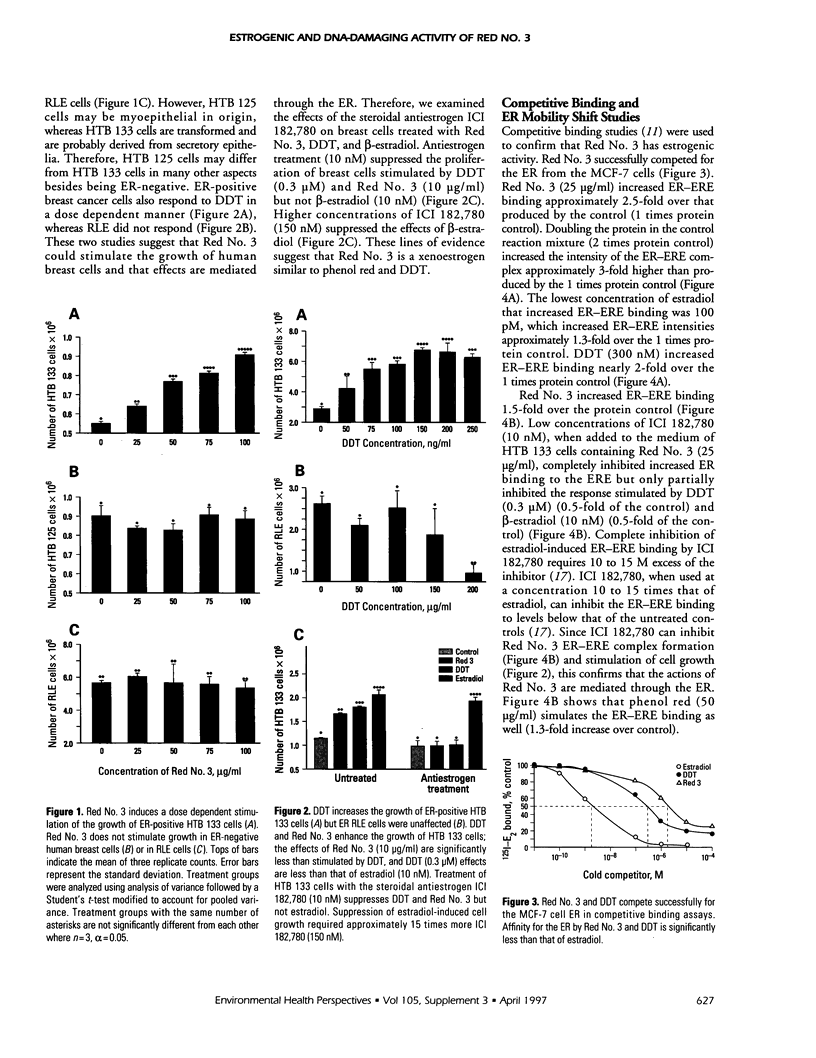
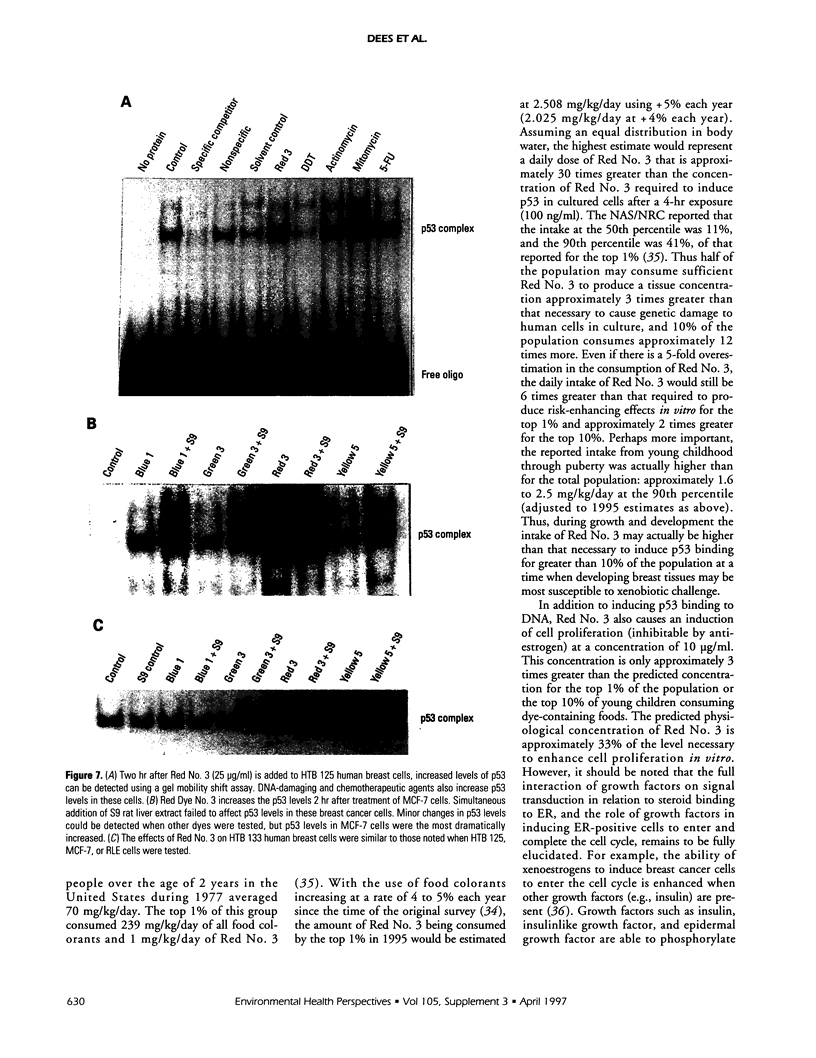
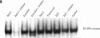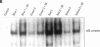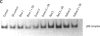Abstract
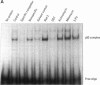
Exposure to pesticides, dyes, and pollutants that mimic the growth promoting effects of estrogen may cause breast cancer. The pesticide DDT and the food colorant Red No. 3 were found to increase the growth of HTB 133 but not estrogen receptor (ER) negative human breast cells (HTB 125) or rat liver epithelial cells (RLE). Red No. 3, beta-estradiol, and DDT increase ER site-specific DNA binding to the estrogen response element in HTB 133 cells and increase cyclin-dependent kinase 2 activity in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Site-specific DNA binding by p53 in RLE, HTB 125, HTB 133, and MCF-7 cells was increased when they were treated with Red No. 3, which suggests that cellular DNA was damaged by this colorant. Red No. 3 increased binding of the ER from MCF-7 cells to the estrogen-responsive element. Consumption of Red No. 3, which has estrogenlike growth stimulatory properties and may be genotoxic, could be a significant risk factor in human breast carcinogenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akiyama T., Ohuchi T., Sumida S., Matsumoto K., Toyoshima K. Phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma protein by cdk2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Sep 1;89(17):7900–7904. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.17.7900. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold S. F., Klotz D. M., Collins B. M., Vonier P. M., Guillette L. J., Jr, McLachlan J. A. Synergistic activation of estrogen receptor with combinations of environmental chemicals. Science. 1996 Jun 7;272(5267):1489–1492. doi: 10.1126/science.272.5267.1489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthois Y., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Phenol red in tissue culture media is a weak estrogen: implications concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2496–2500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunone G., Briand P. A., Miksicek R. J., Picard D. Activation of the unliganded estrogen receptor by EGF involves the MAP kinase pathway and direct phosphorylation. EMBO J. 1996 May 1;15(9):2174–2183. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis D. L., Bradlow H. L., Wolff M., Woodruff T., Hoel D. G., Anton-Culver H. Medical hypothesis: xenoestrogens as preventable causes of breast cancer. Environ Health Perspect. 1993 Oct;101(5):372–377. doi: 10.1289/ehp.93101372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees C., Askari M., Foster J. S., Ahamed S., Wimalasena J. DDT mimicks estradiol stimulation of breast cancer cells to enter the cell cycle. Mol Carcinog. 1997 Feb;18(2):107–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees C., Travis C. C. Increased p53 site-specific DNA binding in cells producing mutant p53. Cancer Lett. 1995 Sep 25;96(2):225–231. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(95)03936-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewailly E., Dodin S., Verreault R., Ayotte P., Sauvé L., Morin J., Brisson J. High organochlorine body burden in women with estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Feb 2;86(3):232–234. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.3.232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elixhauser A. Costs of breast cancer and the cost-effectiveness of breast cancer screening. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 1991;7(4):604–615. doi: 10.1017/s0266462300007169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graeber T. G., Peterson J. F., Tsai M., Monica K., Fornace A. J., Jr, Giaccia A. J. Hypoxia induces accumulation of p53 protein, but activation of a G1-phase checkpoint by low-oxygen conditions is independent of p53 status. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Sep;14(9):6264–6277. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.9.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. R., Lippman M. E., Veronesi U., Willett W. Breast cancer (1) N Engl J Med. 1992 Jul 30;327(5):319–328. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199207303270505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiasa Y., Ohshima M., Kitahori Y., Konishi N., Shimoyama T., Sakaguchi Y., Hashimoto H., Minami S., Kato Y. The promoting effects of food dyes, erythrosine (Red 3) and rose bengal B (Red 105), on thyroid tumors in partially thyroidectomized N-bis(2-hydroxypropyl)-nitrosamine-treated rats. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1988 Mar;79(3):314–319. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1988.tb01593.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaraman J., Prives C. Activation of p53 sequence-specific DNA binding by short single strands of DNA requires the p53 C-terminus. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jobling S., Reynolds T., White R., Parker M. G., Sumpter J. P. A variety of environmentally persistent chemicals, including some phthalate plasticizers, are weakly estrogenic. Environ Health Perspect. 1995 Jun;103(6):582–587. doi: 10.1289/ehp.95103582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joel P. B., Traish A. M., Lannigan D. A. Estradiol and phorbol ester cause phosphorylation of serine 118 in the human estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1995 Aug;9(8):1041–1052. doi: 10.1210/mend.9.8.7476978. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato S., Endoh H., Masuhiro Y., Kitamoto T., Uchiyama S., Sasaki H., Masushige S., Gotoh Y., Nishida E., Kawashima H. Activation of the estrogen receptor through phosphorylation by mitogen-activated protein kinase. Science. 1995 Dec 1;270(5241):1491–1494. doi: 10.1126/science.270.5241.1491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieger N., Wolff M. S., Hiatt R. A., Rivera M., Vogelman J., Orentreich N. Breast cancer and serum organochlorines: a prospective study among white, black, and Asian women. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1994 Apr 20;86(8):589–599. doi: 10.1093/jnci/86.8.589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakdawalla A. A., Netrawali M. S. Erythrosine, a permitted food dye, is mutagenic in the Bacillus subtilis multigene sporulation assay. Mutat Res. 1988 Oct;206(2):171–176. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90157-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakdawalla A. A., Netrawali M. S. Mutagenicity, comutagenicity, and antimutagenicity of erythrosine (FD and C red 3), a food dye, in the Ames/Salmonella assay. Mutat Res. 1988 Feb;204(2):131–139. doi: 10.1016/0165-1218(88)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S., Elenbaas B., Levine A., Griffith J. p53 and its 14 kDa C-terminal domain recognize primary DNA damage in the form of insertion/deletion mismatches. Cell. 1995 Jun 30;81(7):1013–1020. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80006-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippman M. E., Dickson R. B. Mechanisms of growth control in normal and malignant breast epithelium. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1989;45:383–440. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571145-6.50012-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall E. Epidemiology. Search for a killer: focus shifts from fat to hormones. Science. 1993 Jan 29;259(5095):618–621. doi: 10.1126/science.8430308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K. G., Sakai Y., Eitzman B., Steed T., McLachlan J. Exposure to diethylstilbestrol during a critical developmental period of the mouse reproductive tract leads to persistent induction of two estrogen-regulated genes. Cell Growth Differ. 1994 Jun;5(6):595–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagano M., Pepperkok R., Lukas J., Baldin V., Ansorge W., Bartek J., Draetta G. Regulation of the cell cycle by the cdk2 protein kinase in cultured human fibroblasts. J Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;121(1):101–111. doi: 10.1083/jcb.121.1.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price B. D., Calderwood S. K. Increased sequence-specific p53-DNA binding activity after DNA damage is attenuated by phorbol esters. Oncogene. 1993 Nov;8(11):3055–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo J., Gusterson B. A., Rogers A. E., Russo I. H., Wellings S. R., van Zwieten M. J. Comparative study of human and rat mammary tumorigenesis. Lab Invest. 1990 Mar;62(3):244–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherr C. J. G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell. 1994 Nov 18;79(4):551–555. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone R. Environmental estrogens stir debate. Science. 1994 Jul 15;265(5170):308–310. doi: 10.1126/science.8023147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tishler R. B., Calderwood S. K., Coleman C. N., Price B. D. Increases in sequence specific DNA binding by p53 following treatment with chemotherapeutic and DNA damaging agents. Cancer Res. 1993 May 15;53(10 Suppl):2212–2216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willett W. C. Diet and health: what should we eat? Science. 1994 Apr 22;264(5158):532–537. doi: 10.1126/science.8160011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]