Abstract
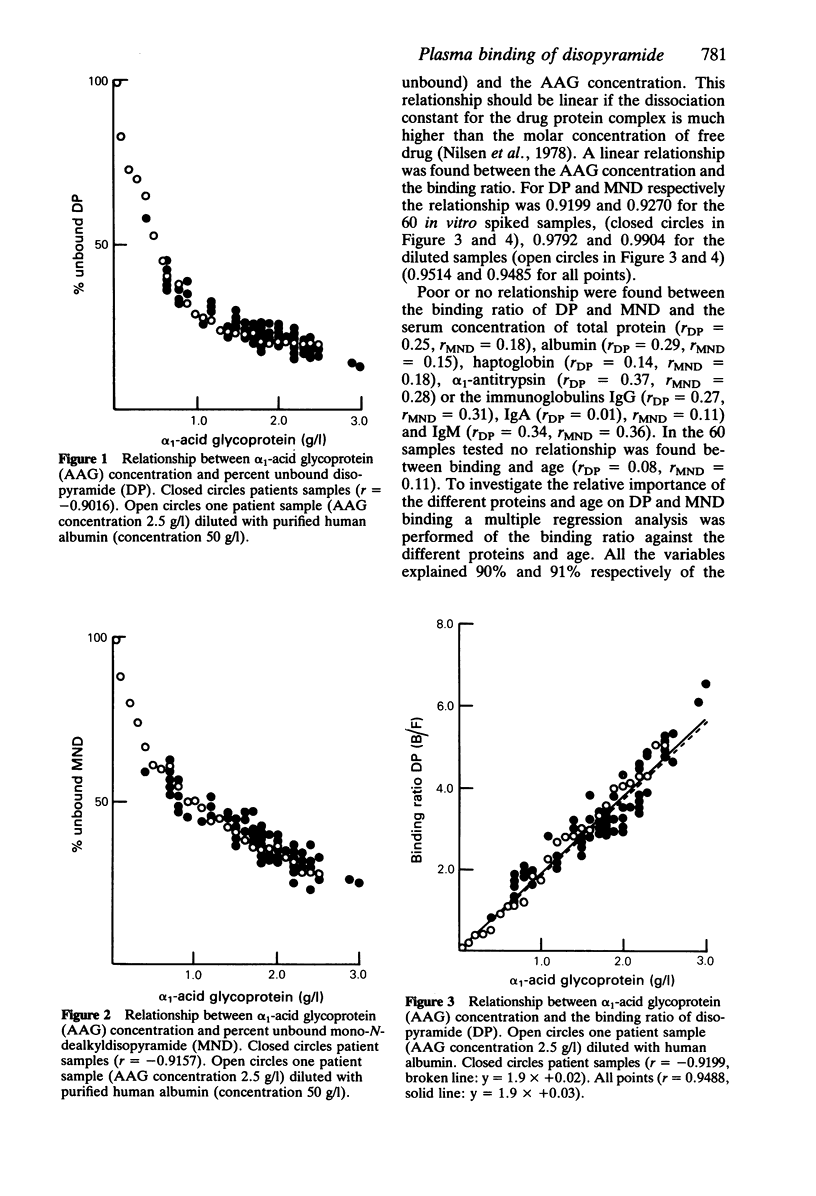
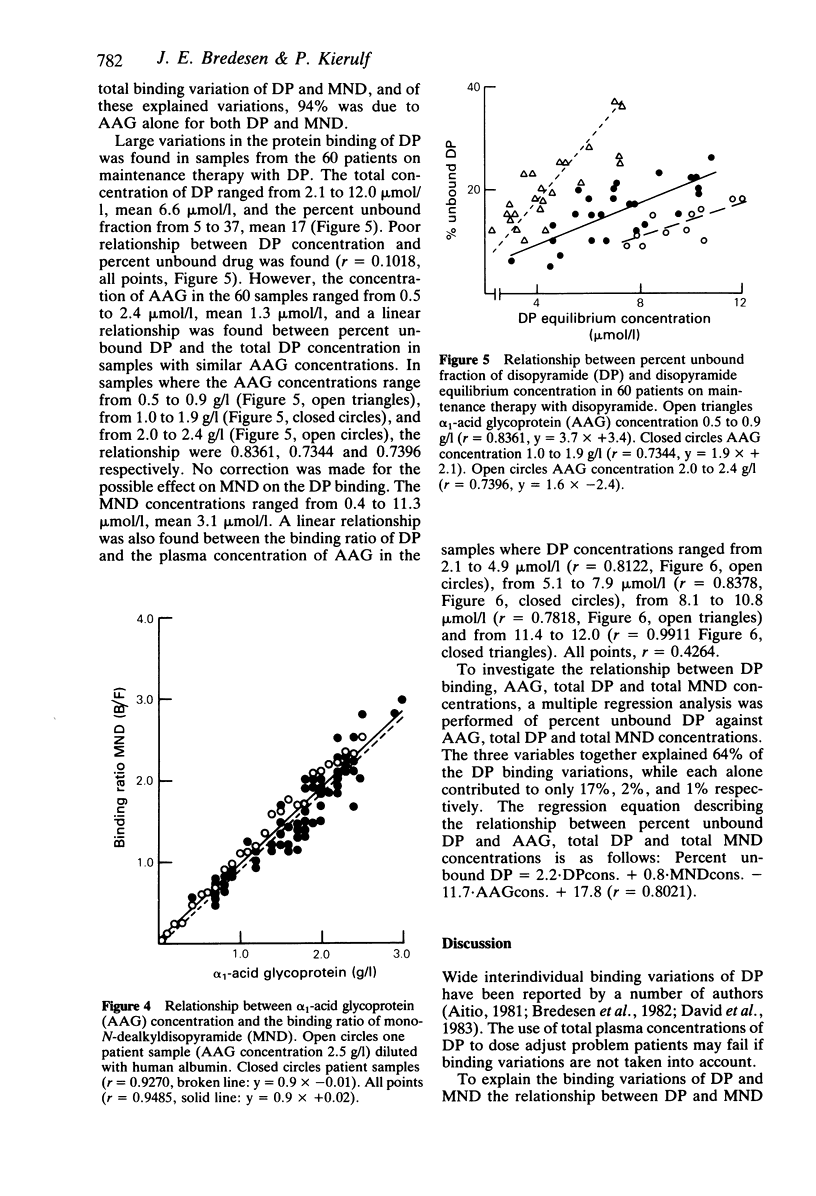
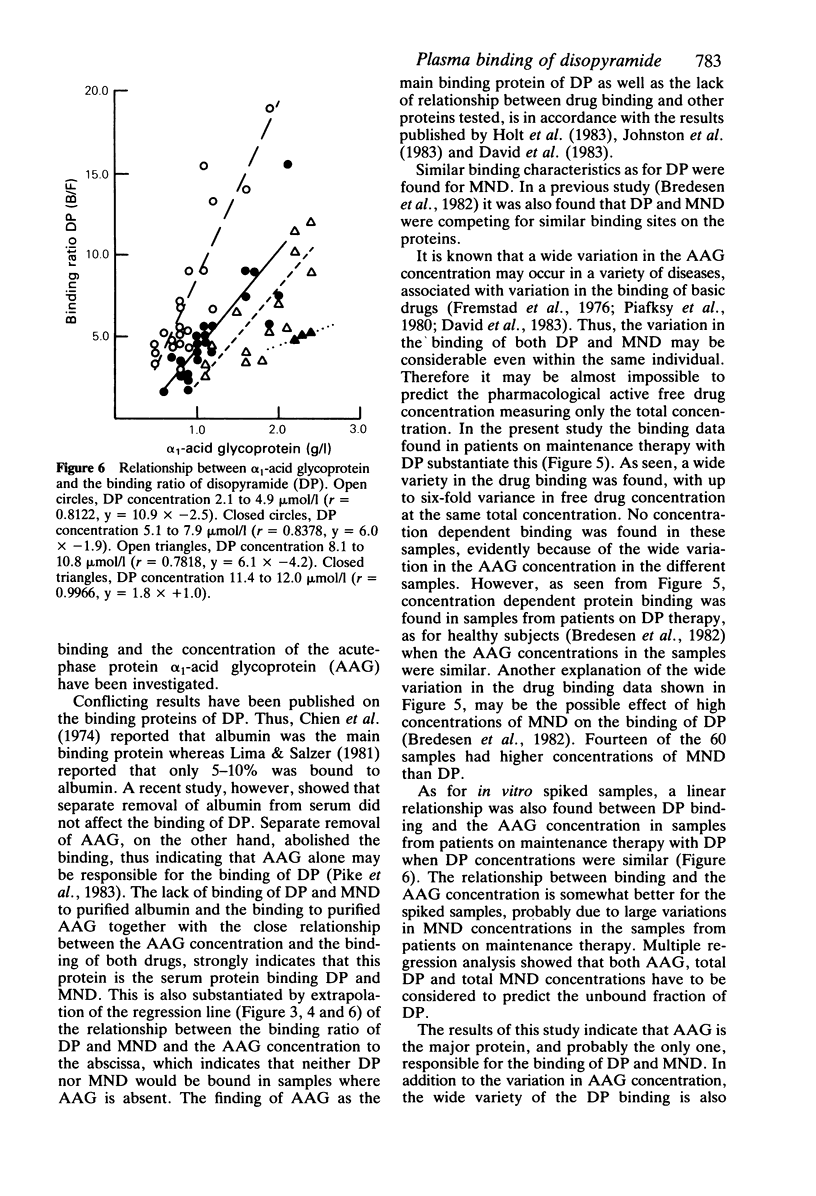
Highly purified serum albumin did not bind either disopyramide (DP) or mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide (MND). The unbound fraction of DP and MND in highly purified serum alpha 1-acid glycoprotein (AAG) at 0.5 g/l was 57 and 62 and at 2.0 g/l 19 and 30% respectively. Unbound DP and MND were measured in spiked plasma (10 mumol/l of DP or MND), from 60 patients, having AAG concentrations varying from 0.4 to 3.0 g/l. Unbound drug varied from 13 to 58 and from 24 to 62% for DP and MND, respectively, and was inversely related to the plasma concentration of AAG (r = -0.9016, r = -0.9157). A linear relationship was found between the binding ratio (moles bound divided by moles unbound) and the plasma concentration of AAG for both DP (r = 0.9199) and MND (r = 0.9270), whereas no relationship was found between the binding ratios of DP or MND and the plasma concentrations of total protein, albumin, haptoglobin, alpha 1-antitrypsin or the immunoglobulins IgG, IgA or IgM. In patients on DP maintenance therapy, a linear relationship was found between percent unbound DP and the plasma concentration of DP in samples with similar AAG concentrations. Furthermore, a linear relationship was found between the binding ratio of DP and the plasma concentration of AAG in samples with similar DP concentrations. The present findings support the concept that AAG is the major serum protein responsible for the binding of DP and MND.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitio M. L. Plasma concentrations and protein binding of disopyramide and mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide during chronic oral disopyramide therapy. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Apr;11(4):369–375. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01134.