Abstract
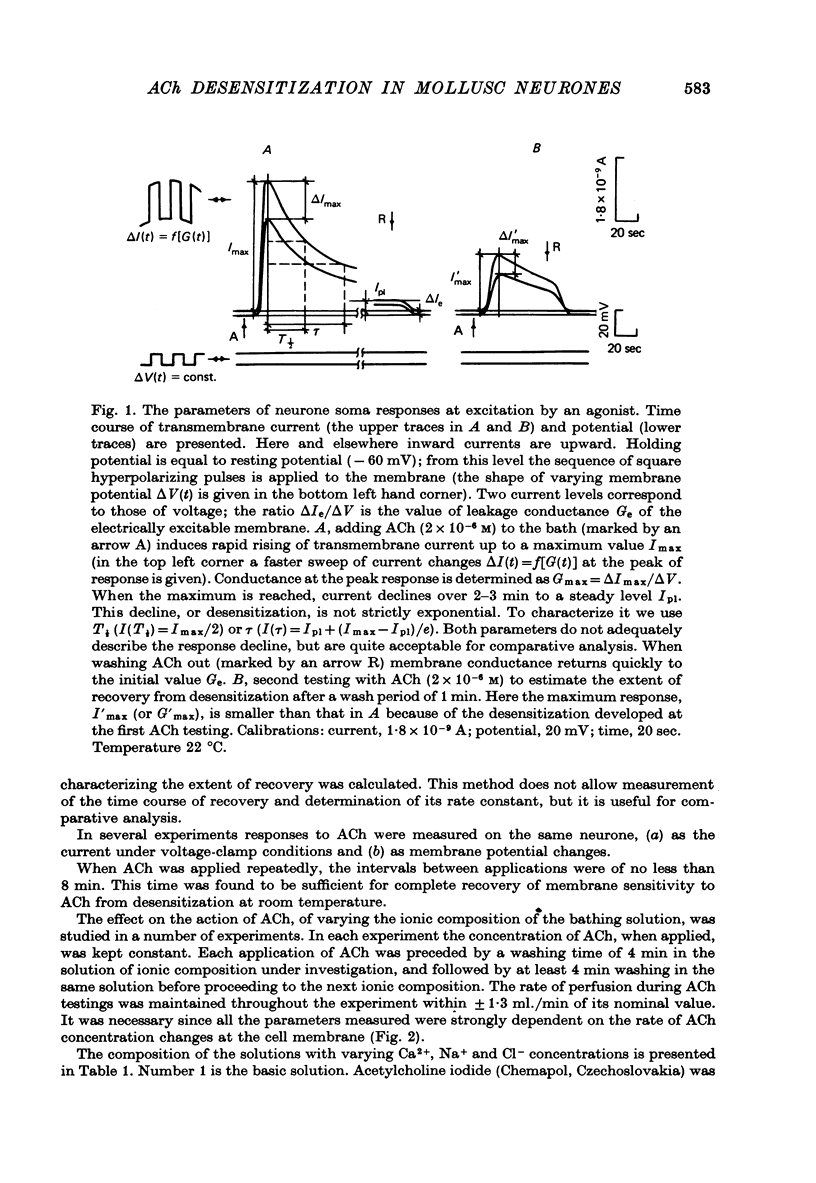
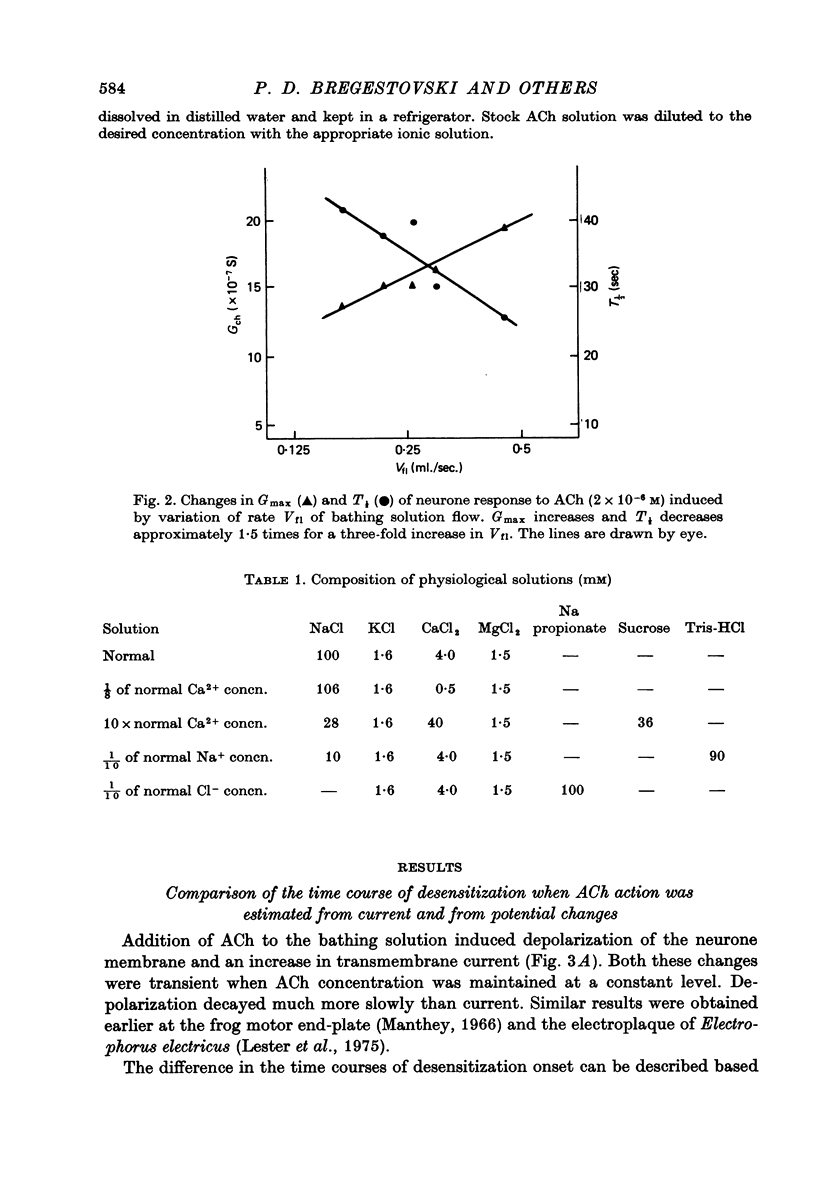
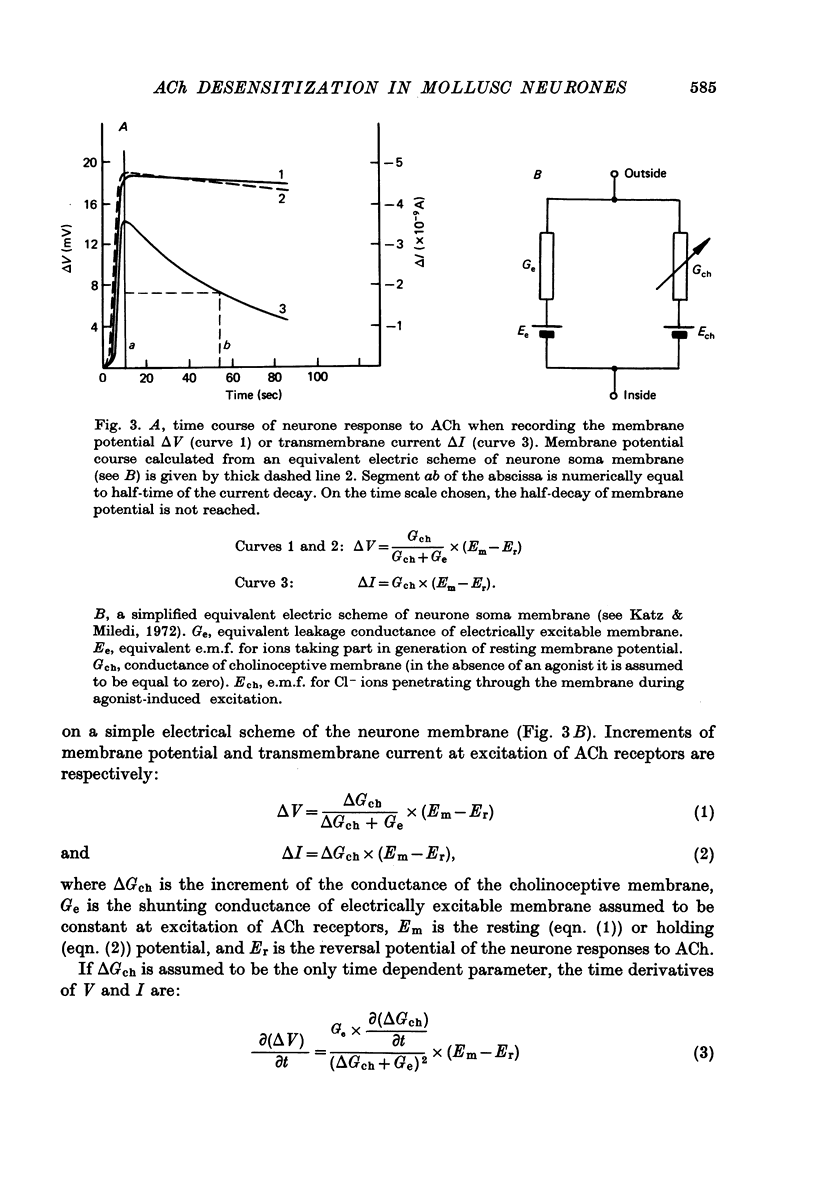
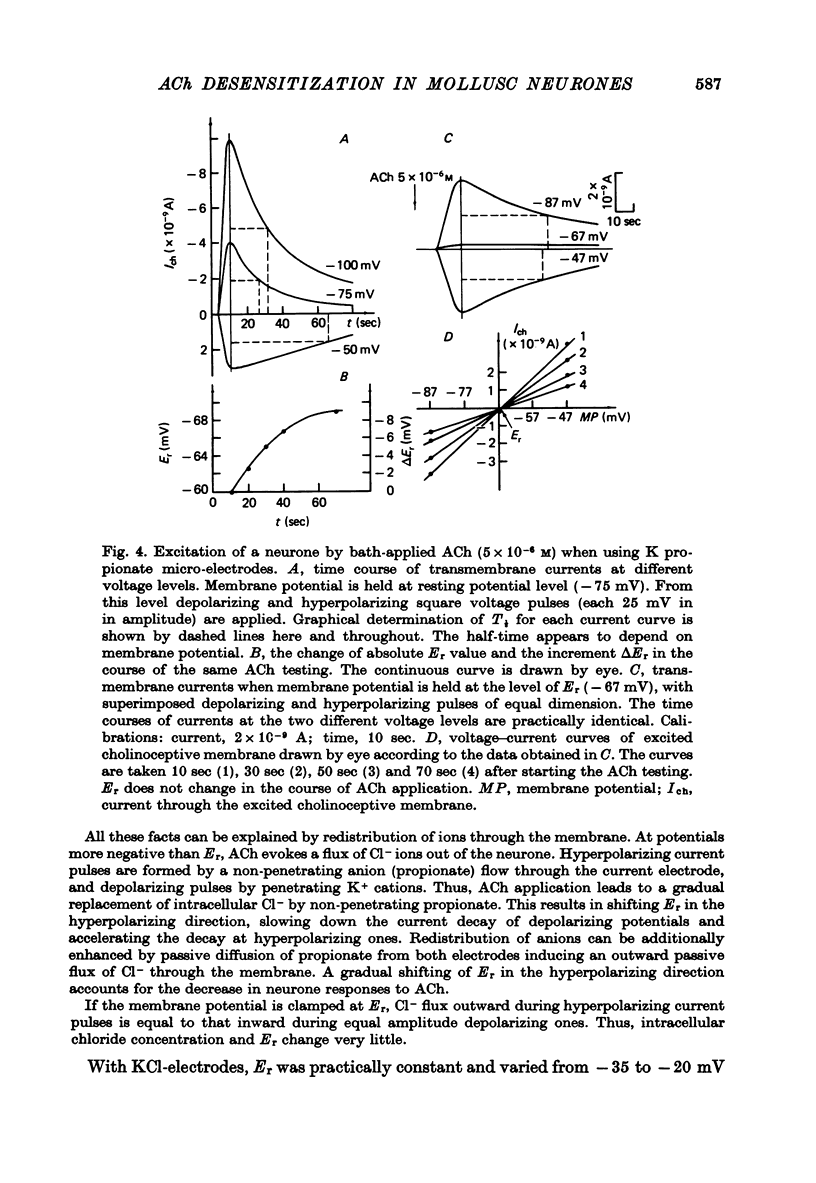
1. Desensitization produced by acetylcholine (ACh) in completely isolated Limnaea stagnalis neurones with chloride-selective membrane channels was studied using a voltage-clamp technique. 2. A difference in the time course of the neurone responses to ACh, depending on whether the measured parameter was voltage or current, was observed and explained on the basis of an equivalent electric scheme of the neurone soma membrane. 3. Desensitization onset was shown not to depend on membrane potential in the range of -30 to -120 mV. 4. Variation of external Ca2+, Na+ and Cl- concentrations over a wide range had little influence on the onset of desensitization and recovery from it. 5. An obvious difference is shown to exist between features of desensitization in mollusc neurone and frog muscle end-plate ACh receptors.
