Abstract
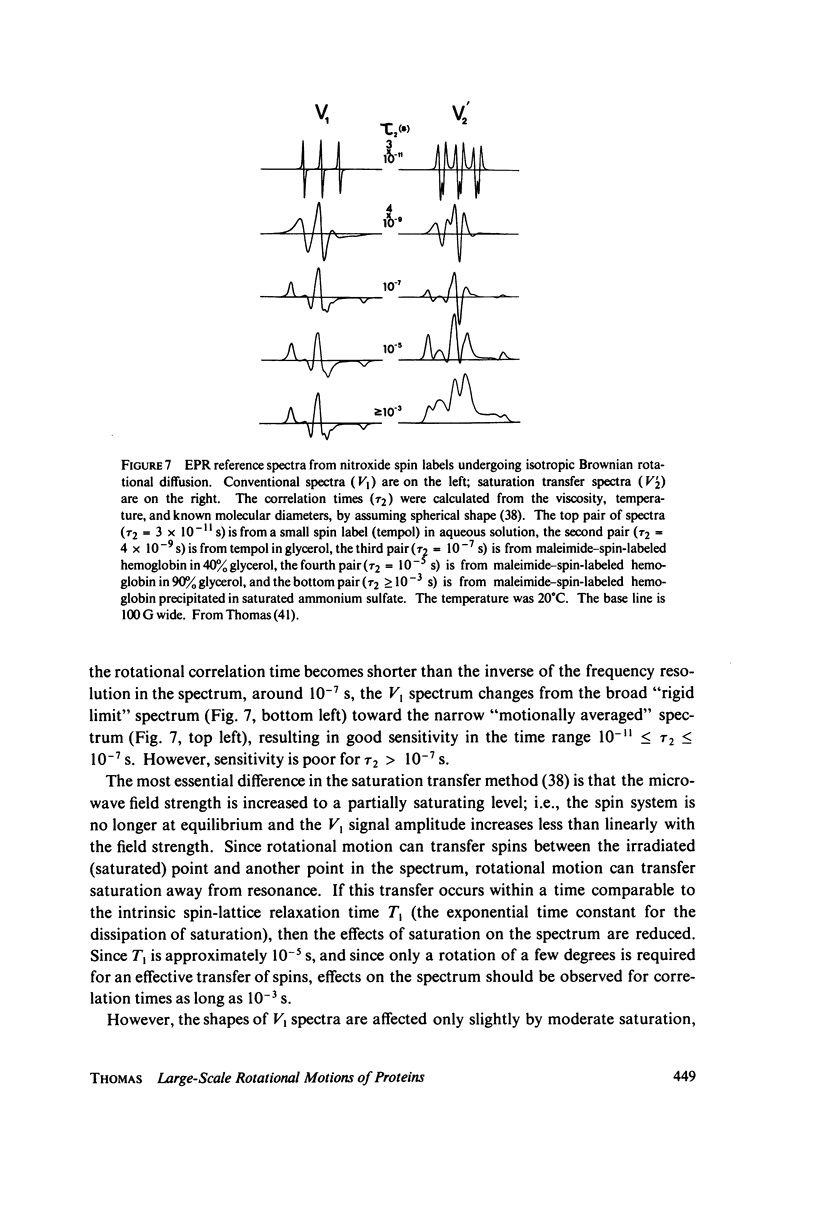
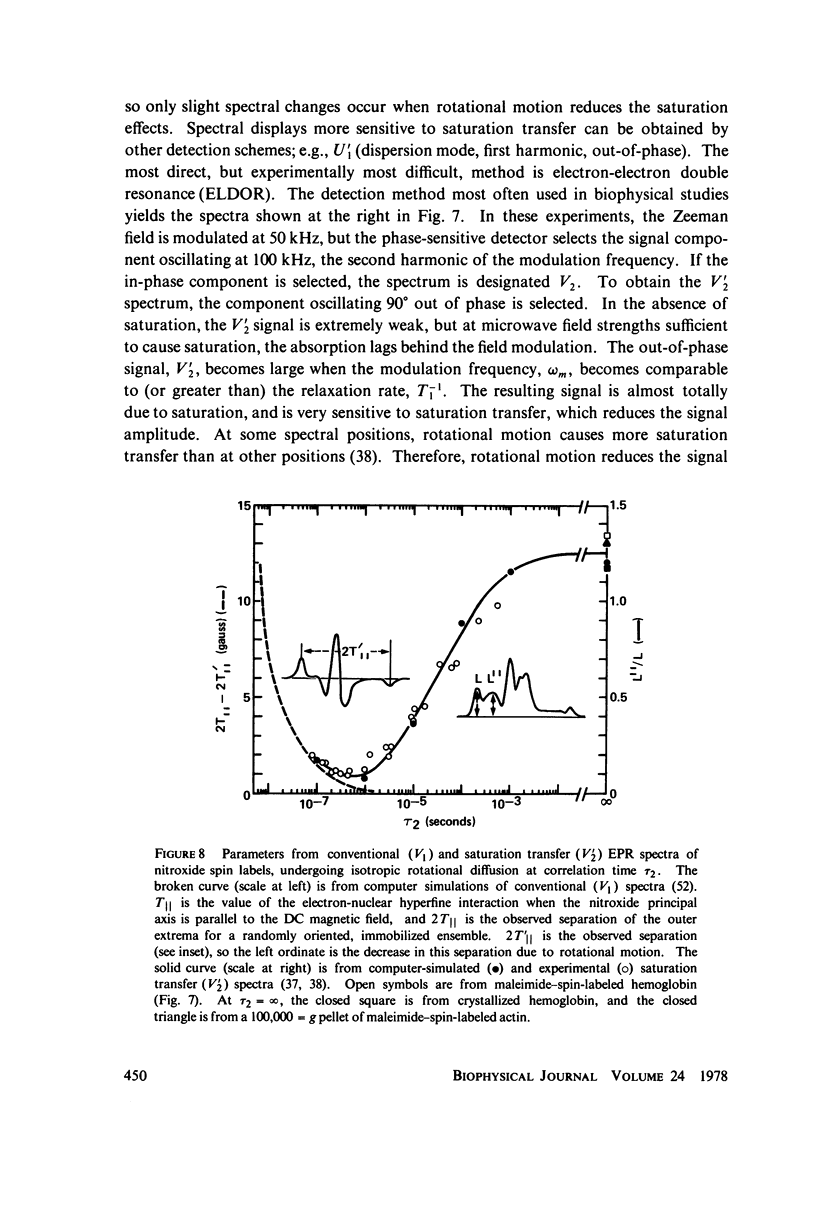
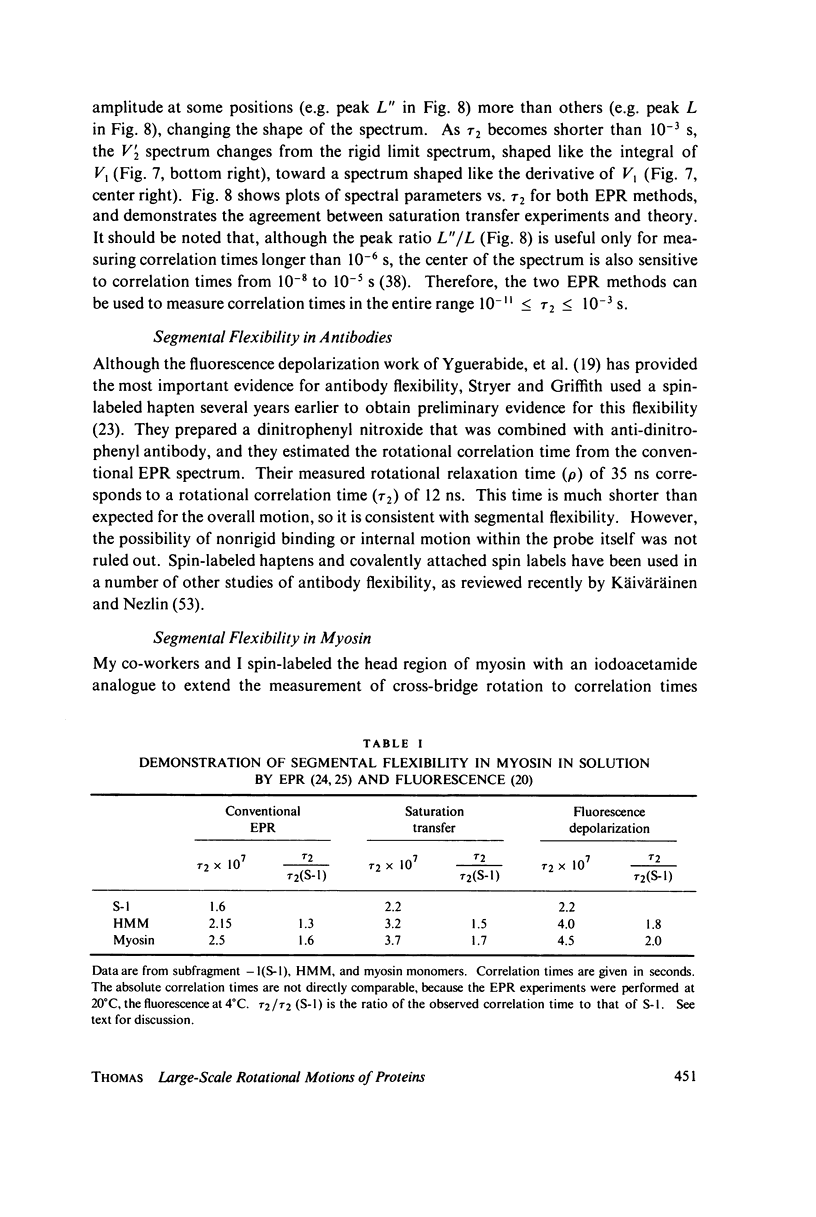
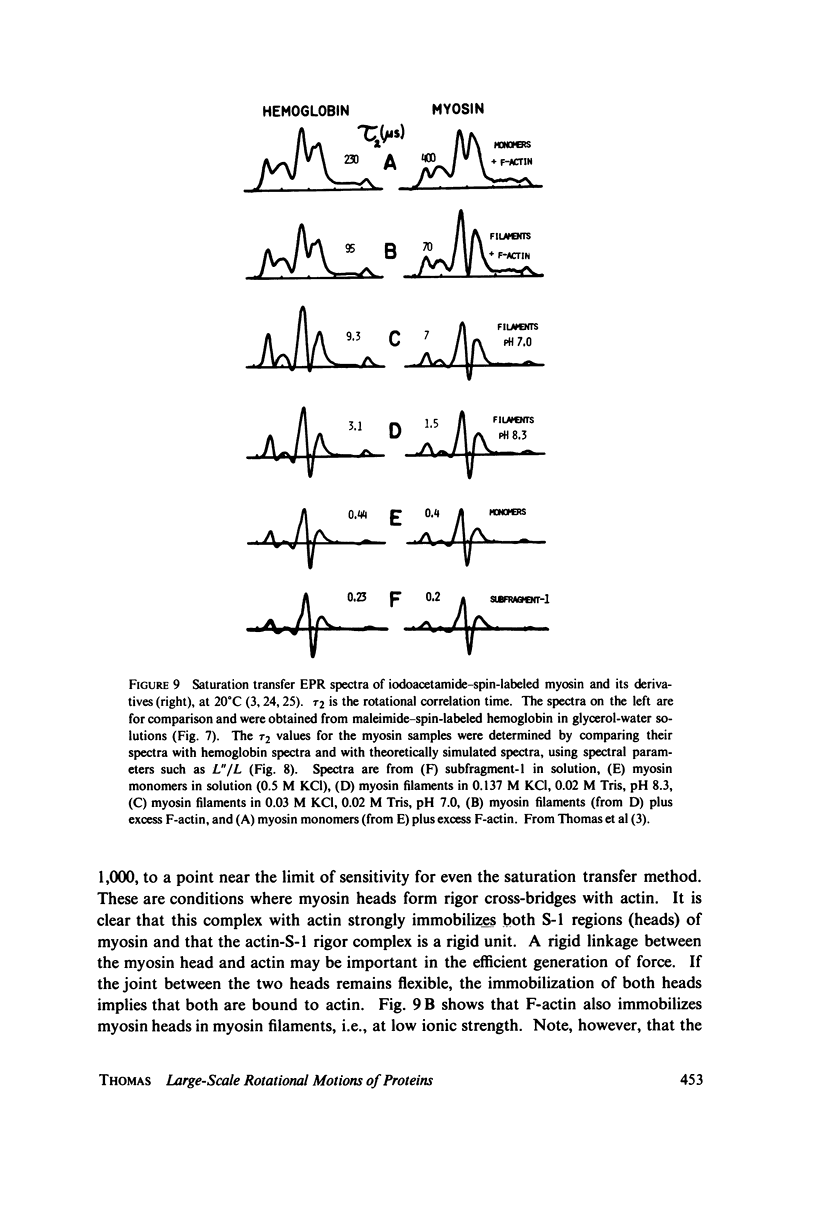
Direct spectroscopic measurements of rotational motions of proteins and large protein segments are crucial to understanding the molecular dynamics of protein function. Fluorescent probes and spin labels attached to proteins have proved to be powerful tools in the study of large-scale protein motions. Fluorescence depolarization and conventional electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) are applicable to the study of rotational motions in the nanosecond-to-microsecond time range, and have been used to demonstrate segmental flexibility in an antibody and in myosin. Very slow rotational motions, occurring in the microsecond-to-millisecond time range, are particularly important in supramolecular assemblies, where protein motions are restricted by association with other molecules. Saturation transfer spectroscopy (ST-EPR), a recently developed electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) technique that permits the detection of rotational correlation times as long as 1 ms, has been used to detect large-scale rotational motions of spin-labeled proteins in muscle filaments and in membranes, providing valuable insights into energy transduction mechanisms in these assemblies.
Full text
PDF







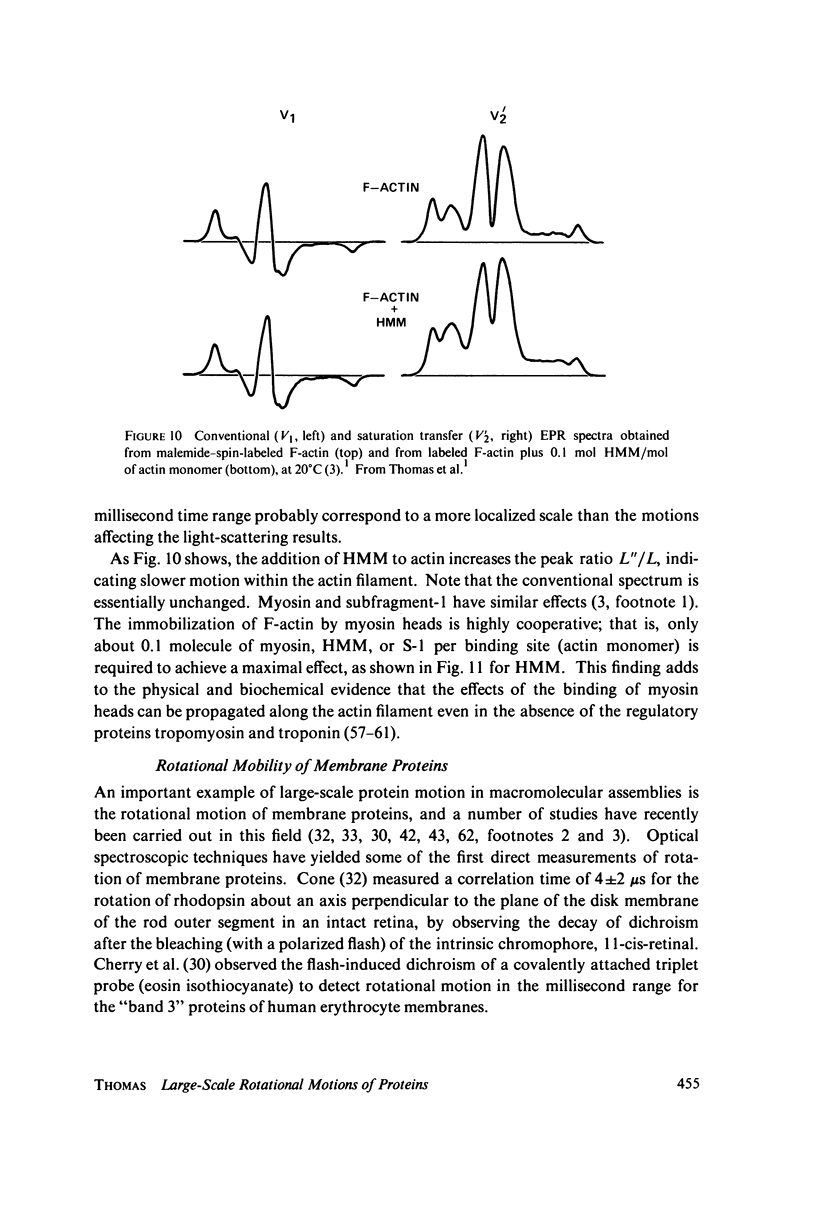
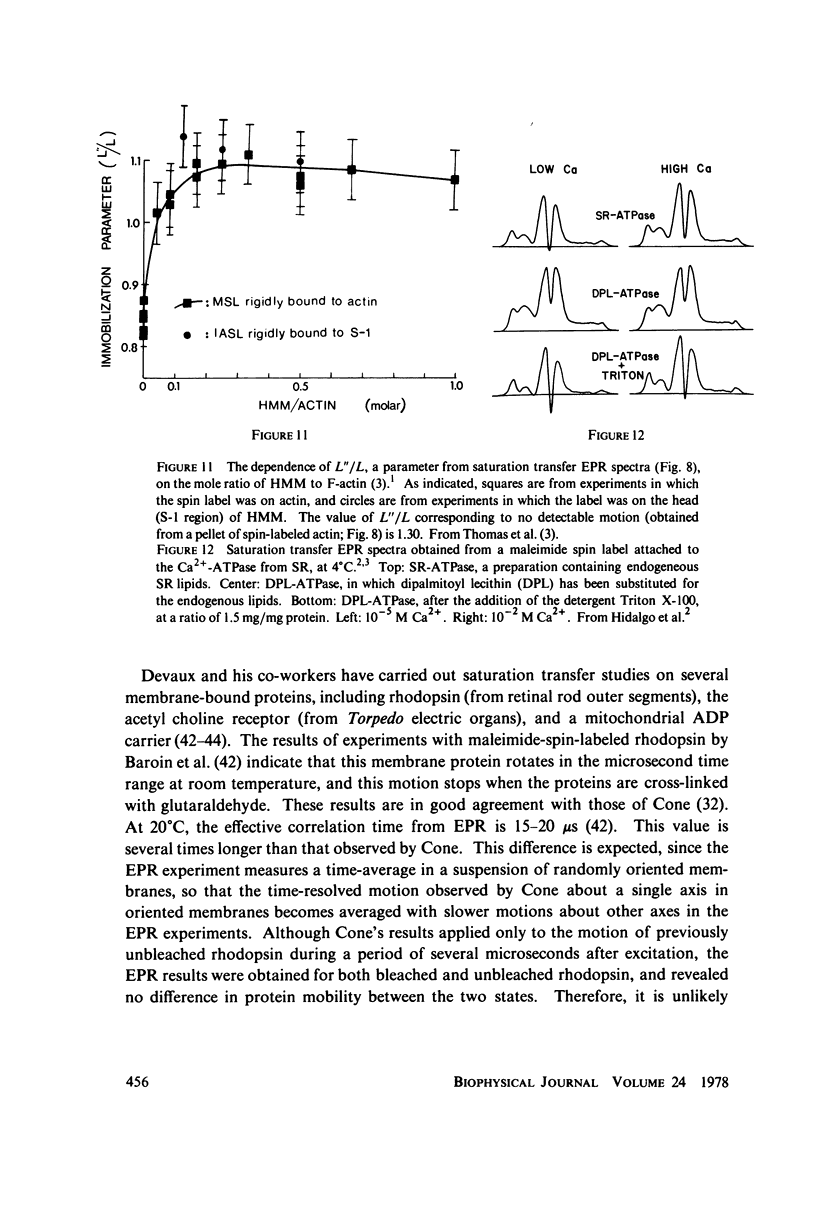