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredesen J. E. Gas-chromatographic determination of disopyramide and its mono-N-dealkylated metabolite in serum with use of a nitrogen-selective detector. Clin Chem. 1980 Apr;26(5):638–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bredesen J. E., Pike E., Lunde P. K. Plasma binding of disopyramide and mono-N-dealkyldisopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Nov;14(5):673–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb04955.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chien Y. W., Lambert H. J., Karim A. Comparative binding of disopyramide phosphate and quinidine sulfate to human plasma proteins. J Pharm Sci. 1974 Dec;63(12):1877–1879. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600631210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David B. M., Ilett K. F., Whitford E. G., Stenhouse N. S. Prolonged variability in plasma protein binding of disopyramide after acute myocardial infarction. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Apr;15(4):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David B. M., Madsen B. W., Ilett K. F. Plasma binding of disopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1980 Jun;9(6):614–618. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1980.tb01090.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Follath F., Ganzinger U., Schuetz E. Reliability of antiarrhythmic drug plasma concentration monitoring. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1983 Jan-Feb;8(1):63–82. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198308010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fremstad D., Bergerud K., Haffner J. F., Lunde P. K. Increased plasma binding of quinidine after surgery: a preliminary report. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1976;10(6):441–444. doi: 10.1007/BF00563081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garfein O. B. Pharmacology of commonly used antiarrhythmic drugs and comments on the use of therapeutic drug monitoring. Ther Drug Monit. 1982;4(1):1–14. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt D. W., Hayler A. M., Healey G. F. Effect of age and plasma concentrations of albumin and alpha 1-acid glycoprotein on protein binding of disopyramide. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;16(3):344–345. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02175.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch-Weser J. Disopyramide. N Engl J Med. 1979 Apr 26;300(17):957–962. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197904263001705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima J. J., Boudoulas H., Blanford M. Concentration-dependence of disopyramide binding to plasma protein and its influence on kinetics and dynamics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Dec;219(3):741–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lima J. J., Salzer L. B. Contamination of albumin by alpha 1-acid glycoprotein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1981 Sep 15;30(18):2633–2636. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(81)90596-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meffin P. J., Robert E. W., Winkle R. A., Harapat S., Peters F. A., Harrison D. C. Role of concentration-dependent plasma protein binding in disopyramide disposition. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm. 1979 Feb;7(1):29–46. doi: 10.1007/BF01059439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen O. G., Leren P., Aakesson I., Jacobsen S. Binding of quinidine in sera with different levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and orosomucoid protein. Biochem Pharmacol. 1978 Mar 15;27(6):871–876. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(78)90411-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piafsky K. M. Disease-induced changes in the plasma binding of basic drugs. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1980 May-Jun;5(3):246–262. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198005030-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike E., Kierulf P., Skuterud B., Bredesen J. E., Lunde P. K. Drug binding in sera deficient in lipoproteins, albumin or orosomucoid. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Sep;16(3):233–239. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb02155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


