Abstract
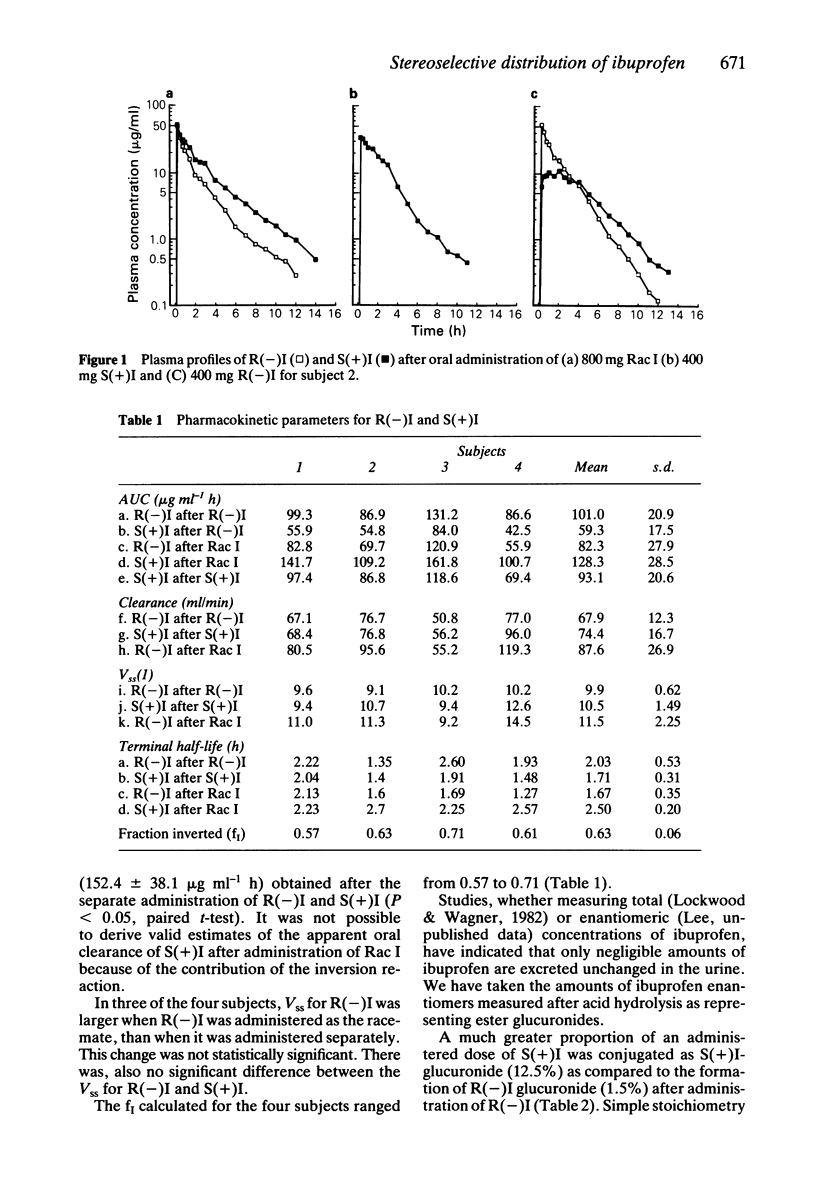
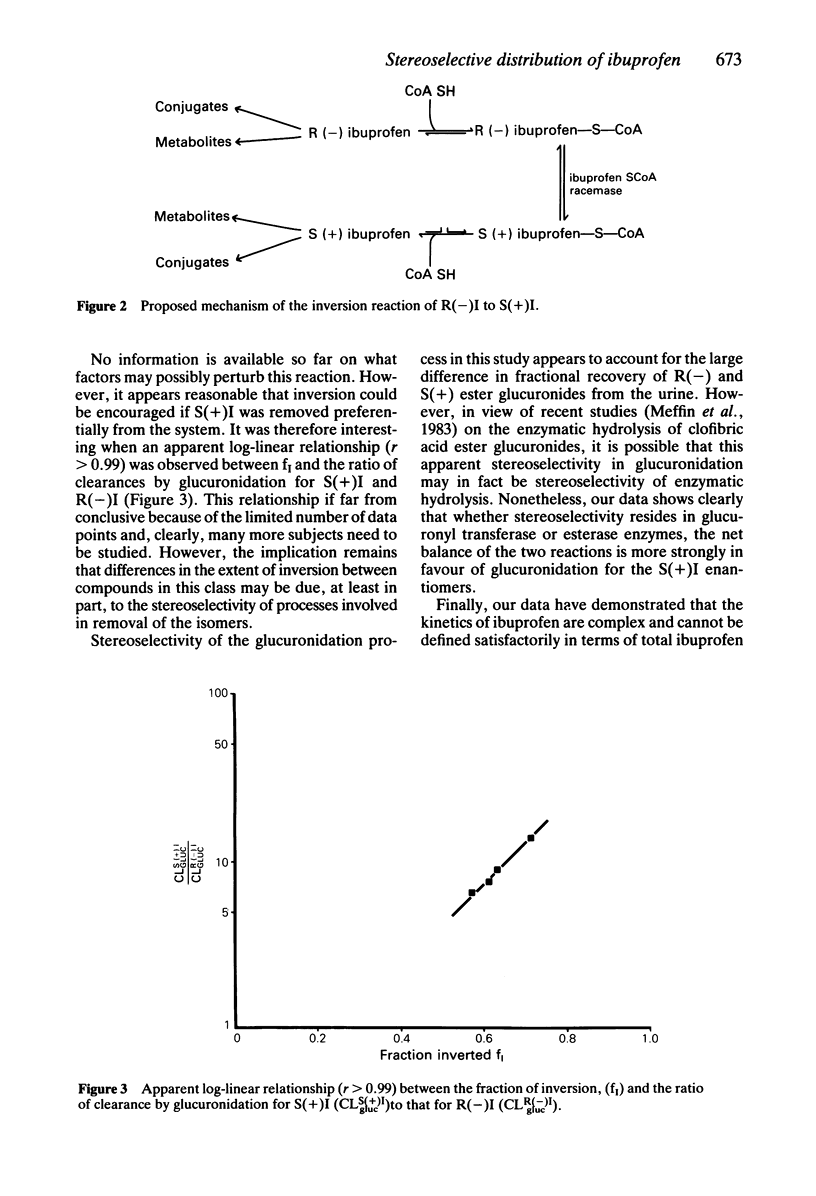
This study has examined the stereoselective disposition of the enantiomers of ibuprofen in four healthy male subjects following separate administration of racemic ibuprofen (800 mg) and of each enantiomer (400 mg). A mean of 63 +/- 6% of an administered dose of R(-) ibuprofen was stereospecifically inverted to the S(+) enantiomer. There were no measurable inversion of the S(+) to R(-) ibuprofen. The kinetics of the individual enantiomers were altered by concurrent administration of the respective optical antipode. It is likely that this change reflects an interaction between the enantiomers at plasma protein binding sites. It was found that formation of ester glucuronide conjugates stereoselectively favoured the S(+) enantiomer. The data have demonstrated that the pharmacokinetics of ibuprofen and other alpha-methylarylacetic acids cannot be interpreted adequately without studying the pharmacokinetics of the individual enantiomers.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams S. S., Bresloff P., Mason C. G. Pharmacological differences between the optical isomers of ibuprofen: evidence for metabolic inversion of the (-)-isomer. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;28(3):256–257. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04144.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bopp R. J., Nash J. F., Ridolfo A. S., Shepard E. R. Stereoselective inversion of (R)-(-)-benoxaprofen to the (S)-(+)-enantiomer in humans. Drug Metab Dispos. 1979 Nov-Dec;7(6):356–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaut Z. N., Baruth H., Randall L. O., Ashley C., Paulsrud J. R. Stereoisomeric relationships among anti-inflammatory activity, inhibition of platelet aggregation, and inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase. Prostaglandins. 1975 Jul;10(1):59–66. doi: 10.1016/0090-6980(75)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie W. R., DiSanto A. R., Monovich R. E., Albert K. S. Relative bioavailability of commercially available ibuprofen oral dosage forms in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Sep;71(9):1034–1038. