: 10.1042/bj1510751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Eady R. P., Hough D. W., Jurd R. D., Stevenson F. K. Surface immunoglobulin of guinea-pig leukaemic lymphocytes. Immunology. 1975 May;28(5):807–820. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson G. T., Elliott E. V., Stevenson F. K. Idiotypic determinants on the surface immunoglobulin of neoplastic lymphocytes: a therapeutic target. Fed Proc. 1977 Aug;36(9):2268–2271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


