Abstract
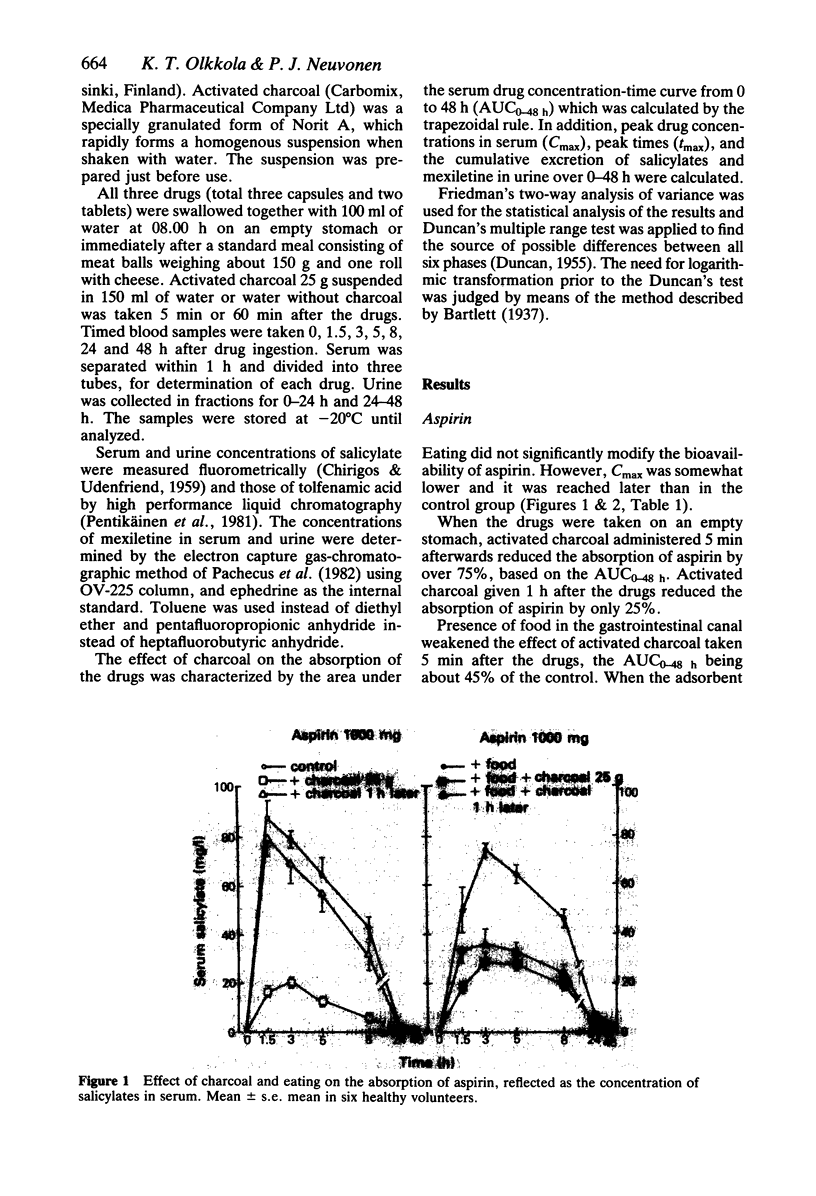
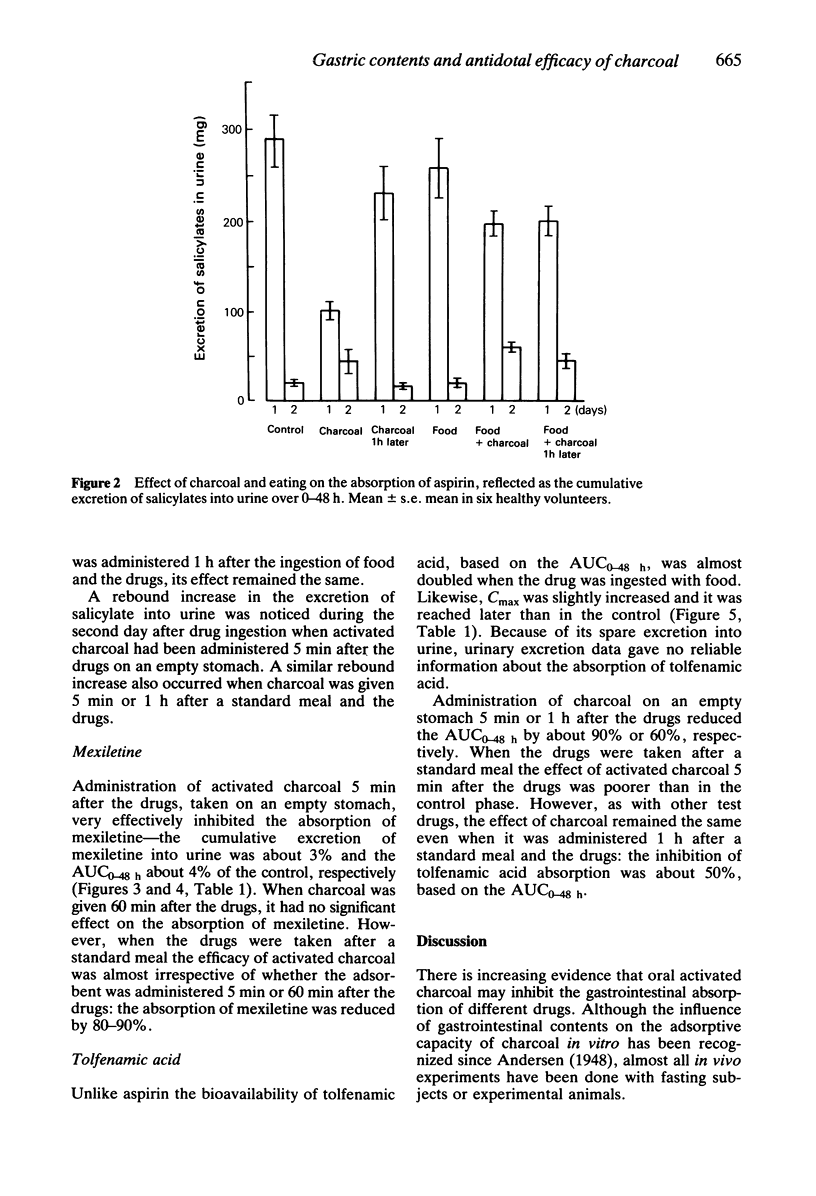
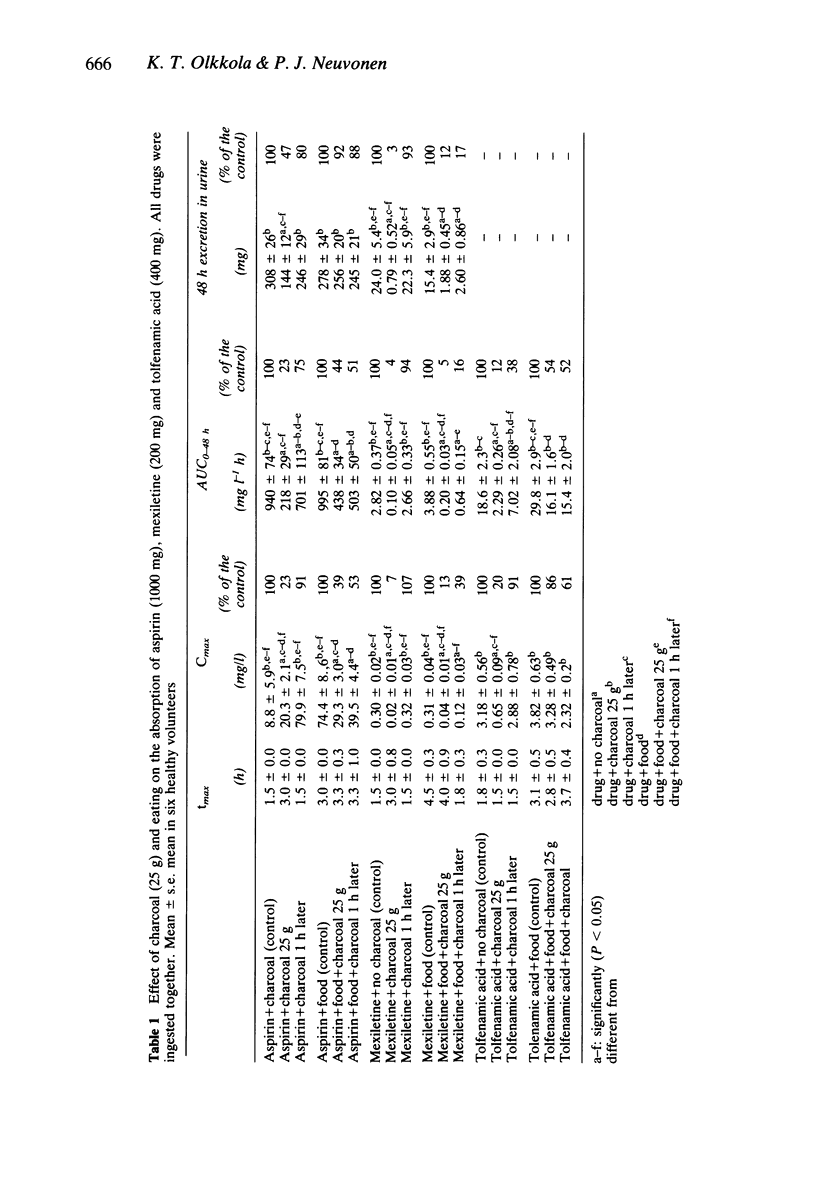
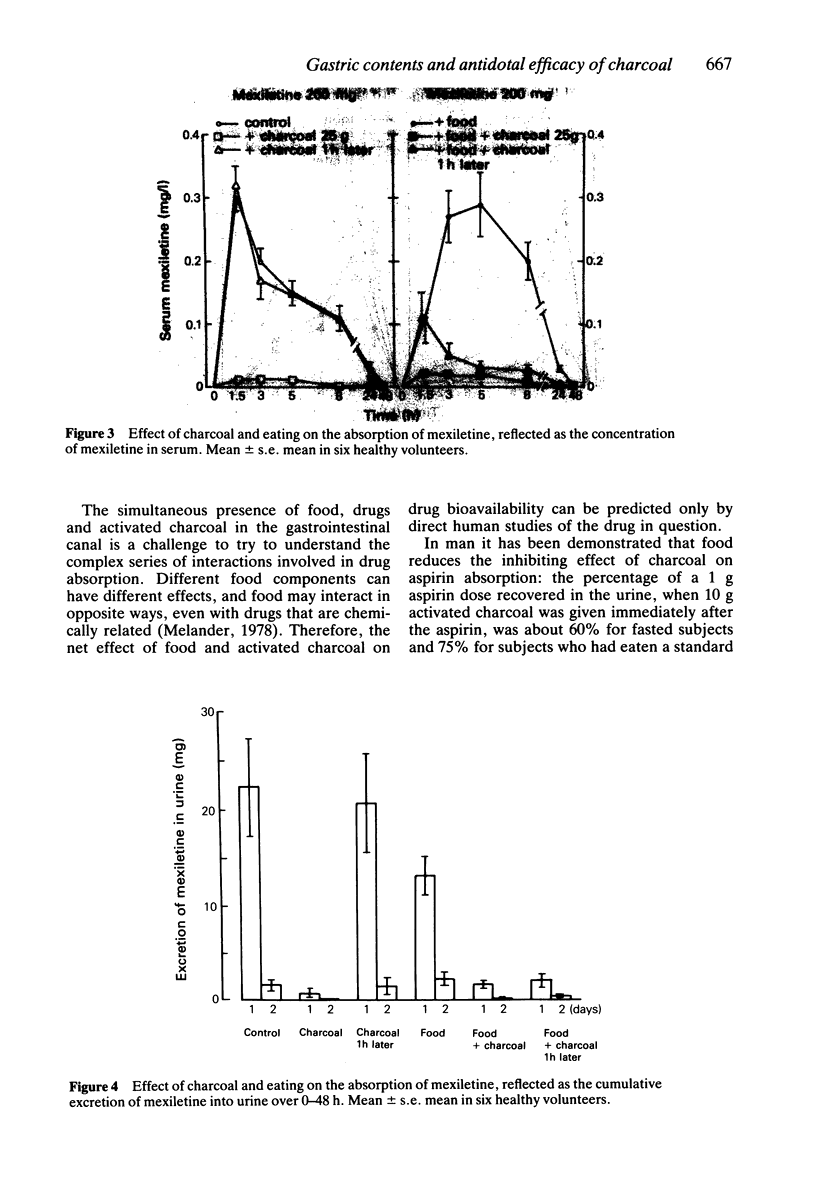
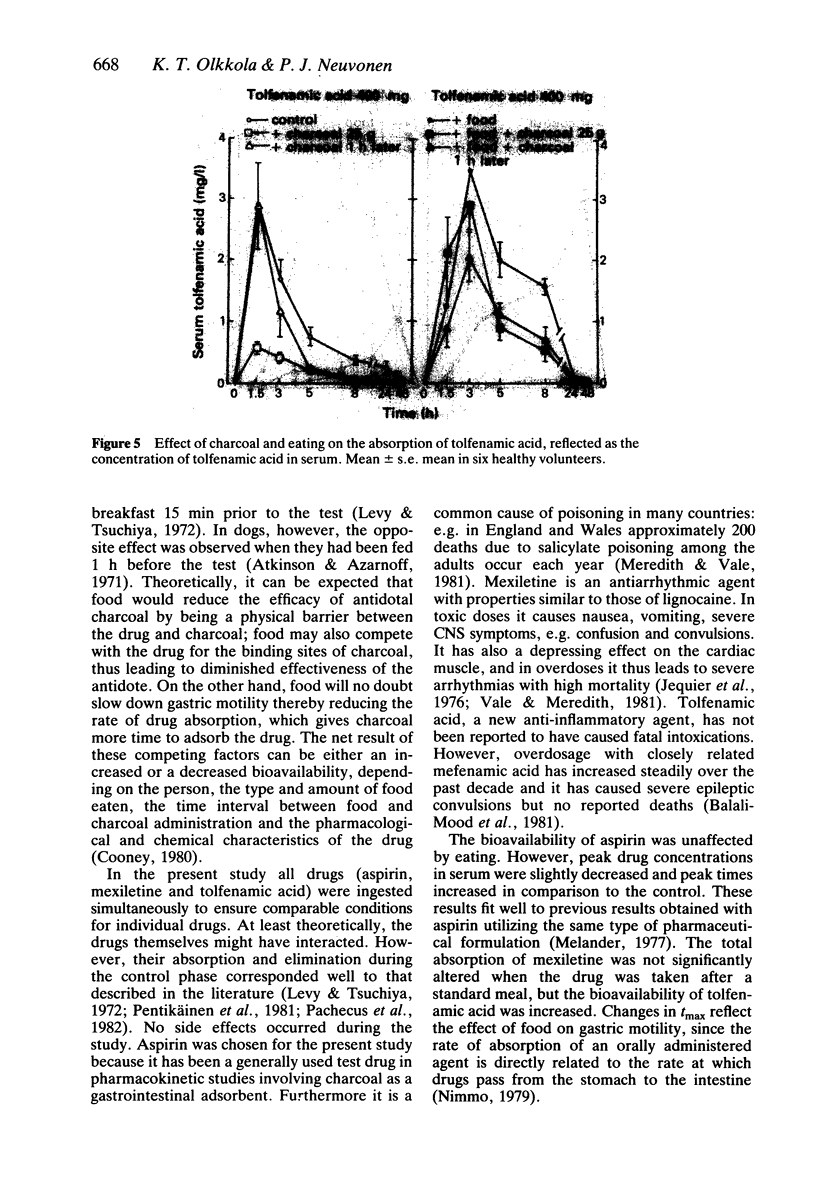
The effect of food on the antidotal efficacy of activated charcoal was studied in six healthy volunteers, who ingested aspirin 1000 mg, mexiletine 200 mg and tolfenamic acid 400 mg in a randomized cross-over study. Activated charcoal 25 g, suspended in water, was administered 5 min or 60 min after the drugs were taken on an empty stomach or after a standard meal. The serum concentrations and the cumulative excretion into urine of the drugs were followed for 48 h. When the drugs were taken on an empty stomach, activated charcoal given 5 min or 60 min afterwards reduced the bioavailability of the drugs by 75-98% or 10-60%, respectively. Food moderately weakened the effect of activated charcoal administered 5 min after the drugs, but when the