Abstract
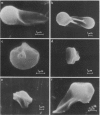
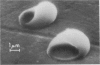
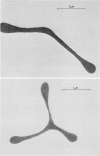
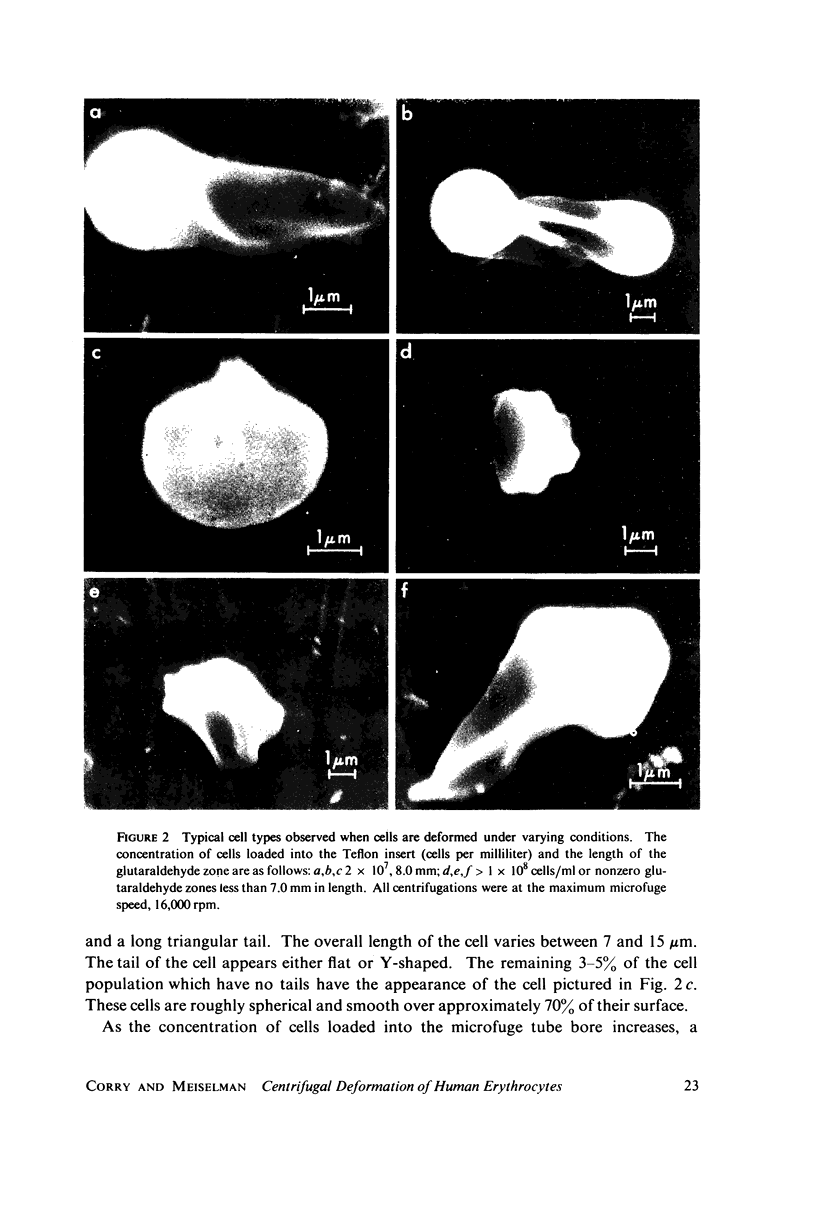
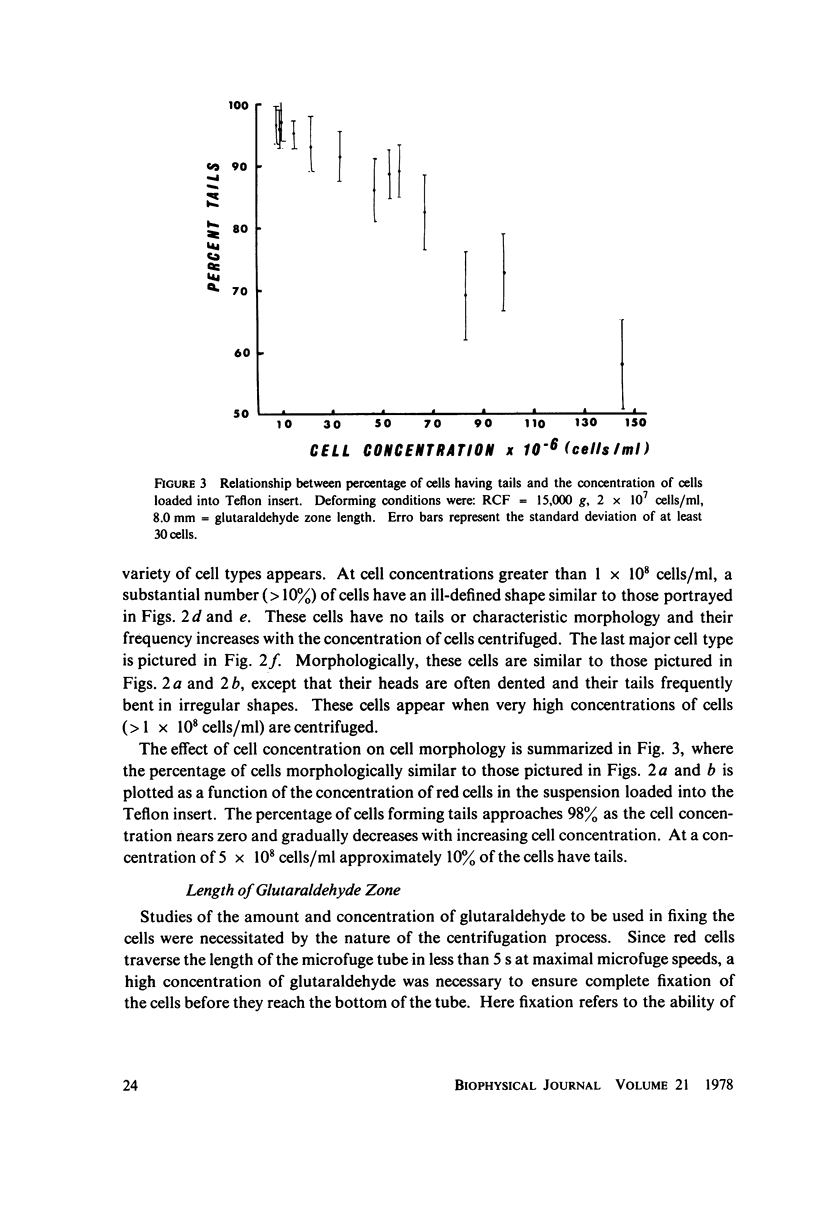
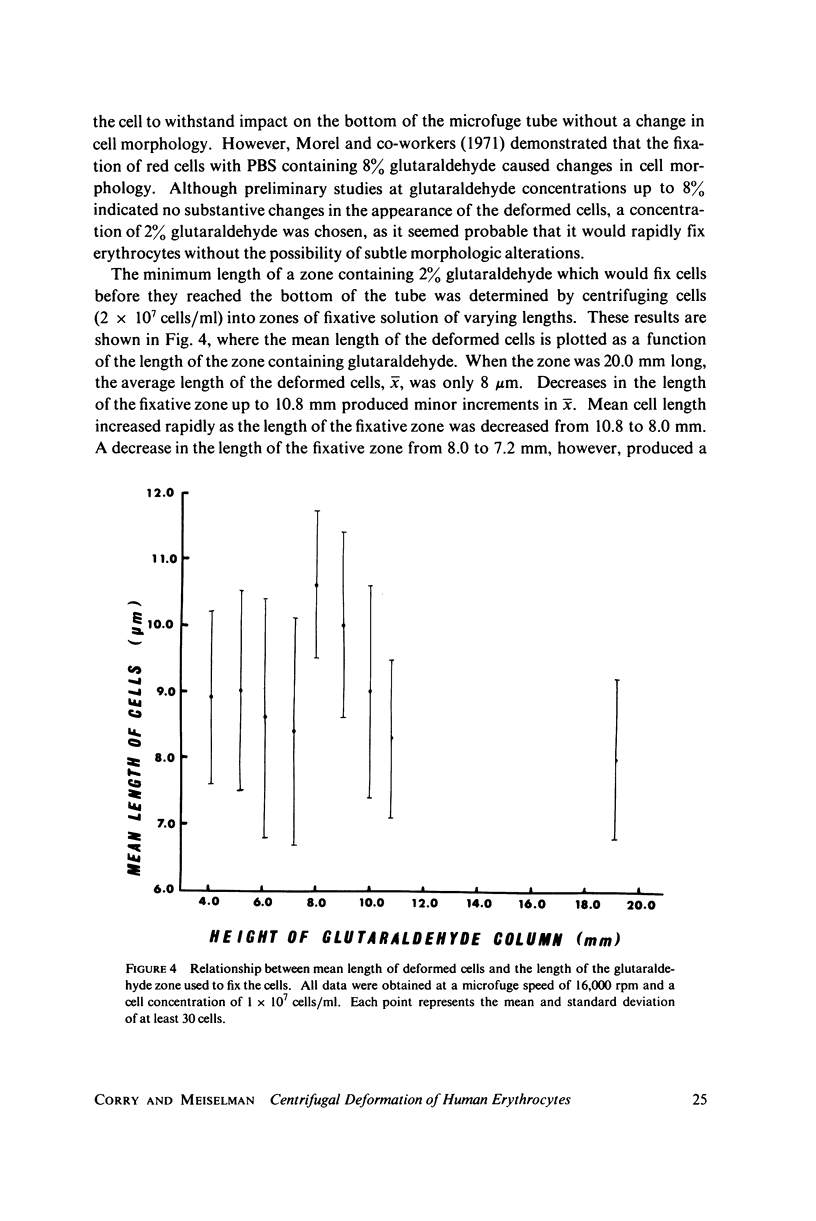
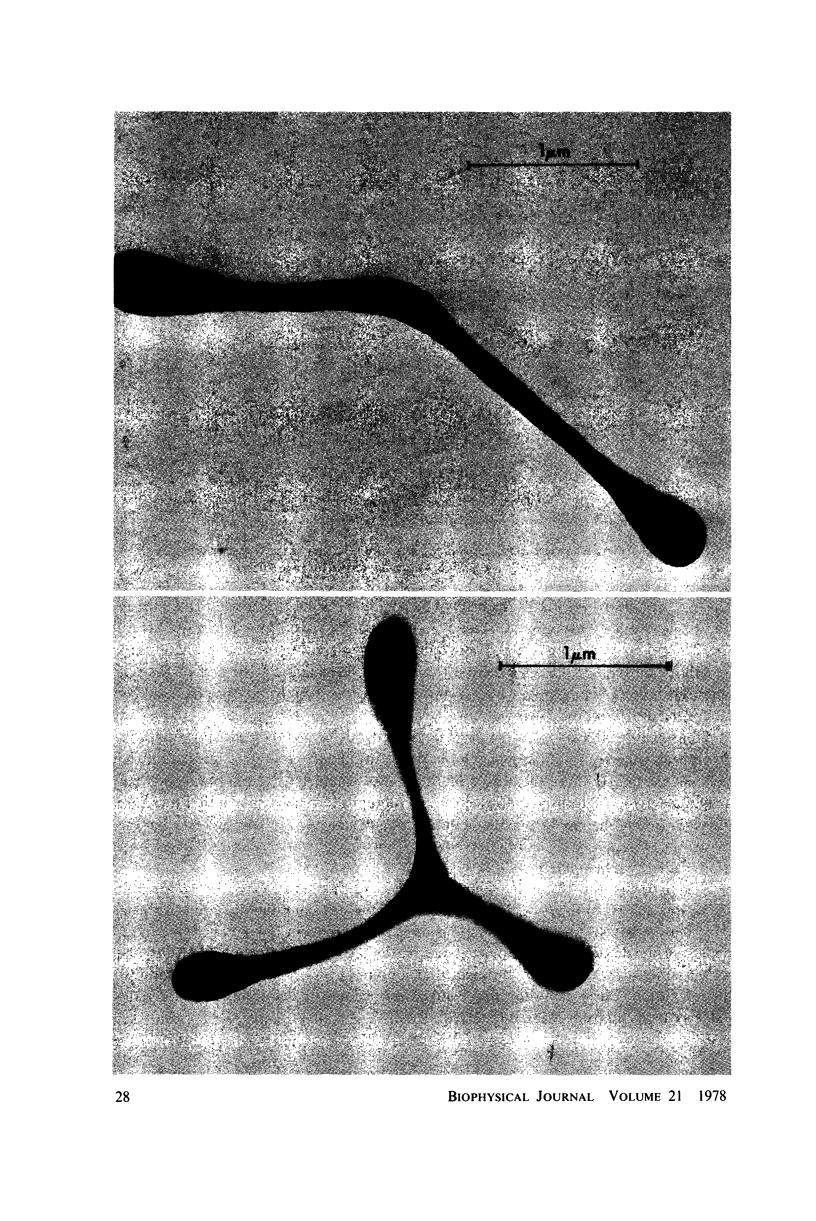
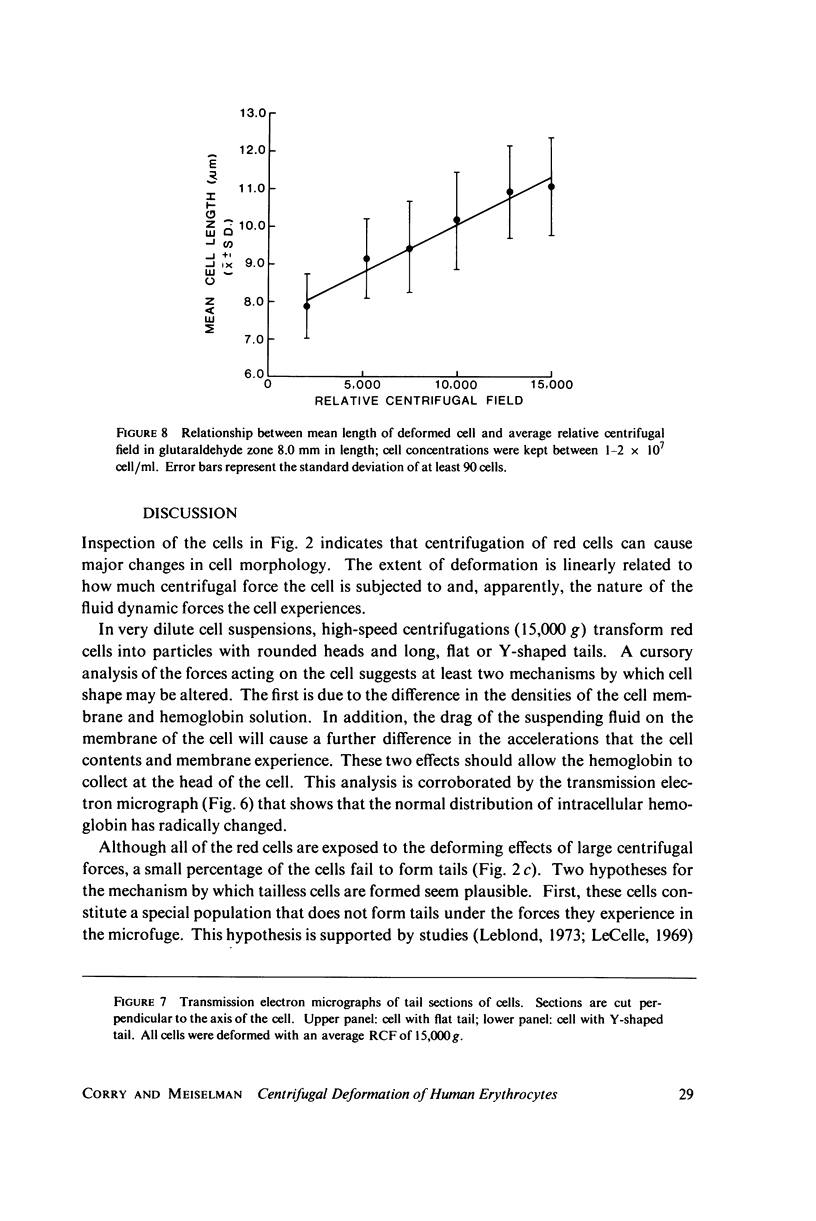
A new method for altering red cell morphology by high-speed centrifugation of cells through a physiological medium is described. Cell shape is preserved for microscopic analysis by allowing the sedimenting cells to pass from the physiological medium into a glutaraldehyde fixative solution. Examination of the deformed, fixed cells indicates that the vast majority resemble spheres with a flat, triangular tail. Measurements of the overall length of deformed cells show a nearly