Abstract
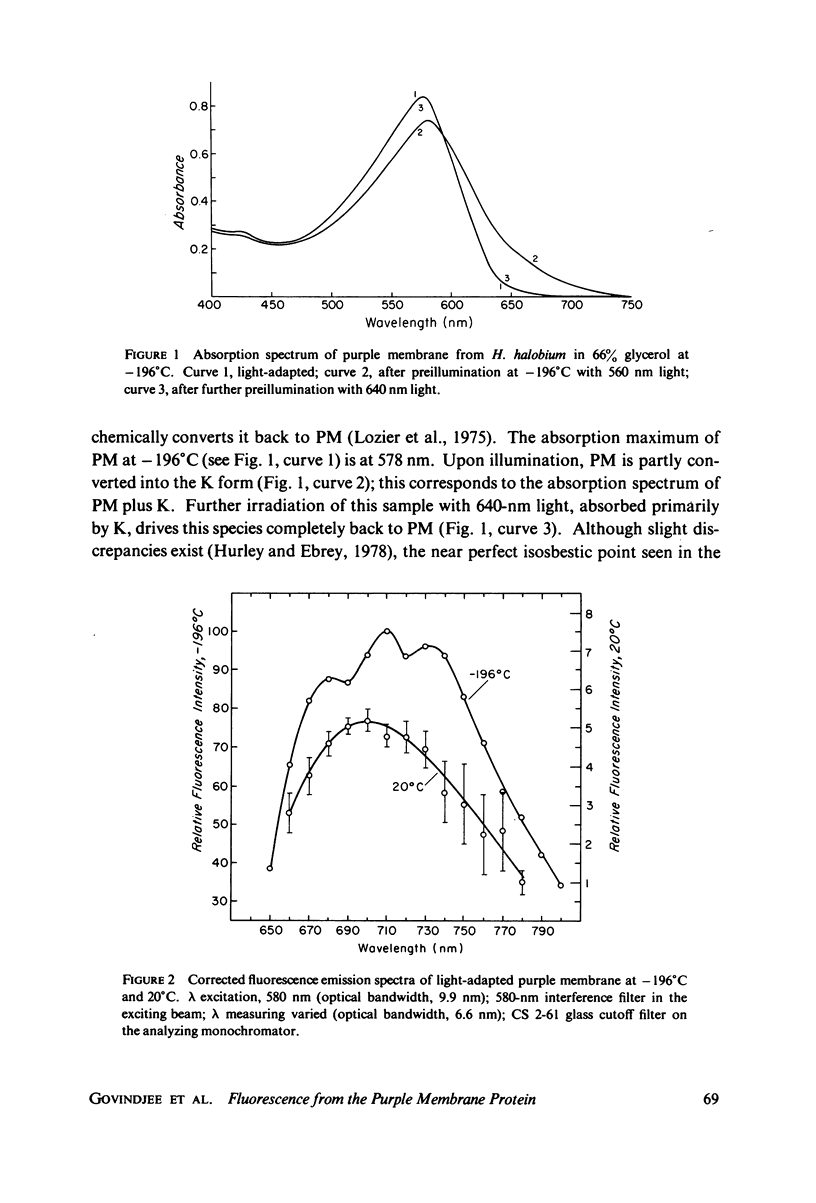
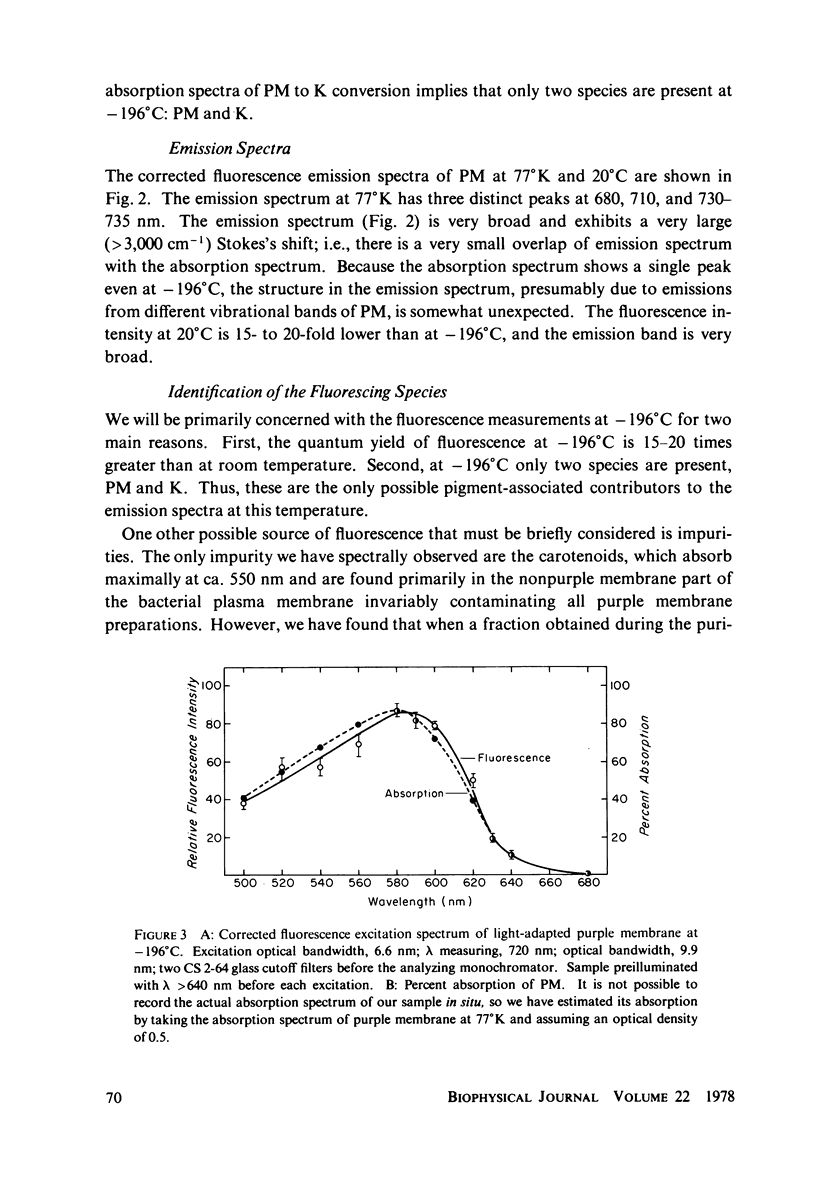
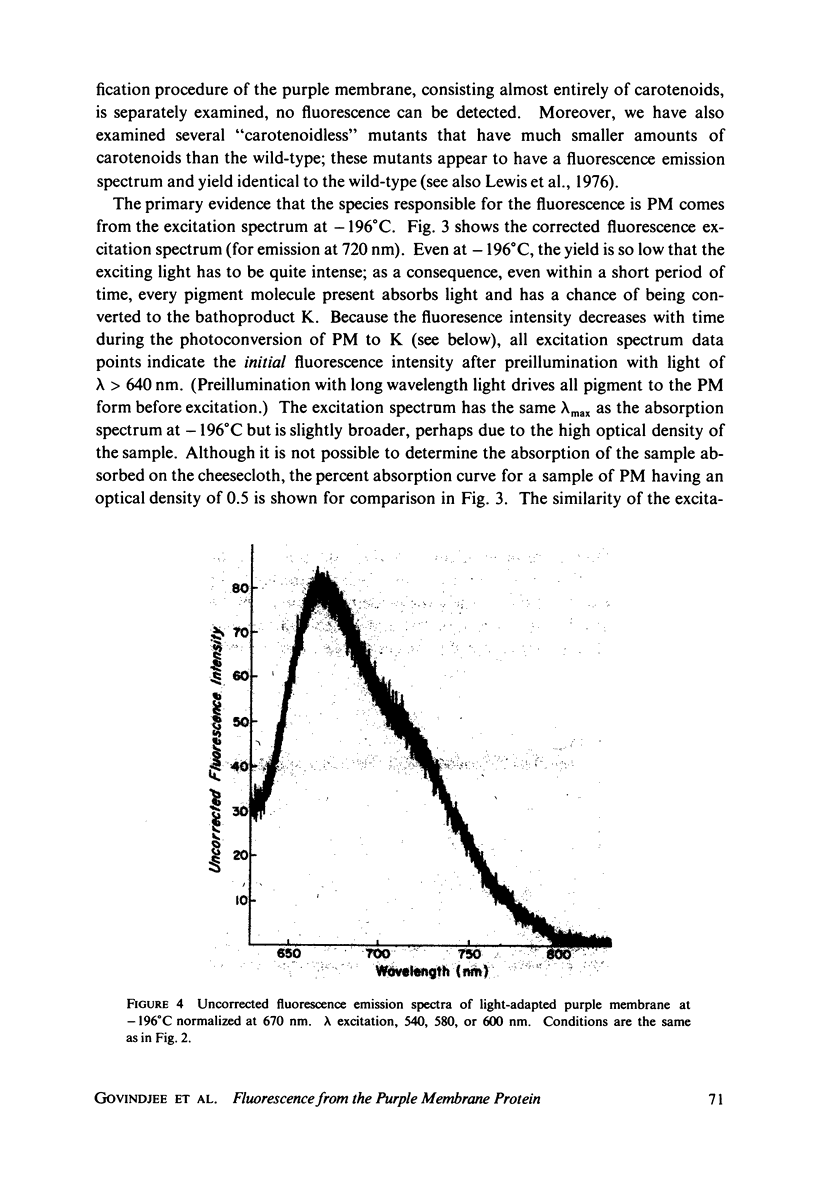
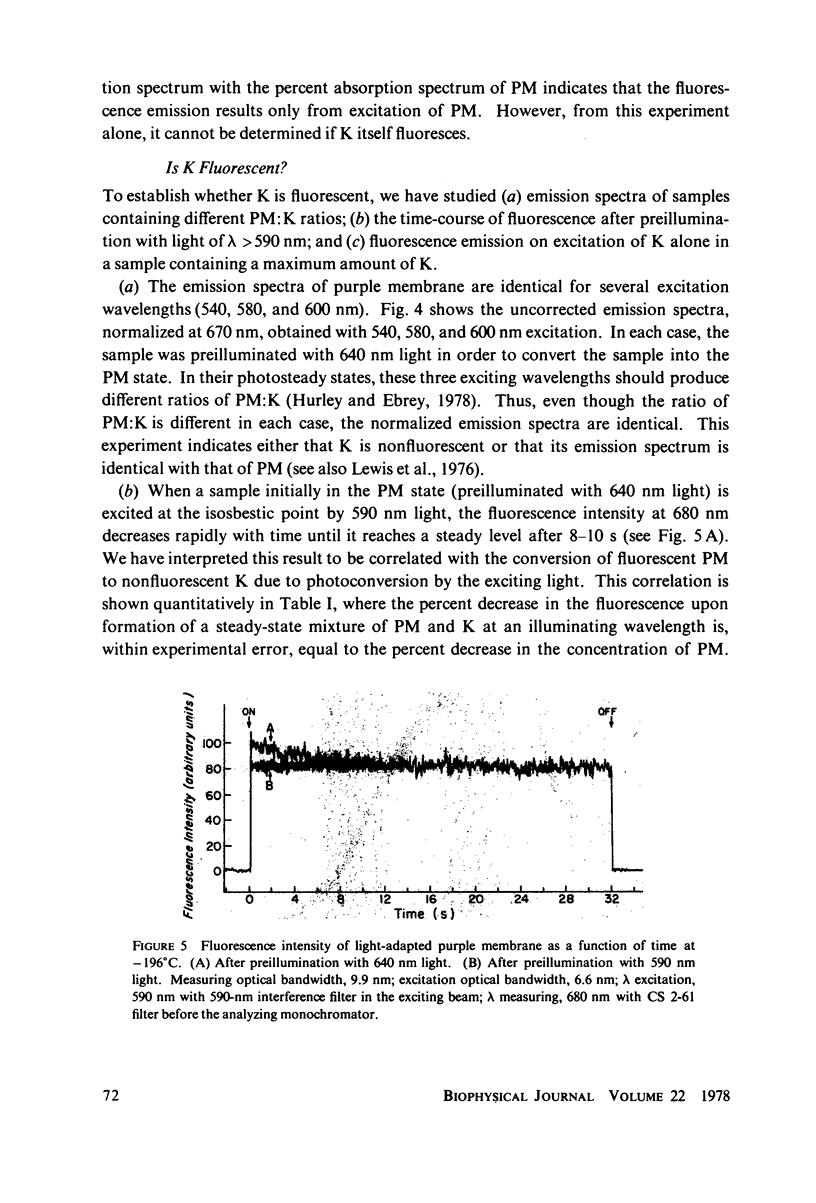
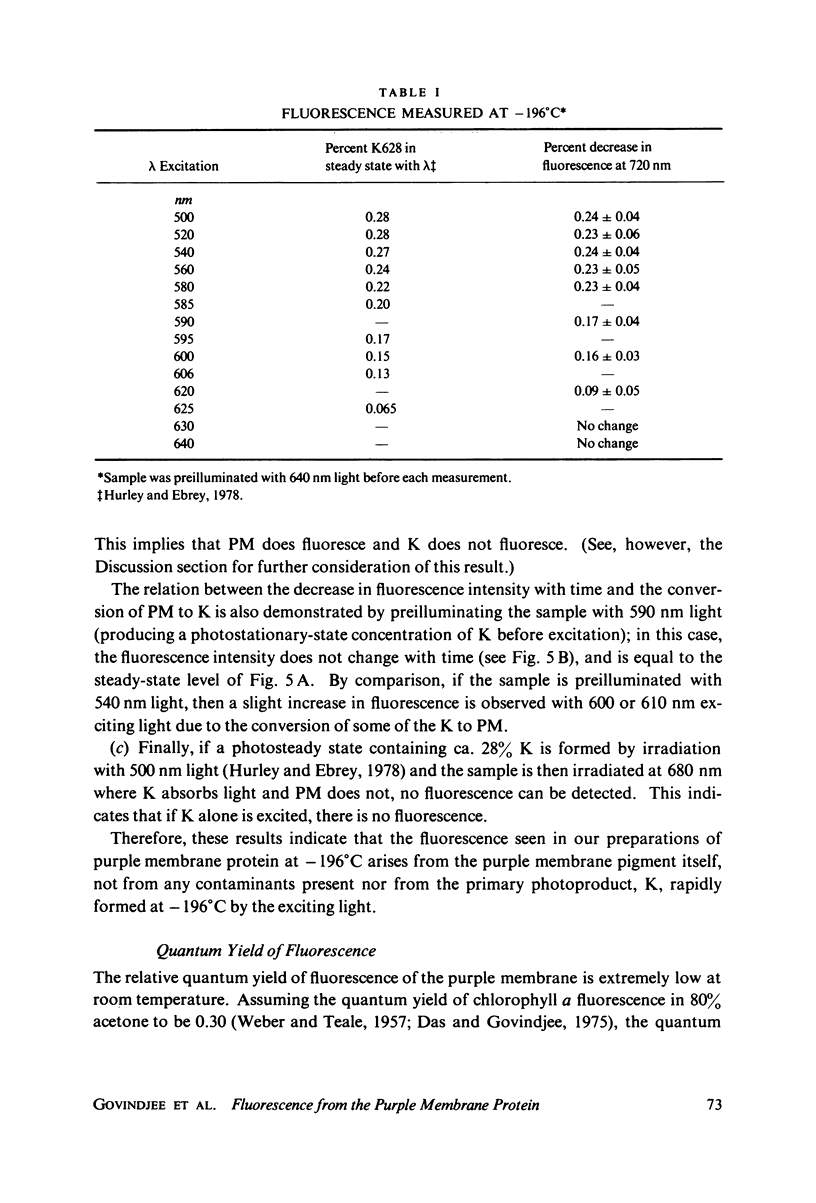
The fluorescence from the purple membrane protein (PM) of Halobacterium halobium and its relation to the primary photochemical events have been studied. The emission spectrum at 77 degrees K has structure, with peaks at 680, 710-715, and 730-735 nm. The excitation spectrum shows a single peak centered at 580 nm. This and a comparison of the fluorescence intensity at 77 degrees K under a variety of conditions with the amounts of the bathoproduct (or K, the only photoproduct seen at this temperature) formed suggest that the source of the fluorescence is the purple membrane itself, not the photoproduct. From the difference in several of their properties, we suggest that the fluorescing state of the pigment is different from the excited state which leads to photoconversion.
