Abstract
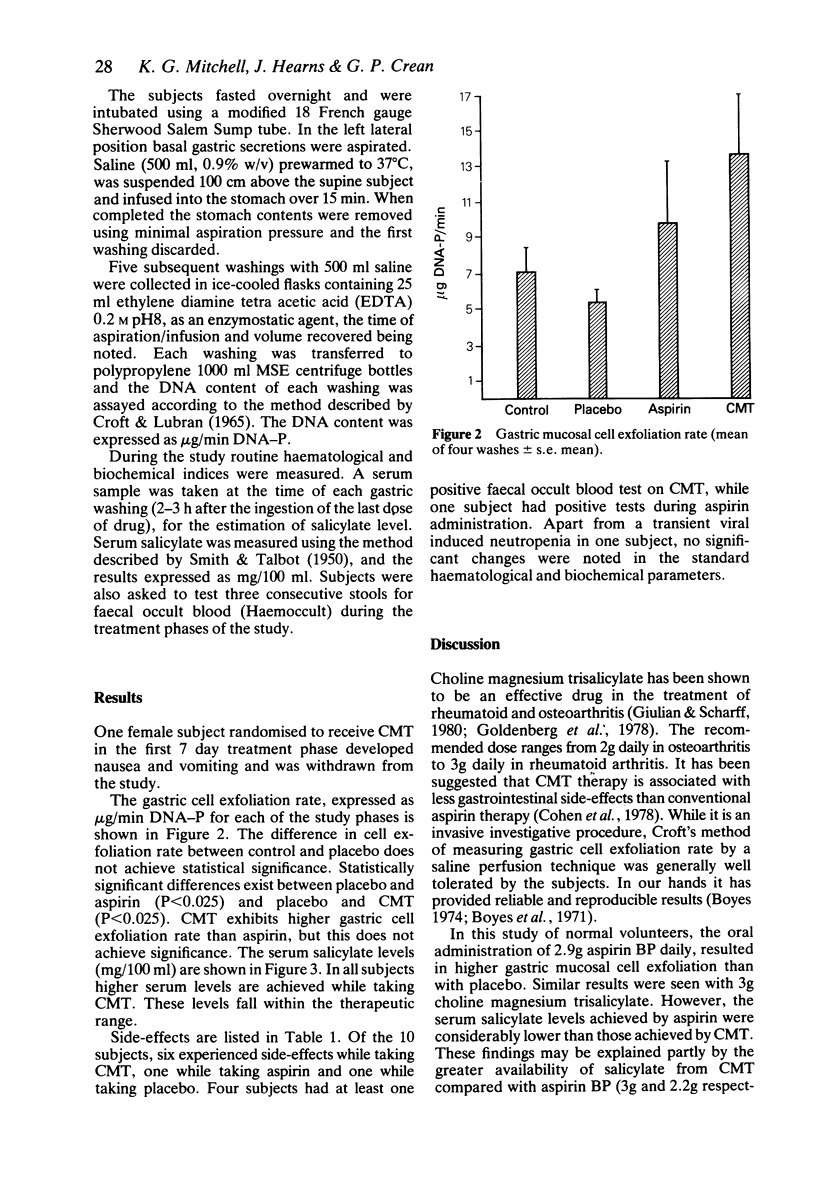
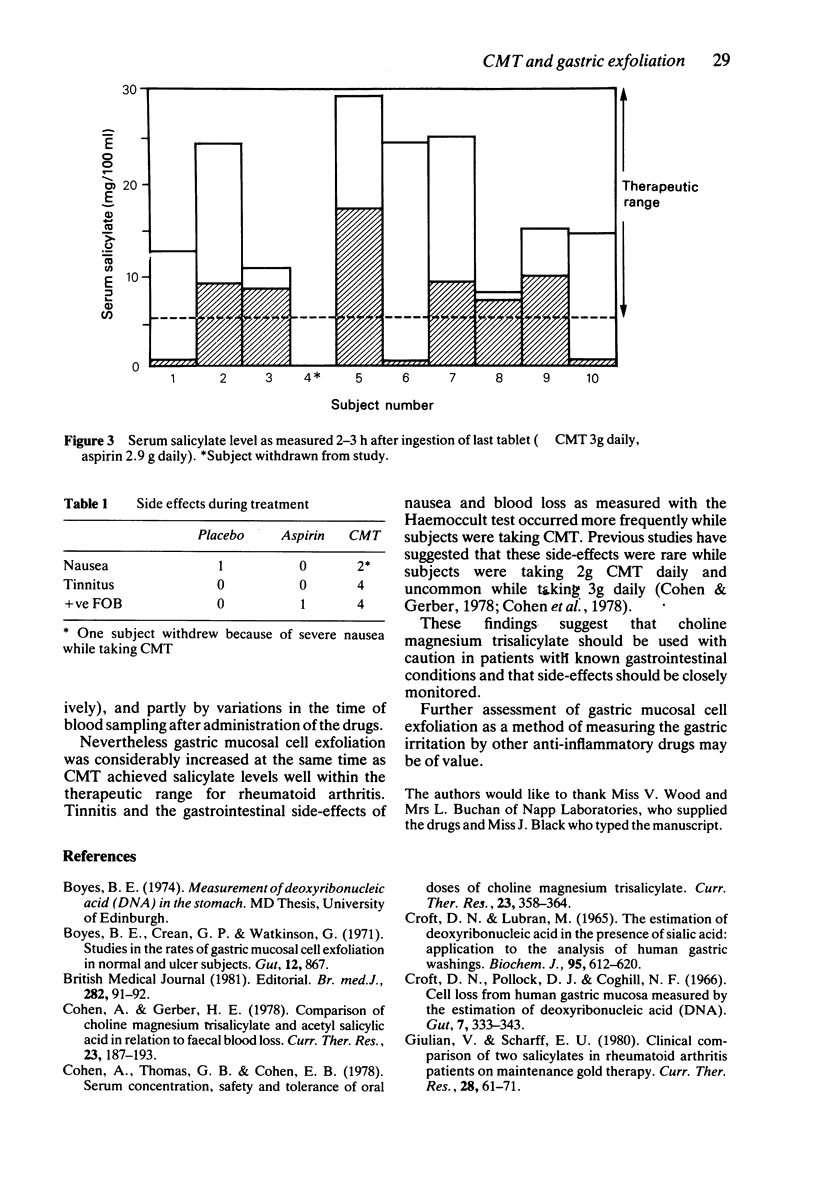
Gastric mucosal cell exfoliation was measured in 10 normal subjects taking choline magnesium trisalicylate (CMT), aspirin and placebo. Both drugs resulted in significantly elevated rates of exfoliation although the serum salicylate levels achieved with aspirin were lower than those achieved by CMT. Side-effects of tinnitus, nausea and increased faecal blood loss were more common while subjects were taking CMT.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyes B. E., Crean G. P., Watkinson G. Studies in the rates of epithelial cell exfoliation from the gastric mucosa in normal and in ulcer subjects. Gut. 1971 Oct;12(10):867–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFT D. N., LUBRAN M. THE ESTIMATION OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID IN THE PRESENCE OF SIALIC ACID: APPLICATION TO ANALYSIS OF HUMAN GASTRIC WASHINGS. Biochem J. 1965 Jun;95:612–620. doi: 10.1042/bj0950612. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft D. N., Pollock D. J., Coghill N. F. Cell loss from human gastric mucosa measured by the estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) in gastric washings. Gut. 1966 Aug;7(4):333–343. doi: 10.1136/gut.7.4.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


