Abstract
The use of the maximum rate-of-rise of the action potential (Vmax) as a measure of the sodium conductance in excitable membranes is invalid. In the case of membrane action potentials, Vmax depends on the total ionic current across the membrane; drugs or conditions that alter the potassium or leak conductances will also affect Vmax. Likewise, long-term depolarization of the membrane lessens the fraction of total ionic current that passes through the sodium channels by increasing potassium conductance and inactivating the sodium conductance, and thereby reduces the effect of Vmax of drugs that specifically block sodium channels. The resultant artifact, an apparent voltage-dependent potency of such drugs, is theoretically simulated for the effects of tetrodotoxin on the Hodgkin-Huxley squid axon.
Full text
PDF

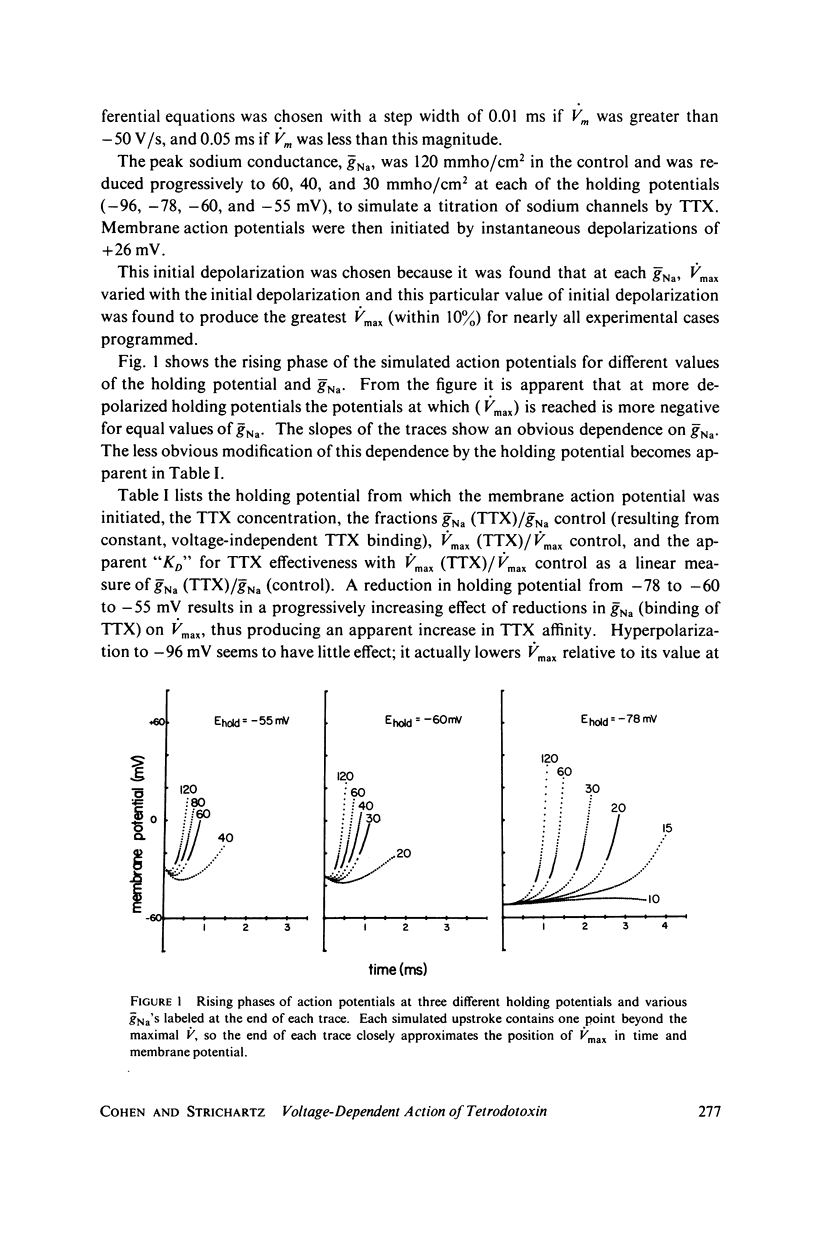
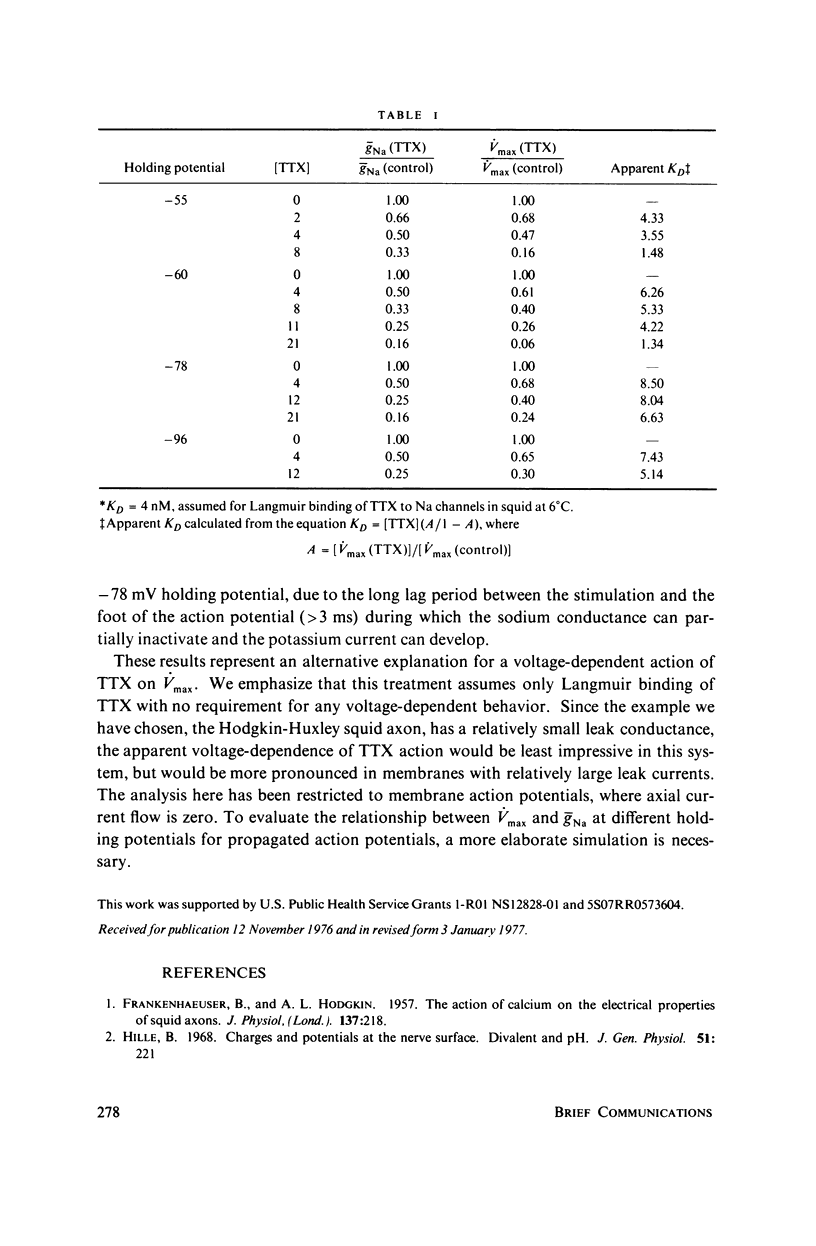

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albuquerque E. X., Daly J. W., Witkop B. Batrachotoxin: chemistry and pharmacology. Science. 1971 Jun 4;172(3987):995–1002. doi: 10.1126/science.172.3987.995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer M., Best P. M., Reuter H. Voltage-dependent action of tetrodotoxin in mammalian cardiac muscle. Nature. 1976 Sep 23;263(5575):344–345. doi: 10.1038/263344a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D. Modification of sodium channel gating in frog myelinated nerve fibres by Centruroides sculpturatus scorpion venom. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):511–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deguchi T. Structure and activity of tetrodotoxin derivaties. Jpn J Pharmacol. 1967 Jun;17(2):267–278. doi: 10.1254/jjp.17.267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. H. Tetrodotoxin, saxitoxin, and related substances: their applications in neurobiology. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1972;15:83–166. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7742(08)60329-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRANKENHAEUSER B., HODGKIN A. L. The action of calcium on the electrical properties of squid axons. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):218–244. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005808. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S. Ca spike. Adv Biophys. 1973;4:71–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Marshall M. W. Tetrodotoxin-resistant action potentials in newborn rat muscle. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jun 6;243(127):191–192. doi: 10.1038/newbio243191a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris J. B., Thesleff S. Studies on tetrodotoxin resistant action potentials in denervated skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand. 1971 Nov;83(3):382–388. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1971.tb05091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. Evidence that tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin act at a metal cation binding site in the sodium channels of nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3936–3940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. The binding of labelled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in nerve membranes. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):783–804. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Charges and potentials at the nerve surface. Divalent ions and pH. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):221–236. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Ionic channels in nerve membranes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1970;21:1–32. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(70)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Pharmacological modifications of the sodium channels of frog nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Feb;51(2):199–219. doi: 10.1085/jgp.51.2.199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The receptor for tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. A structural hypothesis. Biophys J. 1975 Jun;15(6):615–619. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85842-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B., Woodhull A. M., Shapiro B. I. Negative surface charge near sodium channels of nerve: divalent ions, monovalent ions, and pH. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):301–318. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. Y., Fuhrman F. A. Differentiation of the actions of tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. Toxicon. 1967 Jul;5(1):25–34. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(67)90114-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyama I., Narahashi T. Increase in sodium permeability of squid axon membranes by -dihydrograyanotoxin II. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):299–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strichartz G. Molecular mechanisms of nerve block by local anesthetics. Anesthesiology. 1976 Oct;45(4):421–441. doi: 10.1097/00000542-197610000-00012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAYLOR R. E. Effect of procaine on electrical properties of squid axon membrane. Am J Physiol. 1959 May;196(5):1071–1078. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1959.196.5.1071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twarog B. M., Hidaka T., Yamaguchi H. Resistance to tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin in nerves of bivalve molluscs. A possible correlation with paralytic shellfish poisoning. Toxicon. 1972 May;10(3):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0041-0101(72)90012-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht W. The effect of veratridine on excitable membranes of nerve and muscle. Ergeb Physiol. 1969;61:18–71. doi: 10.1007/BFb0111446. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulbricht W., Wagner H. H. The influence of pH on equilibrium effects of tetrodotoxin on myelinated nerve fibres of Rana esculenta. J Physiol. 1975 Oct;252(1):159–184. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011139. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodhull A. M. Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Jun;61(6):687–708. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.6.687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