Full text
PDF


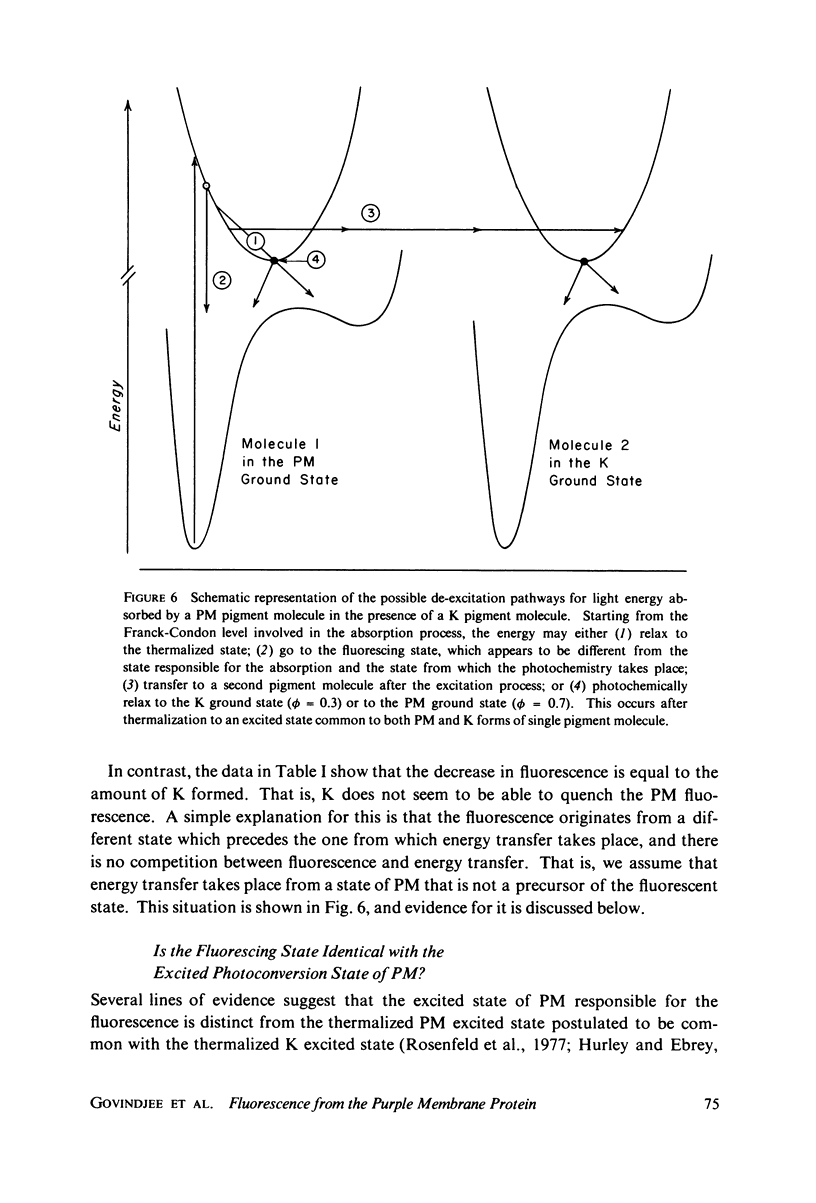


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alfano R. R., Govindjee R., Becher B., Ebrey T. G. Picosecond kinetics of the fluorescence from the chromophore of the purple membrane protein of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1976 May;16(5):541–545. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85709-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B. M., Cassim J. Y. Improved isolation procedures for the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Prep Biochem. 1975;5(2):161–178. doi: 10.1080/00327487508061568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Becher B., Ebrey T. G. The quantum efficiency for the photochemical conversion of the purple membrane protein. Biophys J. 1977 Feb;17(2):185–191. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85636-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt C. R., Kalisky O., Rosenfeld T., Ottolenghi M. The quantum efficiency of the bacteriorhodopsin photocycle. Biophys J. 1977 Feb;17(2):179–183. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85635-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch M. D., Marcus M. A., Lewis A., Mahr H., Frigo N. A method for measuring picosecond phenomena in photolabile species: the emission lifetime of bacteriorhodopsin. Biophys J. 1976 Dec;16(12):1399–1409. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85783-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Ebrey T. G. Energy transfer in the purple membrane of Halobacterium halobium. Biophys J. 1978 Apr;22(1):49–66. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85470-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hurley J. B., Ebrey T. G., Honig B., Ottolenghi M. Temperature and wavelength effects on the photochemistry of rhodopsin, isorhodopsin, bacteriorhodopsin and their photoproducts. Nature. 1977 Dec 8;270(5637):540–542. doi: 10.1038/270540a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufmann K. J., Rentzepis P. M., Stoeckenius W., Lewis A. Primary photochemical processes in bacteriorhodopsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1109–1115. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90310-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A., Spoonhower J. P., Perreault G. J. Observation of light emission from a rhodopsin. Nature. 1976 Apr 22;260(5553):675–678. doi: 10.1038/260675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozier R. H., Bogomolni R. A., Stoeckenius W. Bacteriorhodopsin: a light-driven proton pump in Halobacterium Halobium. Biophys J. 1975 Sep;15(9):955–962. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85875-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesterhelt D., Stoeckenius W. Functions of a new photoreceptor membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sineshchekov V. A., Litvin F. F. Liuminestsentsiia bakteriorodopsina purpurnykh membran iz kletok Halobacterium halobium. Biofizika. 1976 Mar-Apr;21(2):313–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


