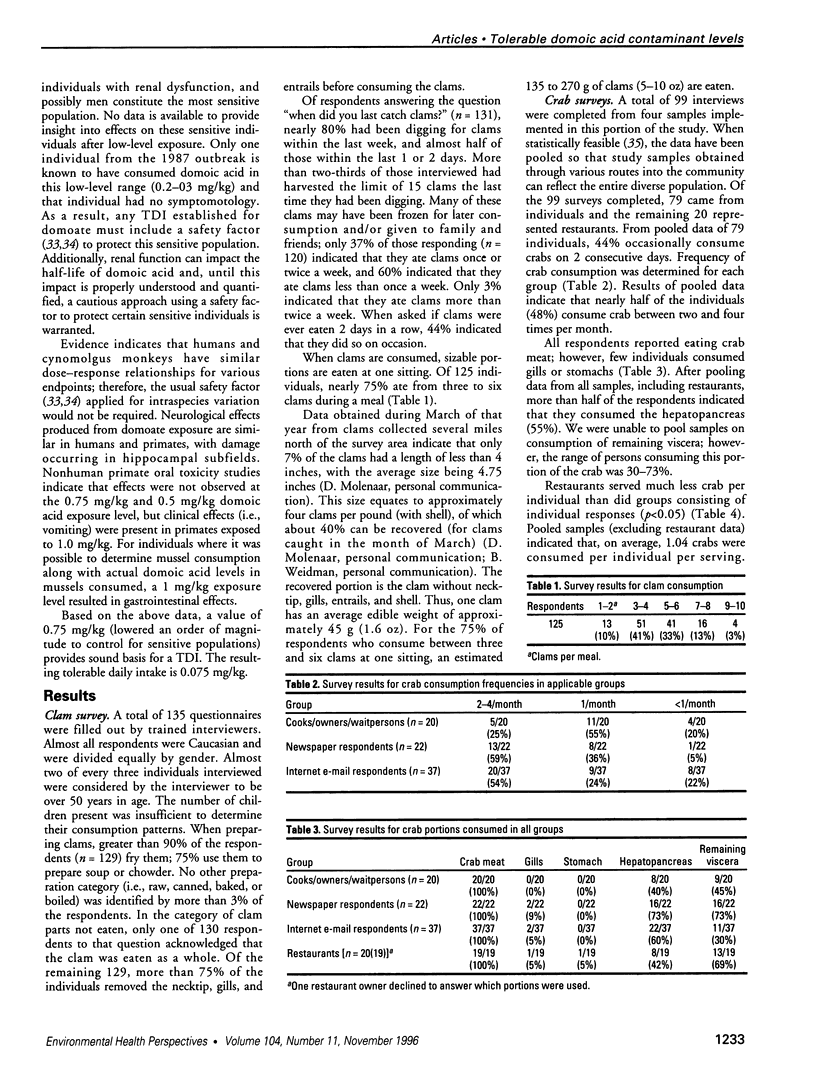
Abstract
Domoic acid has been found in razor clams (Siliqua patula) and dungeness crabs (Cancer magister) in Washington State and elsewhere on the West Coast of the United States. Due to toxic effects associated with domoic acid exposure, an effort has been made to establish tolerable domoic acid levels in crabs and clams obtained from commercial harvest and sale and from individual recreational harvesting. To accomplish this, the amount of clams and crabs consumed by populations of concern was determined, a tolerable daily intake (TDI) was developed for individuals most sensitive to effects of this compound, and the TDI was equated with consumption patterns to determine tolerable clam and crab domoic acid levels. Results indicate that the primary health effects associated with domoic acid toxicity can be averted in populations of concern and for others consuming crabs or clams less frequently (or in lesser quantity) if domoic acid contaminant concentration does not exceed 30 mg/kg in the hepatopancreas and viscera of dungeness crabs or 20 mg/kg in clams.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes D. G., Dourson M. Reference dose (RfD): description and use in health risk assessments. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 1988 Dec;8(4):471–486. doi: 10.1016/0273-2300(88)90047-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M. L., Lefauconnier J. M., Tremblay E., Ben-Ari Y. Limbic seizures induced by systemically applied kainic acid: how much kainic acid reaches the brain? Adv Exp Med Biol. 1986;203:199–209. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-7971-3_15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter S. The human neuropathology of encephalopathic mussel toxin poisoning. Can Dis Wkly Rep. 1990 Sep;16 (Suppl 1E):73–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chapin R. E., Stevens J. T., Hughes C. L., Kelce W. R., Hess R. A., Daston G. P. Endocrine modulation of reproduction. Fundam Appl Toxicol. 1996 Jan;29(1):1–17. doi: 10.1006/faat.1996.0001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIES D. F., SHOCK N. W. Age changes in glomerular filtration rate, effective renal plasma flow, and tubular excretory capacity in adult males. J Clin Invest. 1950 May;29(5):496–507. doi: 10.1172/JCI102286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debonnel G., Beauchesne L., de Montigny C. Domoic acid, the alleged "mussel toxin," might produce its neurotoxic effect through kainate receptor activation: an electrophysiological study in the dorsal hippocampus. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1989 Jan;67(1):29–33. doi: 10.1139/y89-005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson F., Truelove J., Nera E., Tryphonas L., Campbell J., Lok E. Domoic acid poisoning and mussel-associated intoxication: preliminary investigations into the response of mice and rats to toxic mussel extract. Food Chem Toxicol. 1989 Jun;27(6):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(89)90143-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson F., Truelove J. Toxicology and seafood toxins: domoic acid. Nat Toxins. 1994;2(5):334–339. doi: 10.1002/nt.2620020514. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iverson F., Truelove J., Tryphonas L., Nera E. A. The toxicology of domoic acid administered systemically to rodents and primates. Can Dis Wkly Rep. 1990 Sep;16 (Suppl 1E):15–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel C. A. Quantitative approaches to human risk assessment for noncancer health effects. Neurotoxicology. 