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grennan D. M., Aarons L., Siddiqui M., Richards M., Thompson R., Higham C. Dose-response study with ibuprofen in rheumatoid arthritis: clinical and pharmacokinetic findings. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1983 Mar;15(3):311–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1983.tb01504.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutt A. J., Caldwell J. The metabolic chiral inversion of 2-arylpropionic acids--a novel route with pharmacological consequences. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1983 Nov;35(11):693–704. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1983.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Juhl R. P., Van Thiel D. H., Dittert L. W., Albert K. S., Smith R. B. Ibuprofen and sulindac kinetics in alcoholic liver disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Jul;34(1):104–109. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. G., Vangiessen G. J., Reischer R. J., Wechter W. J. Isomeric inversion of ibuprofen (R)-enantiomer in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1976 Feb;65(2):269–273. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600650222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzuna S., Matsumoto N., Kometani T., Kawai K. Biological activities of optical isomers of 6-chloro-5-cyclohexylindan-1-carboxylic acid (TAI-284: anti-inflammatory agent). Jpn J Pharmacol. 1974 Oct;24(5):695–705. doi: 10.1254/jjp.24.695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lan S. J., Kripalani K. J., Dean A. V., Egli P., Difazio L. T., Schreiber E. C. Inversion of optical configuration of alpha-methylfluorene-2-acetic acid (cicloprofen) in rats and monkeys. Drug Metab Dispos. 1976 Jul-Aug;4(4):330–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. J., Williams K. M., Graham G. G., Day R. O., Champion G. D. Liquid chromatographic determination and plasma concentration profile of optical isomers of ibuprofen in humans. J Pharm Sci. 1984 Nov;73(11):1542–1544. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600731112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood G. F., Albert K. S., Gillespie W. R., Bole G. G., Harkcom T. M., Szpunar G. J., Wagner J. G. Pharmacokinetics of ibuprofen in man. I. Free and total area/dose relationships. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Jul;34(1):97–103. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockwood G. F., Wagner J. G. High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of ibuprofen and its major metabolites in biological fluids. J Chromatogr. 1982 Nov 12;232(2):335–343. doi: 10.1016/s0378-4347(00)84173-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meffin P. J., Zilm D. M., Veenendaal J. R. Reduced clofibric acid clearance in renal dysfunction is due to a futile cycle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Dec;227(3):732–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang K. S., Kwan K. C. A commentary: methods and assumptions in the kinetic estimation of metabolite formation. Drug Metab Dispos. 1983 Mar-Apr;11(2):79–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrier D., Mayersohn M. Noncompartmental determination of the steady-state volume of distribution for any mode of administration. J Pharm Sci. 1982 Mar;71(3):372–373. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600710332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmonds R. G., Woodage T. J., Duff S. M., Green J. N. Stereospecific inversion of (R)-(-)-benoxaprofen in rat and man. Eur J Drug Metab Pharmacokinet. 1980;5(3):169–172. doi: 10.1007/BF03189461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Kuzuna S., Kawai K., Kishimoto S. Optical isomerization of R(-)-clidanac to the biologically active S(+)-isomer in guinea-pigs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1981 Nov;33(11):701–706. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1981.tb13908.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wechter W. J., Loughhead D. G., Reischer R. J., VanGiessen G. J., Kaiser D. G. Enzymatic inversion at saturated carbon: nature and mechanism of the inversion of R(-) p-iso-butyl hydratropic acid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 11;61(3):833–837. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