charcoal was given 1 h later the effect was still practically the same, the reduction of absorption varying in both cases in the range of 45-85%. Thus the efficacy of charcoal given 60 min after the drugs was better after a standard meal than on an empty stomach. Presence of food in the stomach of patients with drug overdosage modifies the efficacy of activated charcoal and gives it more time to adsorb drugs in the gastrointestinal canal, possibly by slowing gastric emptying rate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson J. P., Azarnoff D. L. Comparison of charcoal and attapulgite as gastrointestinal sequestrants in acute drug ingestions. Clin Toxicol. 1971 Mar;4(1):31–38. doi: 10.3109/15563657108990145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balali-Mood M., Critchley J. A., Proudfoot A. T., Prescott L. F. Mefenamic acid overdosage. Lancet. 1981 Jun 20;1(8234):1354–1356. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92528-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIRIGOS M. A., UDENFRIEND S. A simple fluorometric procedure for determining salicylic acid in biologic tissues. J Lab Clin Med. 1959 Nov;54:769–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayden J. W., Comstock E. G. Use of activated charcoal in acute poisoning. Clin Toxicol. 1975;8(5):515–533. doi: 10.3109/15563657508988096. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jequier P., Jones R., Mackintosh A. Letter: Fatal mexiletine overdose. Lancet. 1976 Feb 21;1(7956):429–429. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy G., Tsuchiya T. Effect of activated charcoal on aspirin absorption in man. Part I. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1972 May-Jun;13(3):317–322. doi: 10.1002/cpt1972133317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander A., Berlin-Wahlén A., Bodin N. O., Danielson K., Gustafsson B., Lindgren S., Westerlund D. Bioavailability of