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baroin A., Thomas D. D., Osborne B., Devaux P. F. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance on membrane-bound proteins. I-Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):442–447. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91274-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belford G. G., Belford R. L., Weber G. Dynamics of fluorescence polarization in macromolecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1392–1393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley R. W., Seidel J. C., Gergely J. The stoichiometry of the reaction of the spin labeling of F-actin and the effect of orientation of spin-labeled F-actin filaments. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1971 Oct;146(2):597–602. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(71)90167-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson F. D. The application of intensity fluctuation spectroscopy to molecular biology. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1975;4(00):243–264. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.04.060175.001331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan L. M., Cathou R. E. The role of the inter-heavy chain disulfide bond in modulating the flexibility of immunoglobulin G antibody. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 5;112(4):653–656. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80170-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Bürkli A., Busslinger M., Schneider G., Parish G. R. Rotational diffusion of band 3 proteins in the human erythrocyte membrane. Nature. 1976 Sep 30;263(5576):389–393. doi: 10.1038/263389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Cogoli A., Oppliger M., Schneider G., Semenza G. A spectroscopic technique for measuring slow rotational diffusion of macromolecules. 1: Preparation and properties of a triplet probe. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3653–3656. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry R. J., Schneider G. A spectroscopic technique for measuring slow rotational diffusion of macromolecules. 2: Determination of rotational correlation times of proteins in solution. Biochemistry. 1976 Aug 24;15(17):3657–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00662a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cone R. A. Rotational diffusion of rhodopsin in the visual receptor membrane. Nat New Biol. 1972 Mar 15;236(63):39–43. doi: 10.1038/newbio236039a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duke J., Takashi R., Ue K., Morales M. F. Reciprocal reactivities of specific thiols when actin binds to myosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):302–306. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dutton A., Rees E. D., Singer S. J. An experiment eliminating the rotating carrier mechanism for the active transport of Ca ion in sarcoplasmic reticulum membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 May;73(5):1532–1536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.5.1532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg M., Rigler R. Fluorescence correlation spectroscopy applied to rotational diffusion of macromolecules. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Feb;9(1):69–81. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000216x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujime S., Ishiwata S. Dynamic study of F-actin by quasielastic scattering of laser light. J Mol Biol. 1971 Nov 28;62(1):251–265. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUXLEY A. F. Muscle structure and theories of contraction. Prog Biophys Biophys Chem. 1957;7:255–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemminga M. A., de Jager P. A., de Wit J. L. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy of spin labeled tobacco mosaic virus protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Dec 7;79(3):635–639. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91159-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo C., Ikemoto N., Gergely J. Role of phospholipids in the calcium-dependent ATPase of the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Enzymatic and ESR studies with phospholipid-replaced membranes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4224–4232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holowka D. A., Cathou R. E. Conformation of immunoglobulin M. 2. Nanosecond fluorescence depolarization analysis of segmental flexibility in anti-epsilon-l-dimethylamino-5-naphthalenesulfonyl-L-lysine anti-immunoglobulin from horse, pig, and shark. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 27;15(15):3379–3390. doi: 10.1021/bi00660a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S. Saturation-transfer spectroscopy. Methods Enzymol. 1978;49:480–511. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)49021-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde J. S., Thomas D. D. New EPR methods for the study of very slow motion: application to spin-labeled hemoglobin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Dec 31;222:680–692. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb15295.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinosita K., Jr, Kawato S., Ikegami A. A theory of fluorescence polarization decay in membranes. Biophys J. 1977 Dec;20(3):289–305. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85550-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirtley M. E., Koshland D. E., Jr Environmentally sensitive groups attached to proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:578–601. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26027-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunze U., Junge W. Ellipticity of cytochrome alpha3 and rotational mobility of cytochrome c-oxidase in the cristae membrane of mitochondria. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 15;80(2):429–434. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80492-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käiväräinen A. I., Nezlin R. S. Spin-label approach to conformational properties of immunoglobulins. Immunochemistry. 1976 Dec;13(12):1001–1008. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(76)90272-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavalette D., Amand B., Pochon F. Rotational relaxation of 70S ribosomes by a depolarization method using triplet probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Apr;74(4):1407–1411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.4.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linden C. D., Wright K. L., McConnell H. M., Fox C. F. Lateral phase separations in membrane lipids and the mechanism of sugar transport in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2271–2275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J., Reed G. H., Weber A. Conformational change and cooperativity in actin filaments free of tropomyosin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3412–3415. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
