Abstract
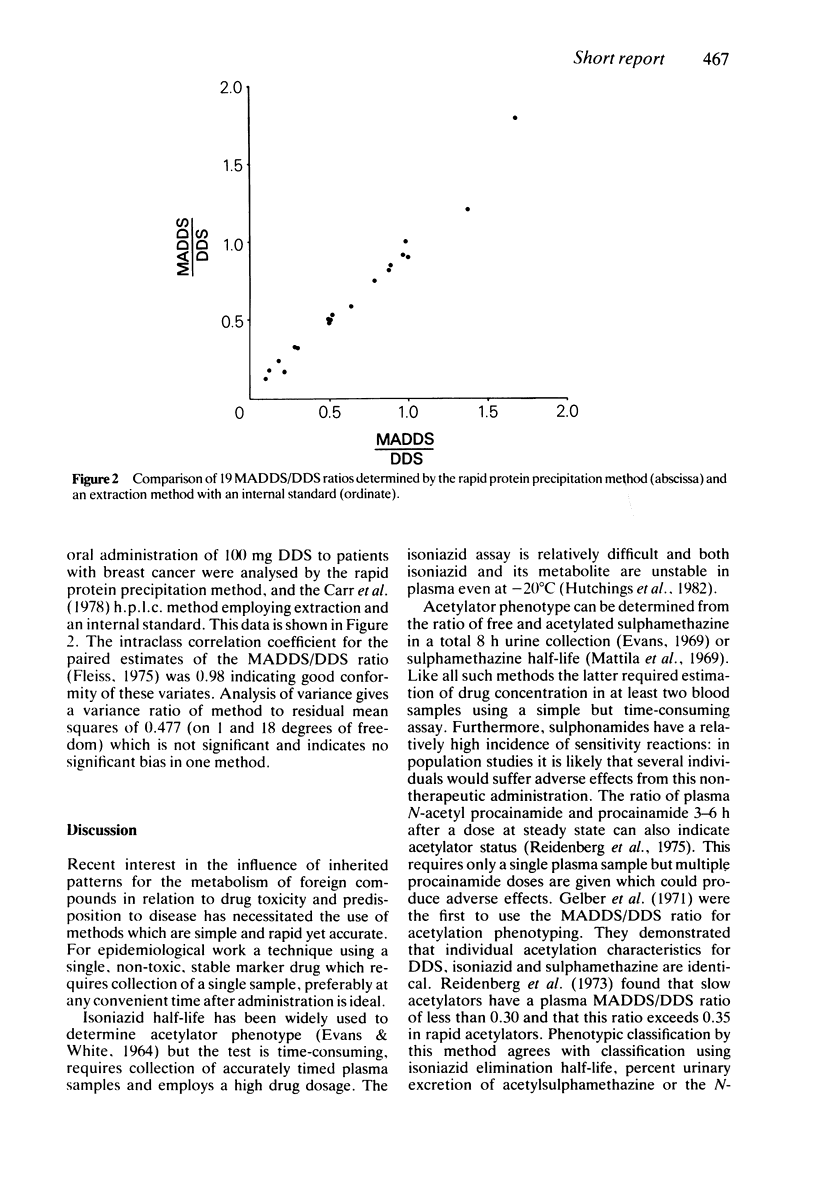
A rapid, simple one-stage protein precipitation method for the estimation of plasma dapsone (DDS) and monoacetyldapsone (MADDS) concentration by high-pressure liquid chromatography (h.p.l.c.) is described. Its performance in the assignment of acetylator phenotype was compared with a reference h.p.l.c. method utilising an extraction procedure and internal standard. The rapid h.p.l.c. technique combined with measurement of the plasma MADDS/DDS ratio is, in our opinion, the method of choice for the determination of the acetylator phenotype in population studies.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmad R. A., Rogers H. J. Plasma and salivary pharmacokinetics of dapsone estimated by a thin layer chromatographic method. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Feb;17(2):129–133. doi: 10.1007/BF00562621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr K., Oates J. A., Nies A. S., Woosley R. L. Simultaneous analysis of dapsone and monoacetyldapsone employing high performance liquid chromatography: a rapid method for determination of acetylator phenotype. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 Nov;6(5):421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1978.tb04606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright R. A., Glashan R. W., Rogers H. J., Ahmad R. A., Barham-Hall D., Higgins E., Kahn M. A. Role of N-acetyltransferase phenotypes in bladder carcinogenesis: a pharmacogenetic epidemiological approach to bladder cancer. Lancet. 1982 Oct 16;2(8303):842–845. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90810-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drayer D. E., Reidenberg M. M. Clinical consequences of polymorphic acetylation of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1977 Sep;22(3):251–258. doi: 10.1002/cpt1977223251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EVANS D. A., WHITE T. A. HUMAN ACETYLATION POLYMORPHISM. J Lab Clin Med. 1964 Mar;63:394–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellard G. A. Absorption, metabolism and excretion of di(rho-aminophenyl) sulphone (dapsone) and di(rho-aminophenyl) sulphoxide in man. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1966 Jan;26(1):212–217. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1966.tb01823.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. A. An improved and simplified method of detecting the acetylator phenotype. J Med Genet. 1969 Dec;6(4):405–407. doi: 10.1136/jmg.6.4.405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleiss J. L. Measuring agreement between two judges on the presence or absence of a trait. Biometrics. 1975 Sep;31(3):651–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelber R., Peters J. H., Gordon G. R., Glazko A. J., Levy L. The polymorphic acetylation of dapsone in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1971 Mar-Apr;12(2):225–238. doi: 10.1002/cpt1971122part1225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glazko A. J., Dill W. A., Montalbo R. G., Holmes E. L. A new analytical procedure for dapsone. Application to blood-level and urinary-excretion studies in normal men. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1968 May;17(3):465–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanson A., Melander A., Wåhlin-Boll E. Acetylator phenotyping: a comparison of the isoniazid and dapsone tests. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;20(3):233–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00544604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lunde P. K., Frislid K., Hansteen V. Disease and acetylation polymorphism. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1977 May-Jun;2(3):182–197. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197702030-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattila M. J., Tiitinen H., Alhava E. Acetylation pattern of different sulphonamides in rapid and slow isoniazid inactivators. Ann Med Exp Biol Fenn. 1969;47(4):308–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. F., Jr, Gordon G. R., Peters J. H. A chromatographic-fluorometric procedure for the determination of nanogram quantities of antileprotic sulfones. J Lab Clin Med. 1971 Sep;78(3):464–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters J. H., Gordon G. R., Colwell W. T., Jr The fluorometric measurement of 4,4'-diaminodiphenyl sulfone and its acetylated derivatives in plasma and urine. J Lab Clin Med. 1970 Aug;76(2):338–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reidenberg M. M., Drayer D. E., Levy M., Warner H. Polymorphic acetylation procainamide in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1975 Jun;17(6):722–730. doi: 10.1002/cpt1975176722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumble R. H., Roberts M. S., Wanwimolruk S. Determination of aspirin and its major metabolites in plasma by high-performance liquid chromatography without solvent extraction. J Chromatogr. 1981 Sep 11;225(1):252–260. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)80270-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuidema J., Modderman E. S., Hilbers H. W., Merkus F. W., Huikeshoven H. Rapid high-performance liquid chromatographic method for the determination of dapsone and monoacetyldapsone in biological fluids. J Chromatogr. 1980 Apr 11;182(1):130–135. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)81662-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


