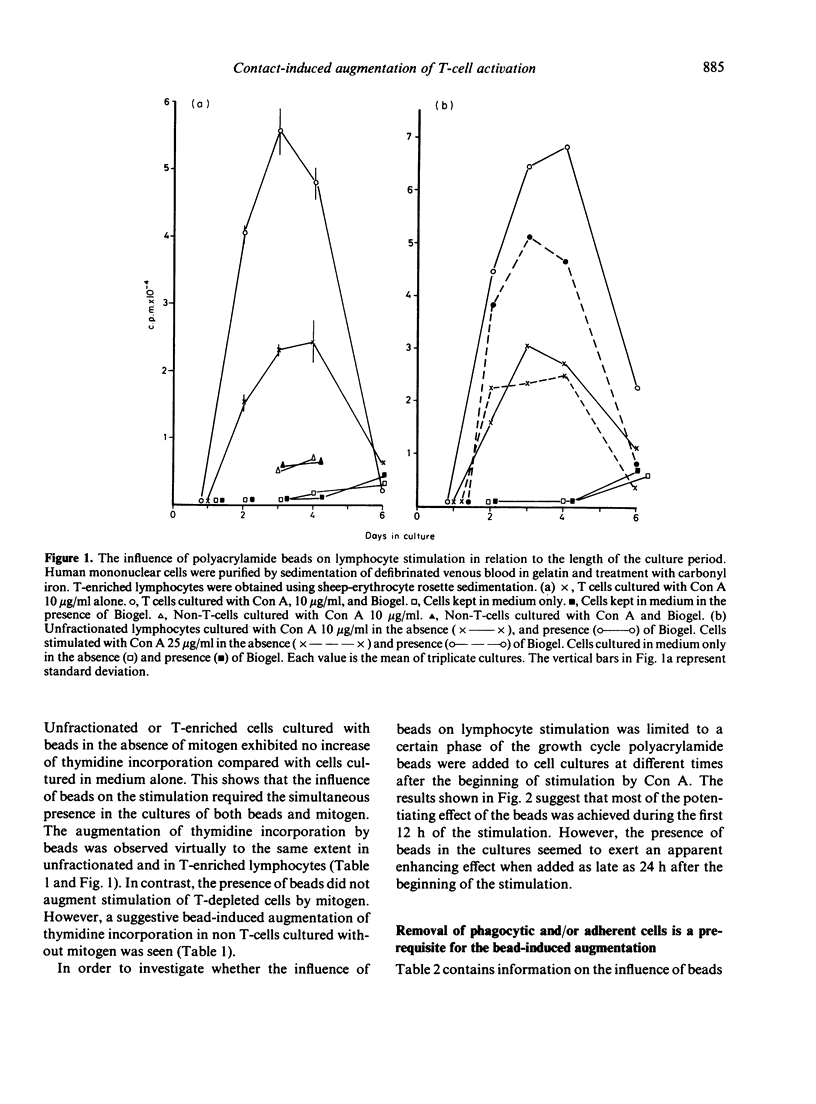
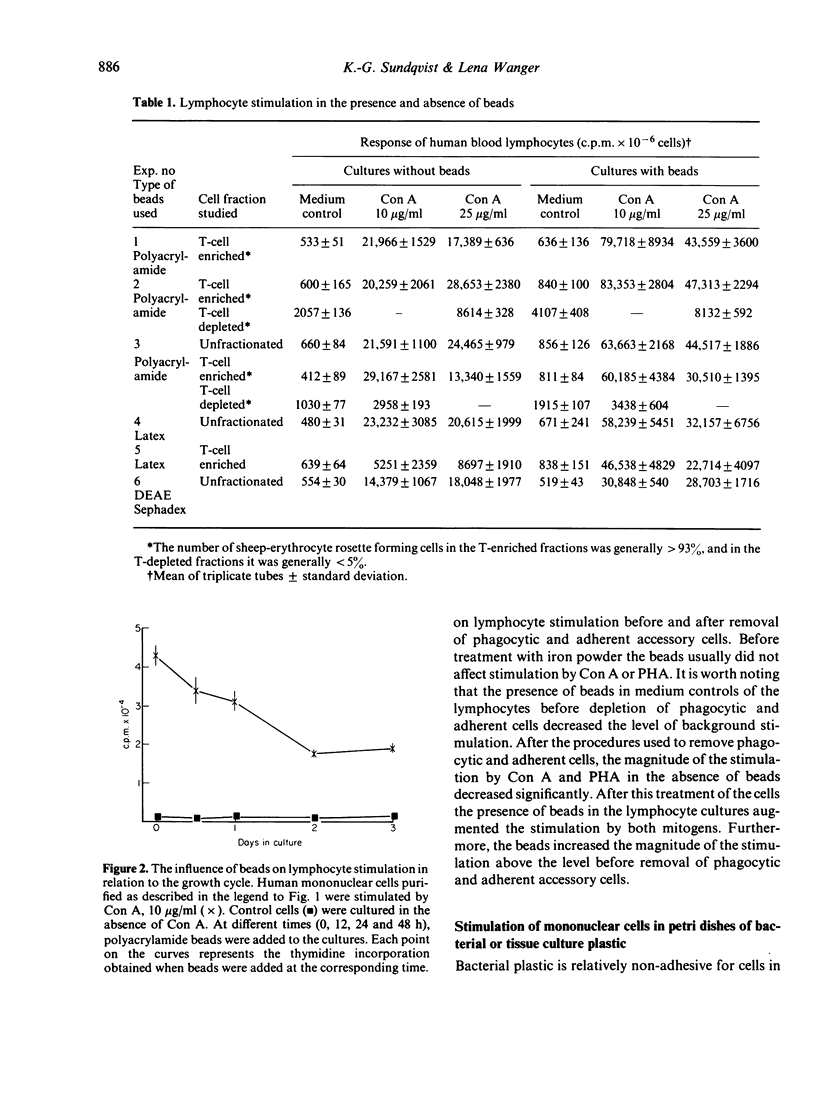
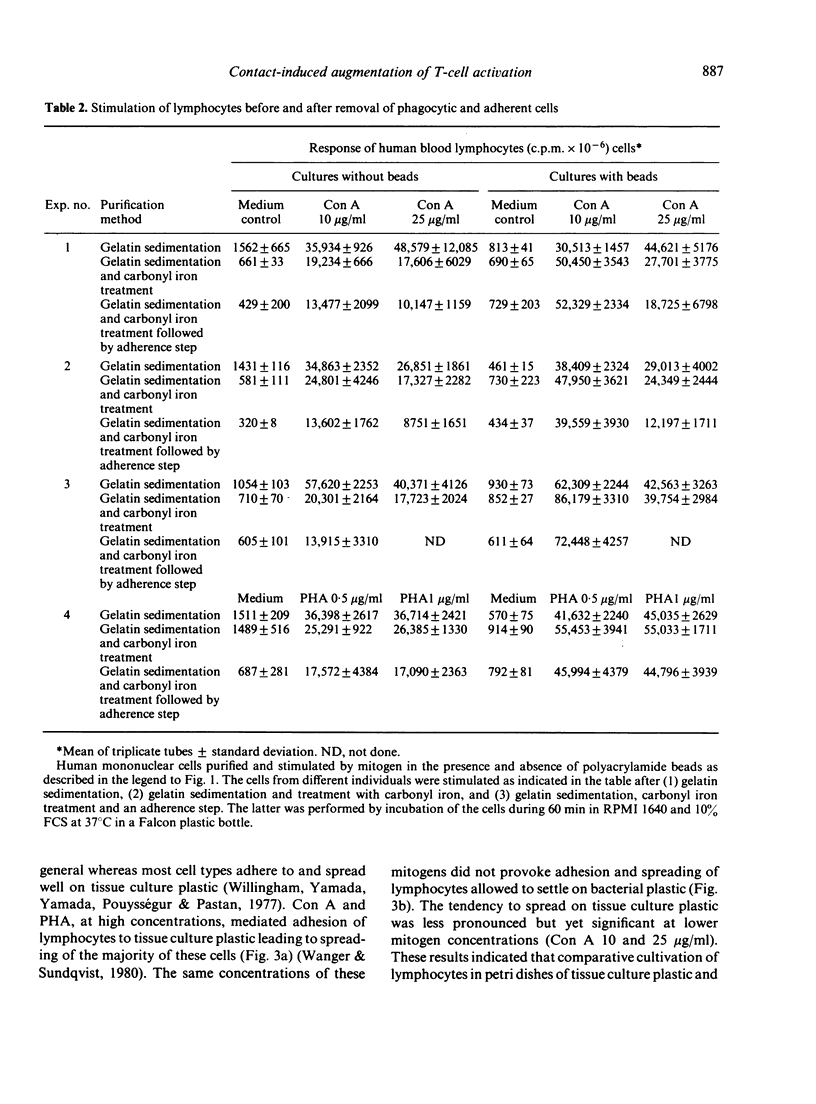
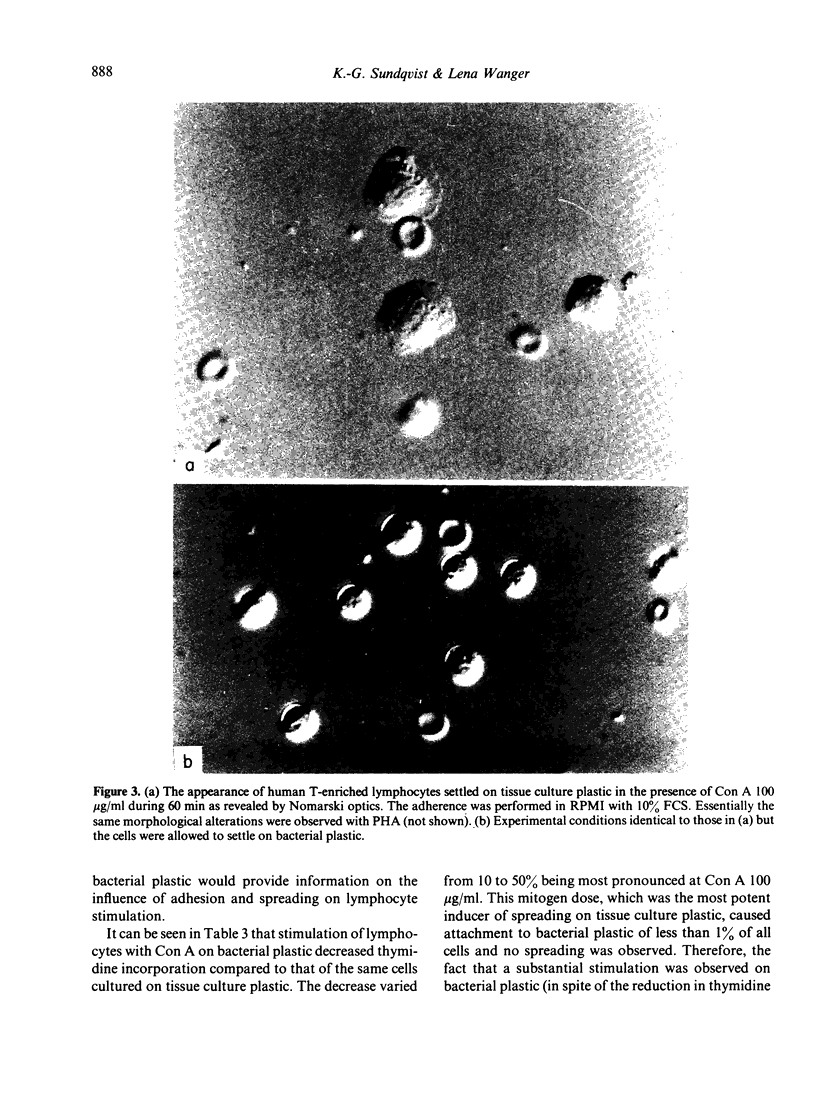
Abstract
Beads of polyacrylamide, latex or DEAE-Sephadex markedly augmented the stimulation of unfractionated or T-enriched lymphocytes by concanavalin A (Con A) or phytohaemagglutinin (PHA). The beads were not mitogenic in the absence of Con A or PHA. A prerequisite for the bead-induced augmentation was that the stimulated lymphocytes had been depleted of phagocytic and/or adherent accessory cells. The enhancing effect of beads was most pronounced during the initial 12 h after the beginning of lymphocyte stimulation, but not limited to this early phase of the growth period. The stimulation of lymphocytes in petri dishes of adhesive tissue culture plastic and non-adhesive bacterial plastic were compared. The magnitude of the stimulation on the non-adhesive surface was 10--50% lower than on the adhesive one, this difference being most pronounced at hyperoptimal mitogen concentrations. These results indicate that contact between some cell type and a solid surface can improve lymphocyte stimulation under experimental conditions when the number of phagocytic and adherent accessory cells is