linear relationship between cell length and centrifugal force; average cell length increased from 8 to 11 micrometer as the centrifugal field was increased from 2,000 to 15,000 g. These data suggest that this centrifugal technique may be useful for evaluating cellular deformability and, potentially, the material properties of red cells.
Full text
PDF









Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bull B. S., Brailsford J. D. A new method of measuring the deformability of the red cell membrane. Blood. 1975 Apr;45(4):581–586. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bull B. S., Brailsford J. D. Red cell membrane deformability: new data. Blood. 1976 Nov;48(5):663–667. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A., Hochmuth R. M. A solid-liquid composite model of the red cell membrane. J Membr Biol. 1977 Jan 28;30(4):351–362. doi: 10.1007/BF01869676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. A. New membrane concept applied to the analysis of fluid shear- and micropipette-deformed red blood cells. Biophys J. 1973 Sep;13(9):941–954. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)86036-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GORDON G. B., MILLER L. R., BENSCH K. G. FIXATION OF TISSUE CULTURE CELLS FOR ULTRASTRUCTURAL CYTOCHEMISTRY. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Aug;31:440–443. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90024-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Mohandas N. Uniaxial loading of the red-cell membrane. J Biomech. 1972 Sep;5(5):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(72)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- La Celle P. L. Alteration of deformability of the erythrocyte membrane in stored blood. Transfusion. 1969 Sep-Oct;9(5):238–245. doi: 10.1111/j.1537-2995.1969.tb04930.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim R. W., Molday R. S., Huang H. V., Yen S. P. Application of latex microspheres in the isolation of plasma membranes. Affinity density perturbation of erythrocyte membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jul 3;394(3):377–387. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morel F. M., Baker R. F., Wayland H. Quantitation of human red blood cell fixation by glutaraldehyde. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jan;48(1):91–100. doi: 10.1083/jcb.48.1.91. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]