Abstract
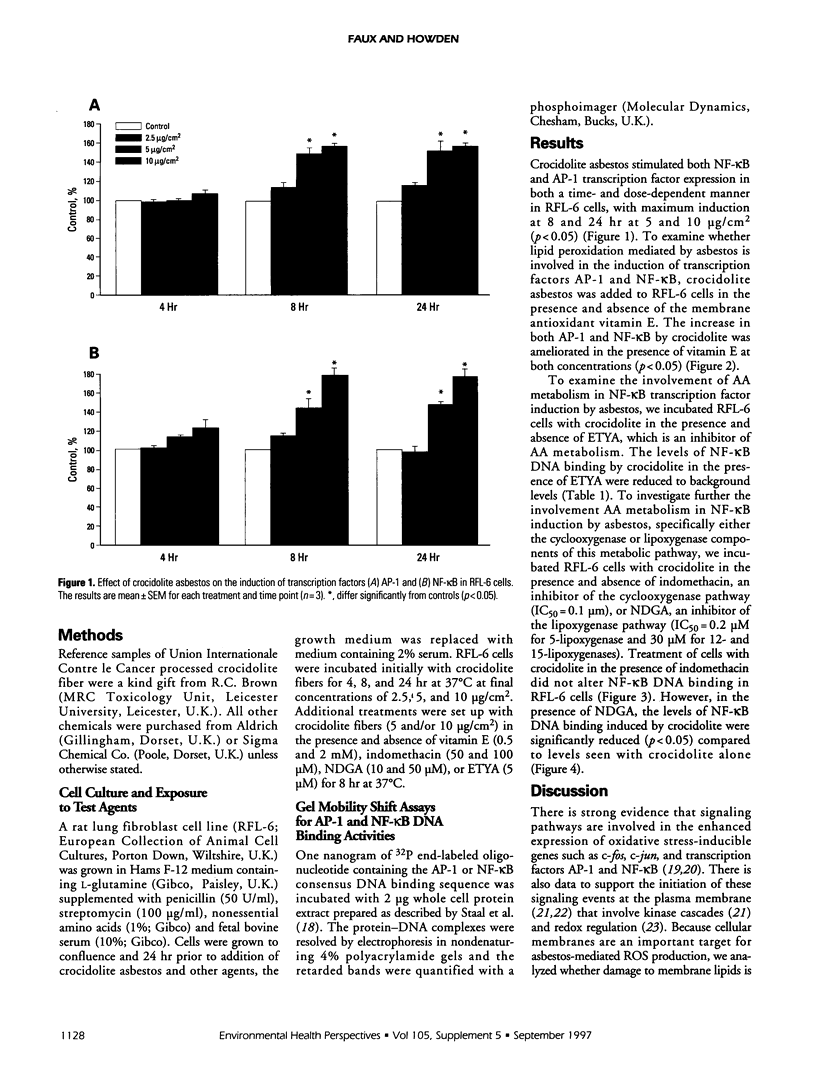
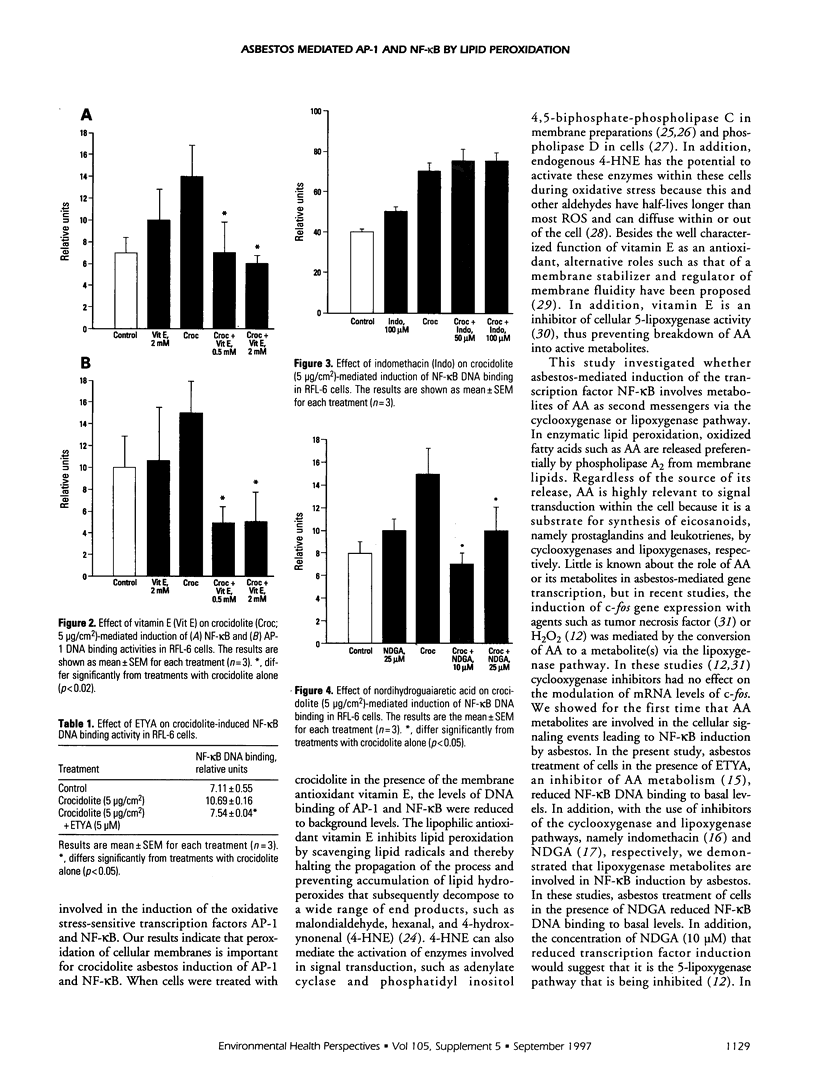
Asbestos fibers cause persistent induction of the oxidative stress sensitive transcription factors nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-kappa B) and activator protein-1 (AP-1) in mammalian cells. These transcription factors play an important role in the regulation of cellular activity. Lipid peroxidation, mediated by reactive oxygen species, is thought to be a possible mechanism in the pathogenicity of asbestos fibers. These studies were designed to determine if crocidolite asbestos-induced lipid peroxidation plays a role in the mechanism of formation of NF-kappa B and AP-1. Treatment of a rat lung fibroblast cell line (RFL-6) with crocidolite asbestos in the presence and absence of the membrane antioxidant vitamin E decreased the levels of crocidolite-induced AP-1 and NF-kappa B to background levels. Preincubation of RFL-6 cells with 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid, an inhibitor of arachidonic acid metabolism, prior to exposure to crocidolite, abrogated crocidolite-induced NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity to background levels. Coincubation with indomethacin, a cyclooxygenase inhibitor, had no effect on NF-kappa B DNA-binding activity induced by crocidolite. However, nordihydroguaiaretic acid, a lipoxygenase inhibitor, decreased levels of NF-kappa B to background levels. This would suggest that lipoxygenase metabolites of arachidonic acid, produced following lipid peroxidation, are involved in the cellular signalling events to NF-kappa B transcription factor induction by asbestos.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Gold L. S. Endogenous mutagens and the causes of aging and cancer. Mutat Res. 1991 Sep-Oct;250(1-2):3–16. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(91)90157-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Angel P., Karin M. The role of Jun, Fos and the AP-1 complex in cell-proliferation and transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Dec 10;1072(2-3):129–157. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(91)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craighead J. E., Mossman B. T. The pathogenesis of asbestos-associated diseases. N Engl J Med. 1982 Jun 17;306(24):1446–1455. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198206173062403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Lau L. F., Karin M. Rapid and preferential activation of the c-jun gene during the mammalian UV response. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2804–2811. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Gottlieb R. A., Smeal T., Karin M. The mammalian ultraviolet response is triggered by activation of Src tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1992 Dec 24;71(7):1081–1091. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(05)80058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devary Y., Rosette C., DiDonato J. A., Karin M. NF-kappa B activation by ultraviolet light not dependent on a nuclear signal. Science. 1993 Sep 10;261(5127):1442–1445. doi: 10.1126/science.8367725. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois C. M., Bissonnette E., Rola-Pleszczynski M. Asbestos fibers and silica particles stimulate rat alveolar macrophages to release tumor necrosis factor. Autoregulatory role of leukotriene B4. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1989 May;139(5):1257–1264. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm/139.5.1257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esterbauer H., Zollner H. Methods for determination of aldehydic lipid peroxidation products. Free Radic Biol Med. 1989;7(2):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(89)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faux S. P., Howden P. J., Levy L. S. Iron-dependent formation of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in isolated DNA and mutagenicity in Salmonella typhimurium TA102 induced by crocidolite. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Aug;15(8):1749–1751. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.8.1749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faux S. P., Michelangeli F., Levy L. S. Calcium chelator Quin-2 prevents crocidolite-induced DNA strand breakage in human white blood cells. Mutat Res. 1994 Dec 1;311(2):209–215. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(94)90178-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haliday E. M., Ramesha C. S., Ringold G. TNF induces c-fos via a novel pathway requiring conversion of arachidonic acid to a lipoxygenase metabolite. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):109–115. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07926.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heintz N. H., Janssen Y. M., Mossman B. T. Persistent induction of c-fos and c-jun expression by asbestos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 15;90(8):3299–3303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.8.3299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howden P. J., Faux S. P. Fibre-induced lipid peroxidation leads to DNA adduct formation in Salmonella typhimurium TA104 and rat lung fibroblasts. Carcinogenesis. 1996 Mar;17(3):413–419. doi: 10.1093/carcin/17.3.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen Y. M., Barchowsky A., Treadwell M., Driscoll K. E., Mossman B. T. Asbestos induces nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kappa B) DNA-binding activity and NF-kappa B-dependent gene expression in tracheal epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Aug 29;92(18):8458–8462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.18.8458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leanderson P., Söderkvist P., Tagesson C., Axelson O. Formation of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine by asbestos and man made mineral fibres. Br J Ind Med. 1988 May;45(5):309–311. doi: 10.1136/oem.45.5.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer M., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. H2O2 and antioxidants have opposite effects on activation of NF-kappa B and AP-1 in intact cells: AP-1 as secondary antioxidant-responsive factor. EMBO J. 1993 May;12(5):2005–2015. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05850.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mossman B. T., Bignon J., Corn M., Seaton A., Gee J. B. Asbestos: scientific developments and implications for public policy. Science. 1990 Jan 19;247(4940):294–301. doi: 10.1126/science.2153315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura Y., Colburn N. H., Gindhart T. D. Role of reactive oxygen in tumor promotion: implication of superoxide anion in promotion of neoplastic transformation in JB-6 cells by TPA. Carcinogenesis. 