a limiting factor. The fact that cultivation on bacterial plastic, where adhesion and spreading were abolished, produced substantial stimulation (albeit reduced) demonstrates that substrate contact may be important, but is not a prerequisite, for lymphocyte activation.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Folkman J., Moscona A. Role of cell shape in growth control. Nature. 1978 Jun 1;273(5661):345–349. doi: 10.1038/273345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Habu S., Raff M. C. Accessory cell dependence of lectin-induced proliferation of mouse T lymphocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Jul;7(7):451–457. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsson E. L., Coutinho A. The role of mitogenic lectins in T-cell triggering. Nature. 1979 Jul 19;280(5719):239–241. doi: 10.1038/280239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levis W. R., Robbins J. H. Effect of glass-adherent cells on the blastogenic response of 'purified' lymphocytes to phytohemagglutinin. Exp Cell Res. 1970 Jul;61(1):153–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(70)90269-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H. Contact cooperation in stimulated lymphocytes. I. Influence of cell contact on unspecifically stimulated lymphocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1972 Sep;74(1):179–186. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(72)90495-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Hatfield S. Activation of purified human thymus-derived (T) cells by mitogens. II. Monocyte- macrophage potentiation of mitogen-induced DNA synthesis. J Immunol. 1976 Feb;116(2):357–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanger L., Sundqvist K. G. Contact-induced modification of lymphocyte morphology. Biochem Soc Symp. 1980;45:65–73. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
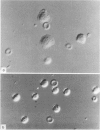
- Willingham M. C., Yamada K. M., Yamada S. S., Pouysségur J., Pastan I. Microfilament bundles and cell shape are related to adhesiveness to substratum and are dissociable from growth control in cultured fibroblasts. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):375–380. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wing E. J., Remington J. S. Studies on the regulation of lymphocyte reactivity by normal and activated macrophages. Cell Immunol. 1977 Apr;30(1):108–121. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(77)90052-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]