Full text
PDF









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AXELSSON J., THESLEFF S. The desensitizing effect of acetylcholine on the mammalian motor end-plate. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Jul 17;43(1):15–26. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01574.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams P. R. A study of desensitization using voltage clamp. Pflugers Arch. 1975 Oct 28;360(2):135–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00580536. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner R., Barrantes F. J., Jovin T. M. Kinetics of agonist-induced intrinsic fluorescence changes in membrane-bound acetylcholine receptor. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):429–431. doi: 10.1038/263429a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Range H. P. Effects of inhibitors of the binding of iodinated alpha-bungarotoxin to acetylcholine receptors in rat muscle. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):519–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünhagen H. H., Changeux J. P. Studies on the electrogenic action of acetylcholine with Torpedo marmorata electric organ. V. Qualitative correlation between pharmacological effects and equilibration processes of the cholinergic receptor protein as revealed by the structural probe quinacrine. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):517–535. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90250-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iljin V. I., Bregestovski P. D. Chemical nature of functional cholinoreceptor groups of Lymnaea stagnalis neurons. Acta Physiol Acad Sci Hung. 1977;49(3-4):221–230. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurchenko O. P., Vulfius C. A., Zeimal E. V. Cholinesterase activity in ganglia of gastropoda, Lymnaea stagnalis and planorbarius corneus. I. Effect of anticholinesterase agents on giant neurone depolarization by acetylcholine and its analogues. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1973 May 1;45(1):45–60. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(73)90007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B., THESLEFF S. A study of the desensitization produced by acetylcholine at the motor end-plate. J Physiol. 1957 Aug 29;138(1):63–80. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The reversal potential at the desensitized endplate. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1977 Nov 14;199(1135):329–334. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1977.0144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The statistical nature of the acetycholine potential and its molecular components. J Physiol. 1972 Aug;224(3):665–699. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostenko M. A., Geletyuk V. I., Veprintsev B. N. Completely isolated neurons in the mollusc, Lymnaea stagnalis. A new objective for nerve cell biology investigation. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol. 1974 Sep 1;49(1A):89–100. doi: 10.1016/0300-9629(74)90544-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert D. H., Spannbauer P. M., Parsons R. L. Desensitisation does not selectively alter sodium channels. Nature. 1977 Aug 11;268(5620):553–555. doi: 10.1038/268553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A., Changeux J. P., Sheridan R. E. Conductance increases produced by bath application of cholinergic agonists to Electrophorus electroplaques. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Jun;65(6):797–816. doi: 10.1085/jgp.65.6.797. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lester H. A. Vulnerability of desensitized or curare-treated acetylcholine receptors to irreversible blockade by cobra toxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1972 Nov;8(6):632–644. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G. O mekhanizme desensitizatsii postsinapticheskoi membrany myshechnogo volokna. Biofizika. 1968 Jan-Feb;13(1):199–203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocil F. Dependence of acetylcholine desensitization on the membrane potential of frog muscle fibre and on the ionic changes in the medium. J Physiol. 1970 Oct;210(3):507–518. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1970.sp009223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magazanik L. G., Vyskocit F. The effect of temperature on desensitization kinetics at the post-synaptic membrane of the frog muscle fibre. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):285–300. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. Further studies of the effect of calcium on the time course of action of carbamylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Sep;56(3):407–419. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.3.407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. The antagonistic effects of calcium and potassium on the time course of action of carbamylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. J Membr Biol. 1972;9(4):319–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manthey A. A. The effect of calcium on the desensitization of membrane receptors at the neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1966 May;49(5):963–976. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.5.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nastuk W. L., Parsons R. L. Factors in the inactivation of postjunctional membrane receptors of frog skeletal muscle. J Gen Physiol. 1970 Aug;56(2):218–249. doi: 10.1085/jgp.56.2.218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumcke B. Diffusion polarization at lipid bilayer membranes. Biophysik. 1971;7(2):95–105. doi: 10.1007/BF01190141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. A new kind of drug antagonism: evidence that agonists cause a molecular change in acetylcholine receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Jul;5(4):394–411. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. On the mechanism of desensitization at cholinergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):357–382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rang H. P., Ritter J. M. The relationship between desensitization and the metaphilic effect at cholinergic receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Jul;6(4):383–390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scubon-Mulieri B., Parsons R. L. Desensitization and recovery at the frog neuromuscular junction. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Apr;69(4):431–447. doi: 10.1085/jgp.69.4.431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scubon-Mulieri B., Parsons R. L. Desensitization onset and recovery at the potassium-depolarized frog neuromuscular junction are voltage sensitive. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Mar;71(3):285–299. doi: 10.1085/jgp.71.3.285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suarez-Isla B. A., Hucho F. Acetylcholine receptor: SH group reactivity as indicator of conformational changes and functional states. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 15;75(1):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80054-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAUC L., BRUNER J. "Desensitization" of cholinergic receptors by acetylcholine in molluscan central neurones. Nature. 1963 Apr 6;198:33–34. doi: 10.1038/198033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THESLEFT S. The mode of neuromuscular block caused by acetylcholine, nicotine, decamethonium and succinylcholine. Acta Physiol Scand. 1955 Oct 27;34(2-3):218–231. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1955.tb01242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., David-Pfeuty T., Changeux J. P. Regulation of binding properties of the nicotinic receptor protein by cholinergic ligands in membrane fragments from Torpedo marmorata. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziskind L., Werman R. Sodium ions are necessary for cholinergic desensitization in molluscan neurons. Brain Res. 1975 Apr 25;88(1):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90968-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