1985 Feb;6(2):229–235. doi: 10.1093/carcin/6.2.229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Natarajan V., Scribner W. M., Taher M. M. 4-Hydroxynonenal, a metabolite of lipid peroxidation, activates phospholipase D in vascular endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med. 1993 Oct;15(4):365–375. doi: 10.1016/0891-5849(93)90036-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ondrey F., Harris J. E., Anderson K. M. Inhibition of U937 eicosanoid and DNA synthesis by 5,8,11,14-eicosatetraynoic acid, an inhibitor of arachidonic acid metabolism and its partial reversal by leukotriene C4. Cancer Res. 1989 Mar 1;49(5):1138–1142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L., Landvik S. Vitamin E: introduction to biochemistry and health benefits. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;570:1–6. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14903.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Packer L. Protective role of vitamin E in biological systems. Am J Clin Nutr. 1991 Apr;53(4 Suppl):1050S–1055S. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/53.4.1050S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradisi L., Panagini C., Parola M., Barrera G., Dianzani M. U. Effects of 4-hydroxynonenal on adenylate cyclase and 5'-nucleotidase activities in rat liver plasma membranes. Chem Biol Interact. 1985 Feb-Apr;53(1-2):209–217. doi: 10.1016/s0009-2797(85)80097-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plummer S. M., Faux S. P. Induction of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine in isolated DNA and HeLa cells exposed to fecapentaene-12: evidence for the involvement of prostaglandin H synthase and iron. Carcinogenesis. 1994 Mar;15(3):449–453. doi: 10.1093/carcin/15.3.449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao G. N., Lasségue B., Griendling K. K., Alexander R. W., Berk B. C. Hydrogen peroxide-induced c-fos expression is mediated by arachidonic acid release: role of protein kinase C. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1259–1263. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddanna P., Whelan J., Burgess J. R., Eskew M. L., Hildenbrandt G., Zarkower A., Scholz R. W., Reddy C. C. The role of vitamin E and selenium on arachidonic acid oxidation by way of the 5-lipoxygenase pathway. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;570:136–145. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb14914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi M. A., Fidale F., Garramone A., Esterbauer H., Dianzani M. U. Effect of 4-hydroxylalkenals on hepatic phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate-phospholipase C. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990 Jun 1;39(11):1715–1719. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(90)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreck R., Rieber P., Baeuerle P. A. Reactive oxygen intermediates as apparently widely used messengers in the activation of the NF-kappa B transcription factor and HIV-1. EMBO J. 1991 Aug;10(8):2247–2258. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07761.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staal F. J., Roederer M., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Intracellular thiols regulate activation of nuclear factor kappa B and transcription of human immunodeficiency virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9943–9947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turver C. J., Brown R. C. The role of catalytic iron in asbestos induced lipid peroxidation and DNA-strand breakage in C3H10T1/2 cells. Br J Cancer. 1987 Aug;56(2):133–136. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