D-propoxyphene, acetyl salicylic acid, and phenazone in a combination tablet (Doleron): interindividual variation and influence of food intake. Acta Med Scand. 1977;202(1-2):119–124. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1977.tb16796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melander A. Influence of food on the bioavailability of drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1978 Sep-Oct;3(5):337–351. doi: 10.2165/00003088-197803050-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J. Clinical pharmacokinetics of oral activated charcoal in acute intoxications. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Nov-Dec;7(6):465–489. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207060-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Elfving S. M., Elonen E. Reduction of absorption of digoxin, phenytoin and aspirin by activated charcoal in man. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1978 May 31;13(3):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00609985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuvonen P. J., Vartiainen M., Tokola O. Comparison of activated charcoal and ipecac syrup in prevention of drug absorption. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1983;24(4):557–562. doi: 10.1007/BF00609903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pachecus A., Santoni Y., Fornaris M., Magnan S., Aubert C., Ragon A., Cano J. P. Simultaneous plasma levels determination of mexiletine and one of its metabolites by electron capture gas-liquid chromatography. Arzneimittelforschung. 1982;32(6):688–693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pentikäinen P. J., Neuvonen P. J., Backman C. Human pharmacokinetics of tolfenamic acid, a new anti-inflammatory agent. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1981;19(5):359–365. doi: 10.1007/BF00544587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


