Abstract
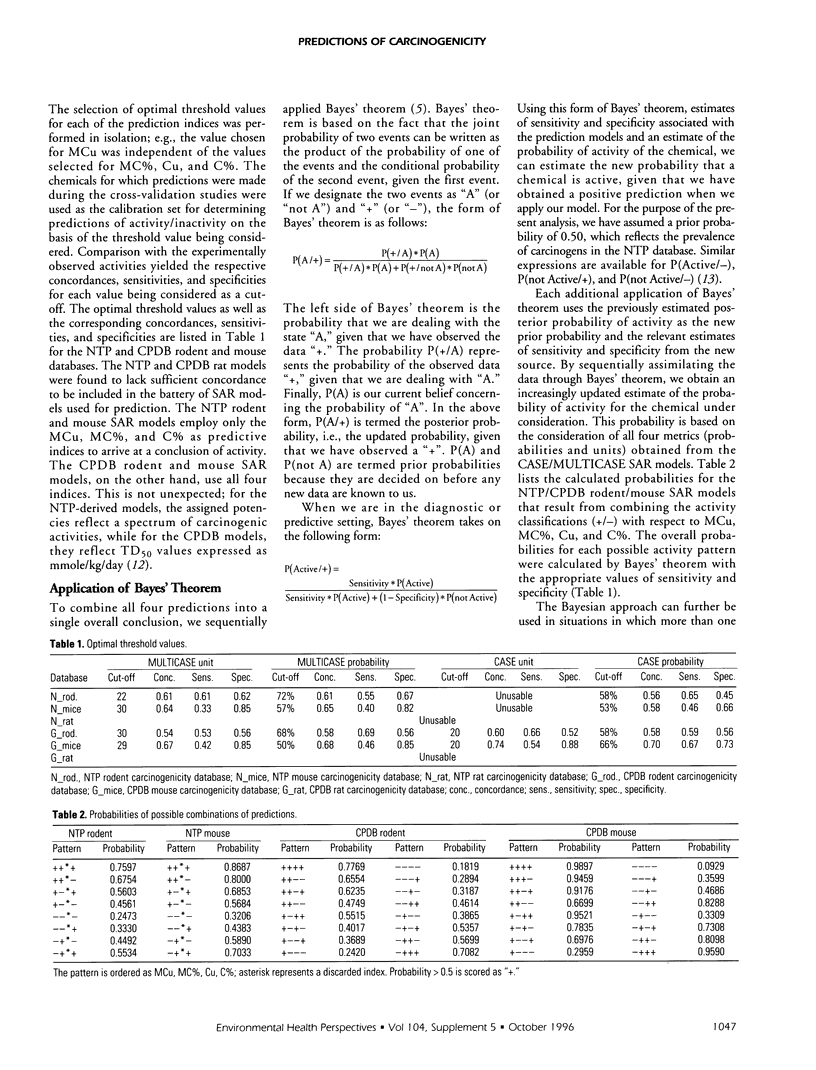
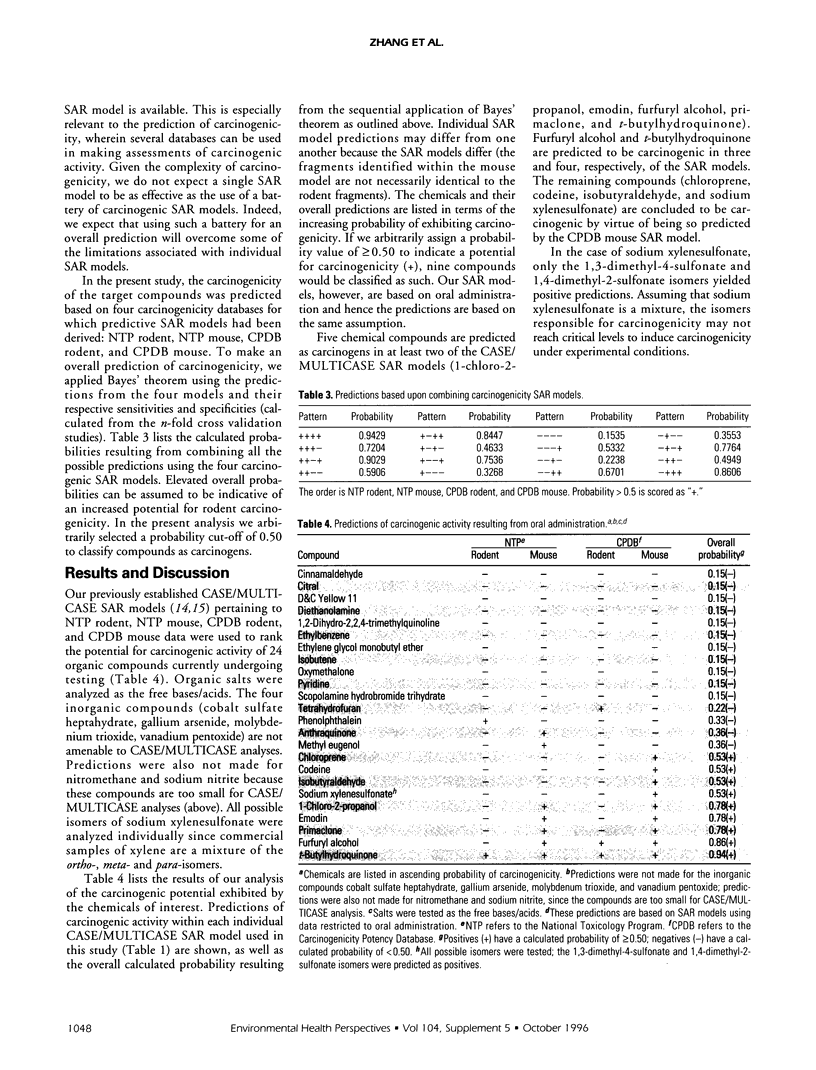
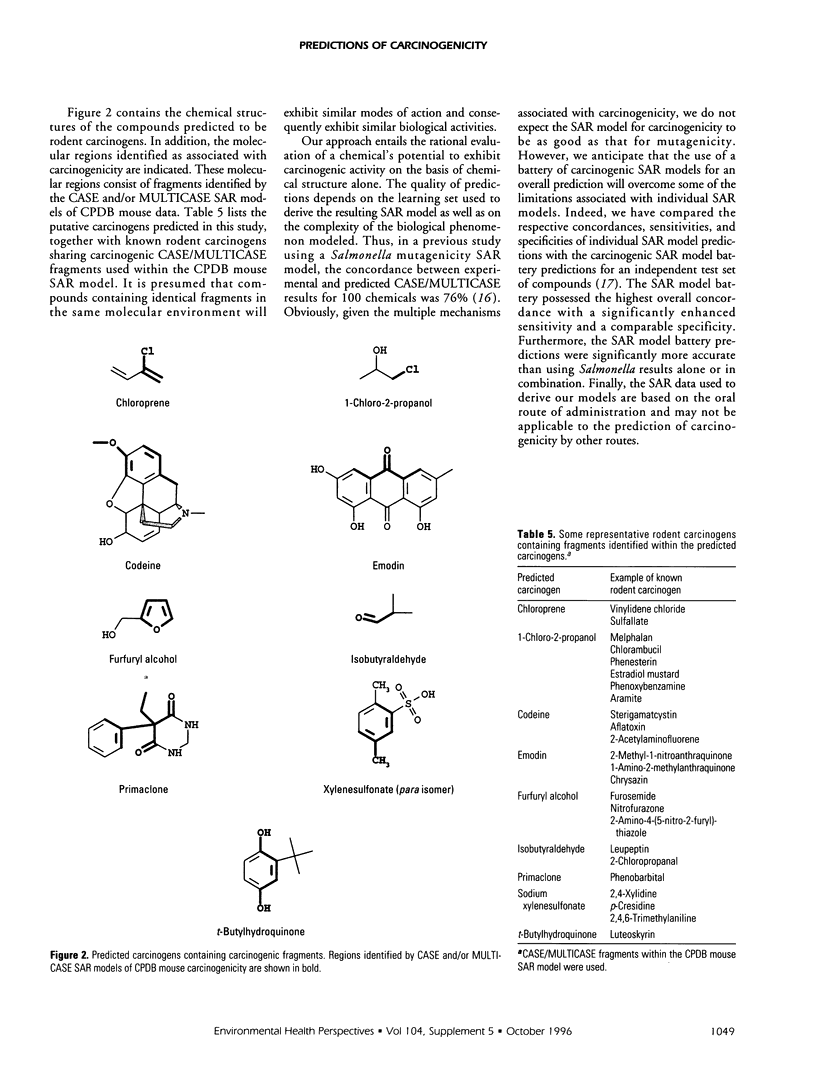
Twenty-four organic compounds currently undergoing testing within cancer bioassays under the aegis of the U.S. National Toxicology Program (NTP) were submitted to the computer automated structure evaluation (CASE) and multiple computer automated structure evaluation (MULTICASE) system for predictions of activity. Individual predictions resulting from the NTP combined rodent, NTP mouse, Carcinogenic Potency Database (CPDB) combined rodent, and CPDB mouse databases were combined using Bayes' theorem to yield an overall probability of rodent carcinogenicity. Based upon an arbitrary probability cut-off of 0.50, nine compounds were predicted to be rodent carcinogens. The predicted carcinogens are chloroprene, 1-chloro-2-propanol, codeine, emodin, furfuryl alcohol, isobutyraldehyde, primaclone, sodium xylenesulfonate, and t-butylhydroquinone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby J., Tennant R. W. Definitive relationships among chemical structure, carcinogenicity and mutagenicity for 301 chemicals tested by the U.S. NTP. Mutat Res. 1991 May;257(3):229–306. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(91)90003-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chankong V., Haimes Y. Y., Rosenkranz H. S., Pet-Edwards J. The carcinogenicity prediction and battery selection (CPBS) method: a Bayesian approach. Mutat Res. 1985 May;153(3):135–166. doi: 10.1016/0165-1110(85)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cunningham A., Klopman G., Rosenkranz H. S. A study of the structural basis of the carcinogenicity of tamoxifen, toremifene and their metabolites. Mutat Res. 1996 Jan 17;349(1):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(95)00163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Sawyer C. B., Magaw R., Backman G. M., de Veciana M., Levinson R., Hooper N. K., Havender W. R., Bernstein L., Peto R. A carcinogenic potency database of the standardized results of animal bioassays. Environ Health Perspect. 1984 Dec;58:9–319. doi: 10.1289/ehp.84589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Backman G. M., Eisenberg S., Da Costa M., Wong M., Manley N. B., Rohrbach L., Ames B. N. Third chronological supplement to the carcinogenic potency database: standardized results of animal bioassays published through December 1986 and by the National Toxicology Program through June 1987. Environ Health Perspect. 1990 Mar;84:215–286. doi: 10.1289/ehp.9084215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., Slone T. H., Backman G. M., Magaw R., Da Costa M., Lopipero P., Blumenthal M., Ames B. N. Second chronological supplement to the Carcinogenic Potency Database: standardized results of animal bioassays published through December 1984 and by the National Toxicology Program through May 1986. Environ Health Perspect. 1987 Oct;74:237–329. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8774237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L. S., de Veciana M., Backman G. M., Magaw R., Lopipero P., Smith M., Blumenthal M., Levinson R., Bernstein L., Ames B. N. Chronological supplement to the Carcinogenic Potency Database: standardized results of animal bioassays published through December 1982. Environ Health Perspect. 1986 Aug;67:161–200. doi: 10.1289/ehp.8667161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Ennever F. K., Chankong V., Pet-Edwards J., Haimes Y. Y. Invited contribution: an objective approach to the development of short-term tests predictive of carcinogenicity. Cell Biol Toxicol. 1986 Dec;2(4):425–440. doi: 10.1007/BF00117846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenkranz H. S., Klopman G. Structural basis of carcinogenicity in rodents of genotoxicants and non-genotoxicants. Mutat Res. 1990 Feb;228(2):105–124. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(90)90067-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