1990 Summer;11(2):189–198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Künig G., Hartmann J., Krause F., Deckert J., Heinsen H., Ransmayr G., Beckmann H., Riederer P. Regional differences in the interaction of the excitotoxins domoate and L-beta-oxalyl-amino-alanine with [3H]kainate binding sites in human hippocampus. Neurosci Lett. 1995 Mar 3;187(2):107–110. doi: 10.1016/0304-3940(95)11355-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindeman R. D., Tobin J., Shock N. W. Longitudinal studies on the rate of decline in renal function with age. J Am Geriatr Soc. 1985 Apr;33(4):278–285. doi: 10.1111/j.1532-5415.1985.tb07117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novelli A., Kispert J., Fernández-Sánchez M. T., Torreblanca A., Zitko V. Domoic acid-containing toxic mussels produce neurotoxicity in neuronal cultures through a synergism between excitatory amino acids. Brain Res. 1992 Apr 10;577(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(92)90535-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perl T. M., Bédard L., Kosatsky T., Hockin J. C., Todd E. C., Remis R. S. An outbreak of toxic encephalopathy caused by eating mussels contaminated with domoic acid. N Engl J Med. 1990 Jun 21;322(25):1775–1780. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199006213222504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston E., Hynie I. Transfer constants for blood-brain barrier permeation of the neuroexcitatory shellfish toxin, domoic acid. Can J Neurol Sci. 1991 Feb;18(1):39–44. doi: 10.1017/s0317167100031279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe J. W., Andres R., Tobin J. D., Norris A. H., Shock N. W. The effect of age on creatinine clearance in men: a cross-sectional and longitudinal study. J Gerontol. 1976 Mar;31(2):155–163. doi: 10.1093/geronj/31.2.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scallet A. C., Binienda Z., Caputo F. A., Hall S., Paule M. G., Rountree R. L., Schmued L., Sobotka T., Slikker W., Jr Domoic acid-treated cynomolgus monkeys (M. fascicularis): effects of dose on hippocampal neuronal and terminal degeneration. Brain Res. 1993 Nov 12;627(2):307–313. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(93)90335-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tasker R. A., Connell B. J., Strain S. M. Pharmacology of systemically administered domoic acid in mice. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1991 Mar;69(3):378–382. doi: 10.1139/y91-057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todd E. C. Chronology of the toxic mussels outbreak. Can Dis Wkly Rep. 1990 Sep;16 (Suppl 1E):3–4. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truelove J., Iverson F. Serum domoic acid clearance and clinical observations in the cynomolgus monkey and Sprague-Dawley rat following a single i.v. dose. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. 1994 Apr;52(4):479–486. doi: 10.1007/BF00194132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas L., Truelove J., Iverson F. Acute parenteral neurotoxicity of domoic acid in cynomolgus monkeys (M. fascicularis) Toxicol Pathol. 1990;18(2):297–303. doi: 10.1177/019262339001800208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas L., Truelove J., Iverson F., Todd E. C., Nera E. A. Neuropathology of experimental domoic acid poisoning in non-human primates and rats. Can Dis Wkly Rep. 1990 Sep;16 (Suppl 1E):75–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas L., Truelove J., Nera E., Iverson F. Acute neurotoxicity of domoic acid in the rat. Toxicol Pathol. 1990;18(1 Pt 1):1–9. doi: 10.1177/019262339001800101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tryphonas L., Truelove J., Todd E., Nera E., Iverson F. Experimental oral toxicity of domoic acid in cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) and rats. Preliminary investigations. Food Chem Toxicol. 1990 Oct;28(10):707–715. doi: 10.1016/0278-6915(90)90147-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wekell J. C., Gauglitz E. J., Jr, Barnett H. J., Hatfield C. L., Simons D., Ayres D. Occurrence of domoic acid in Washington state razor clams (Siliqua patula) during 1991-1993. Nat Toxins. 1994;2(4):197–205. doi: 10.1002/nt.2620020408. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