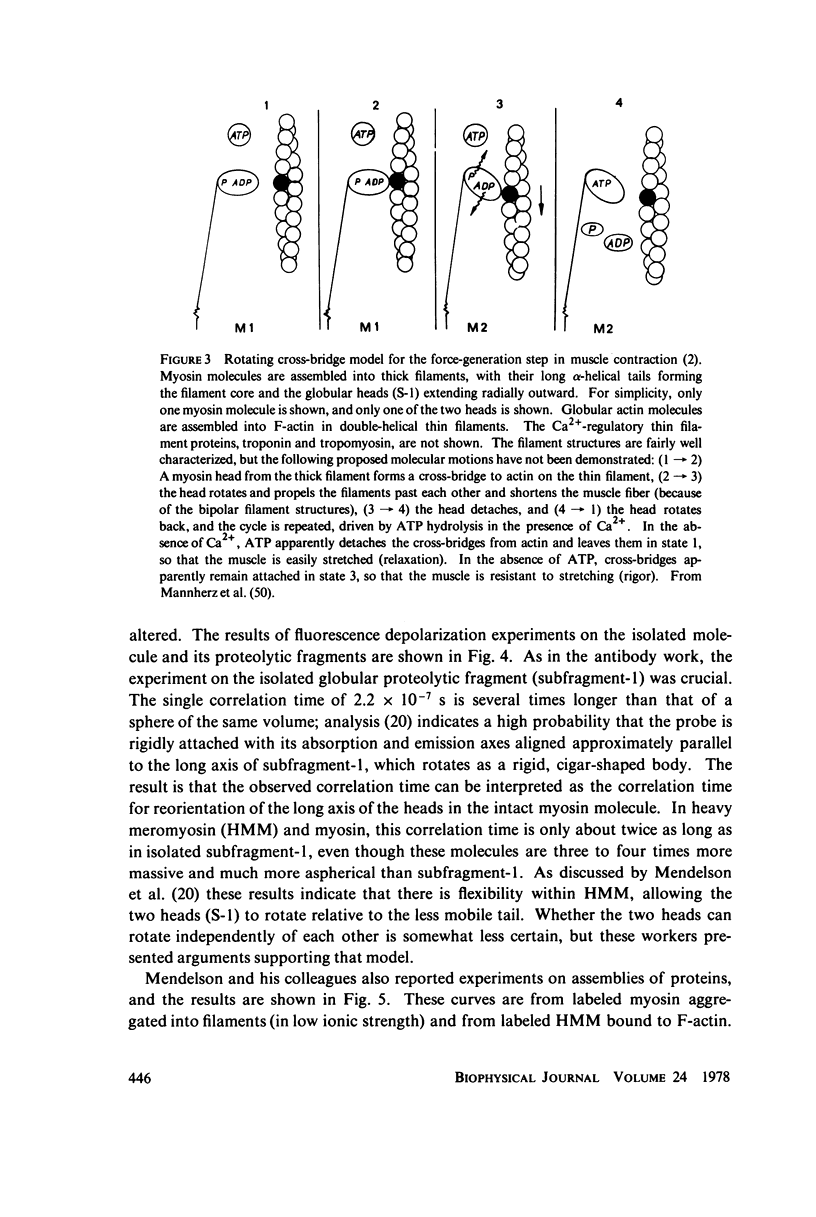
- Mannherz H. G., Leigh J. B., Holmes K. C., Rosenbaum G. Identification of the transitory complex myosin-ATP by the use of , -methylene-ATP. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 21;241(112):226–229. doi: 10.1038/newbio241226a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martonosi A., Fortier F. The effect of anti-ATPase antibodies upon the Ca++ transport of sarcoplasmic reticulum. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Sep 9;60(1):382–389. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(74)90216-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
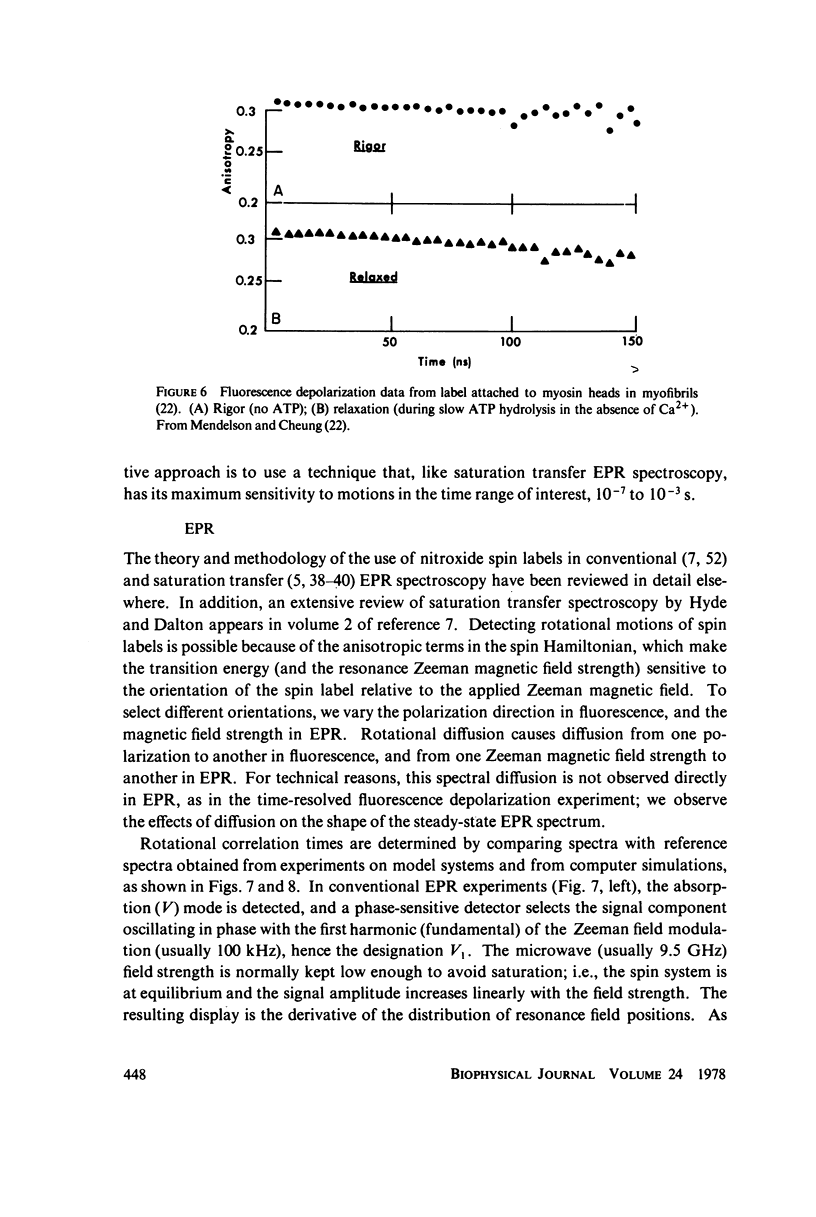
- Mendelson R. A., Cheung P. Muscle crossbridges: absence of direct effect of calcium on movement away from the thick filaments. Science. 1976 Oct 8;194(4261):190–192. doi: 10.1126/science.194.4261.190-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
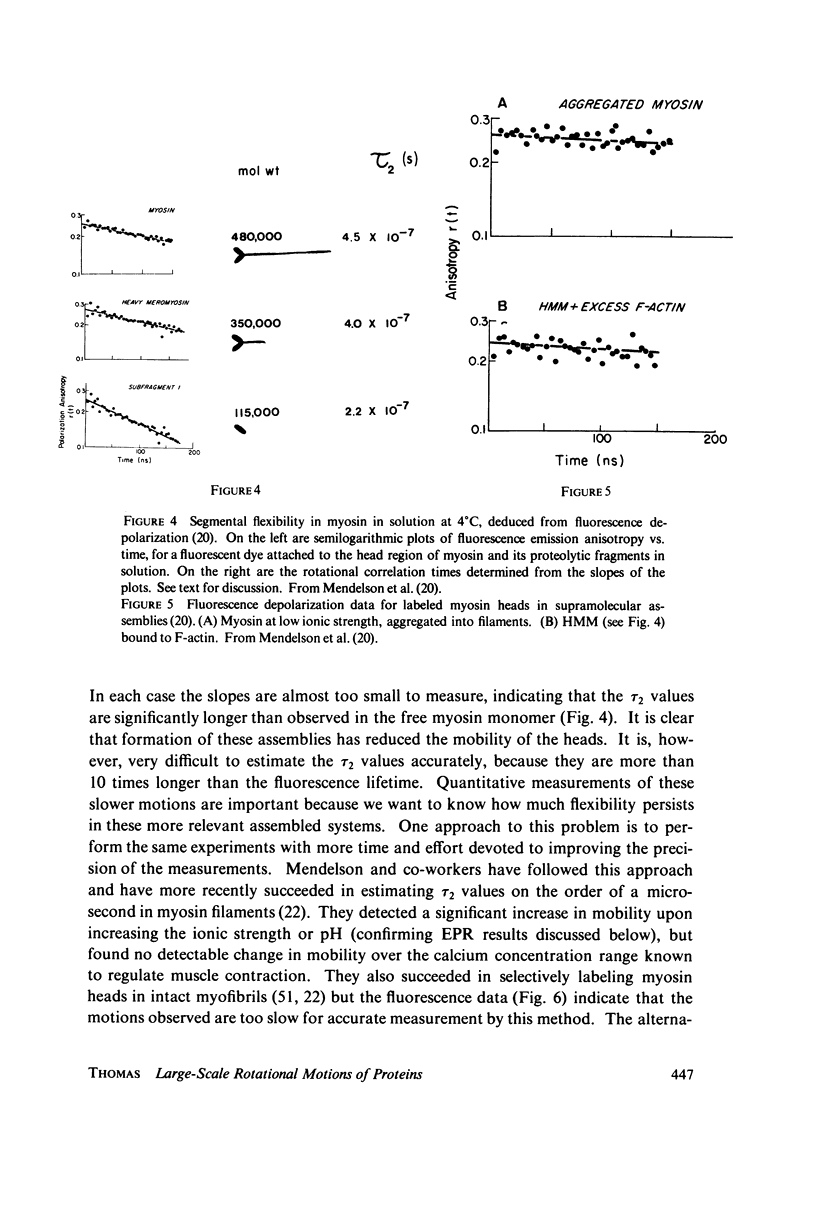
- Mendelson R. A., Morales M. F., Botts J. Segmental flexibility of the S-1 moiety of myosin. Biochemistry. 1973 Jun 5;12(12):2250–2255. doi: 10.1021/bi00736a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelson R., Putnam S., Morales M. Time-dependent fluorescence depolarization and lifetime studies of myosin subfragment-one in the presence of nucleotide and actin. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(2):162–168. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa F., Maeda Y., Fujime S., Ishiwata S., Yanagida T., Taniguchi M. Dynamic characteristics of F-actin and thin filaments in vivo and in vitro. J Mechanochem Cell Motil. 1977 Mar;4(1):63–78. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousselet A., Devaux P. F. Saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance on membrane bound proteins. II-Absence of rotational diffusion of the cholinergic receptor protein in Torpedo marmorata membrane fragments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):448–454. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91275-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schurr J. M. Relaxation of rotational and internal modes of macromolecules determined by dynamic scattering. Q Rev Biophys. 1976 Feb;9(1):109–129. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strambini G. B., Galley W. C. Detection of slow rotational motions of proteins by steady-state phosphorescence anisotropy. Nature. 1976 Apr 8;260(5551):554–556. doi: 10.1038/260554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Griffith O. H. A spin-labeled hapten. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Dec;54(6):1785–1791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.6.1785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tawada K. Physicochemical studies of F-actin-heavy meromyosin solutions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Feb 25;172(2):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(69)90073-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Gergely J., Hyde J. S. The quantitative measurement of rotational motion of the subfragment-1 region of myosin by saturation transfer epr spectroscopy. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(4):376–390. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Seidel J. C., Hyde J. S., Gergely J. Motion of subfragment-1 in myosin and its supramolecular complexes: saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1729–1733. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonomura Y., Morales M. F. Change in state of spin labels bound to sarcoplasmic reticulum with change in enzymic state, as deduced from ascorbate-quenching studies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3687–3691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weltman J. K., Szaro R. P., Frackelton A. R., Jr, Dowben R. M., Bunting J. R., Cathou B. E. N-(3-pyrene)maleimide: a long lifetime fluorescent sulfhydryl reagent. J Biol Chem. 1973 May 10;248(9):3173–3177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson L. S., Perkins R. C., Jr, Roelofs R., Swift L., Dalton L. R., Park J. H. Erythrocyte membrane abnormalities in Duchenne muscular dystrophy monitored by saturation transfer electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Feb;75(2):838–841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.2.838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
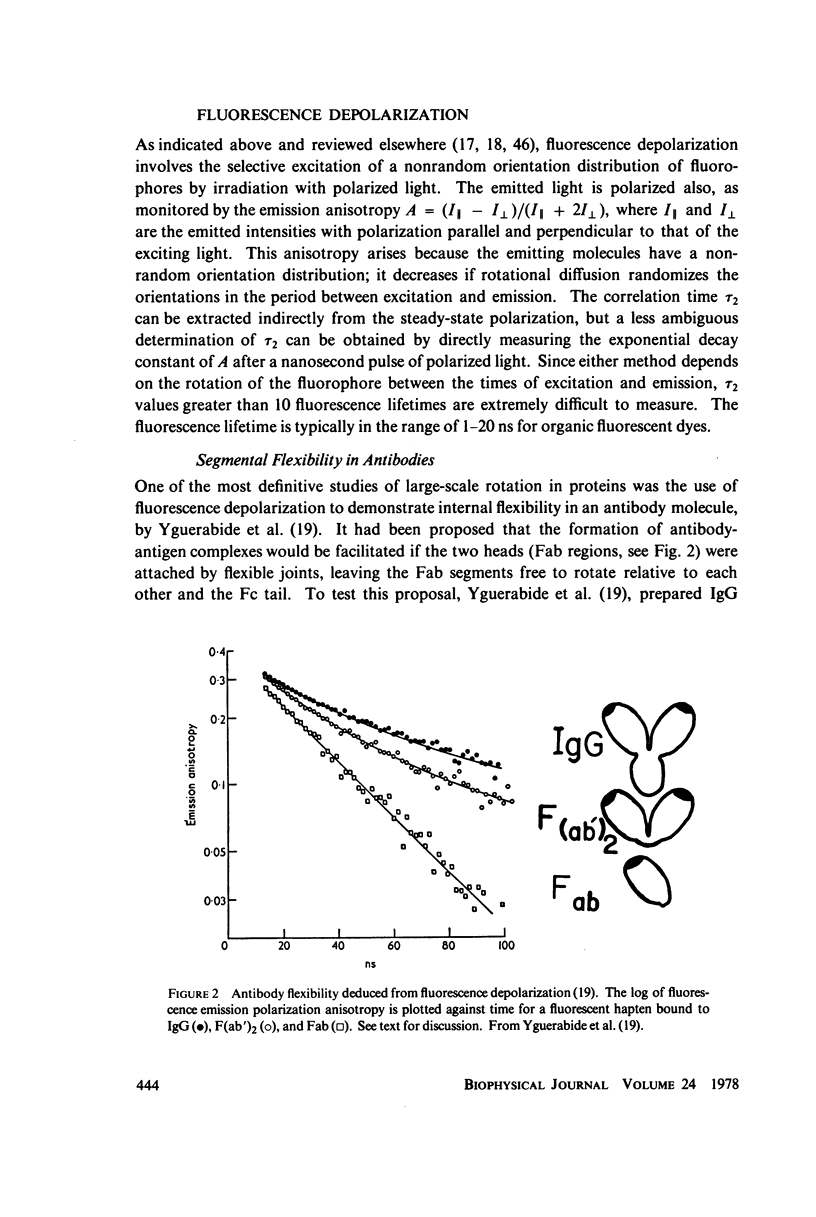
- Yguerabide J., Epstein H. F., Stryer L. Segmental flexibility in an antibody molecule. J Mol Biol. 1970 Aug;51(3):573–590. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yguerabide J. Nanosecond fluorescence spectroscopy of macromolecules. Methods Enzymol. 1972;26:498–578. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(72)26026-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


