Abstract
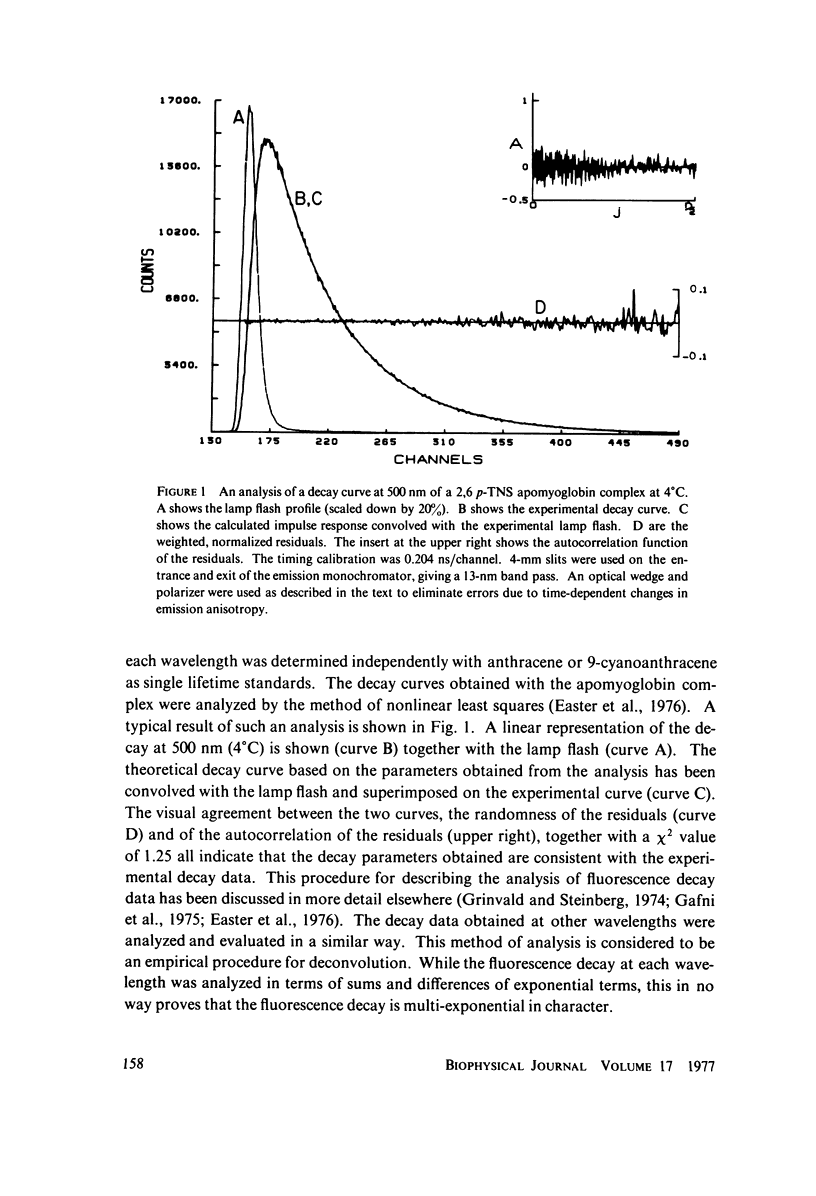
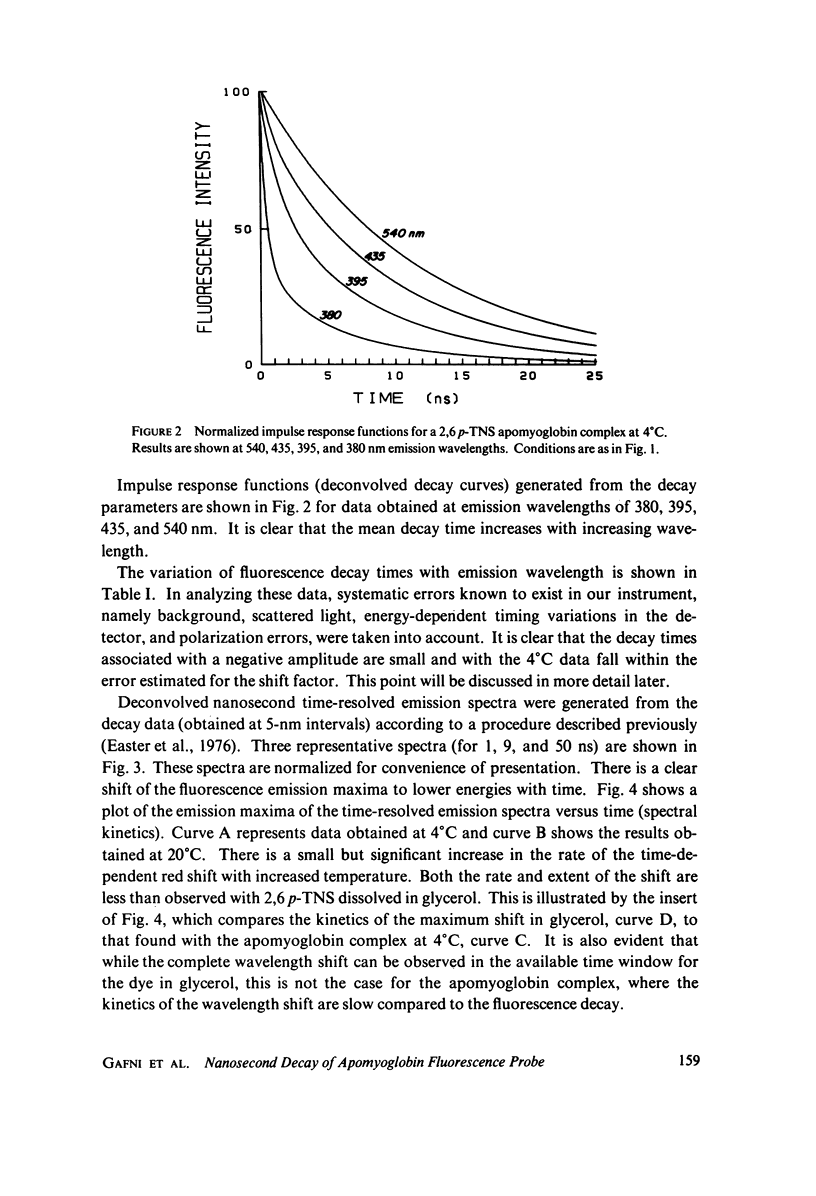
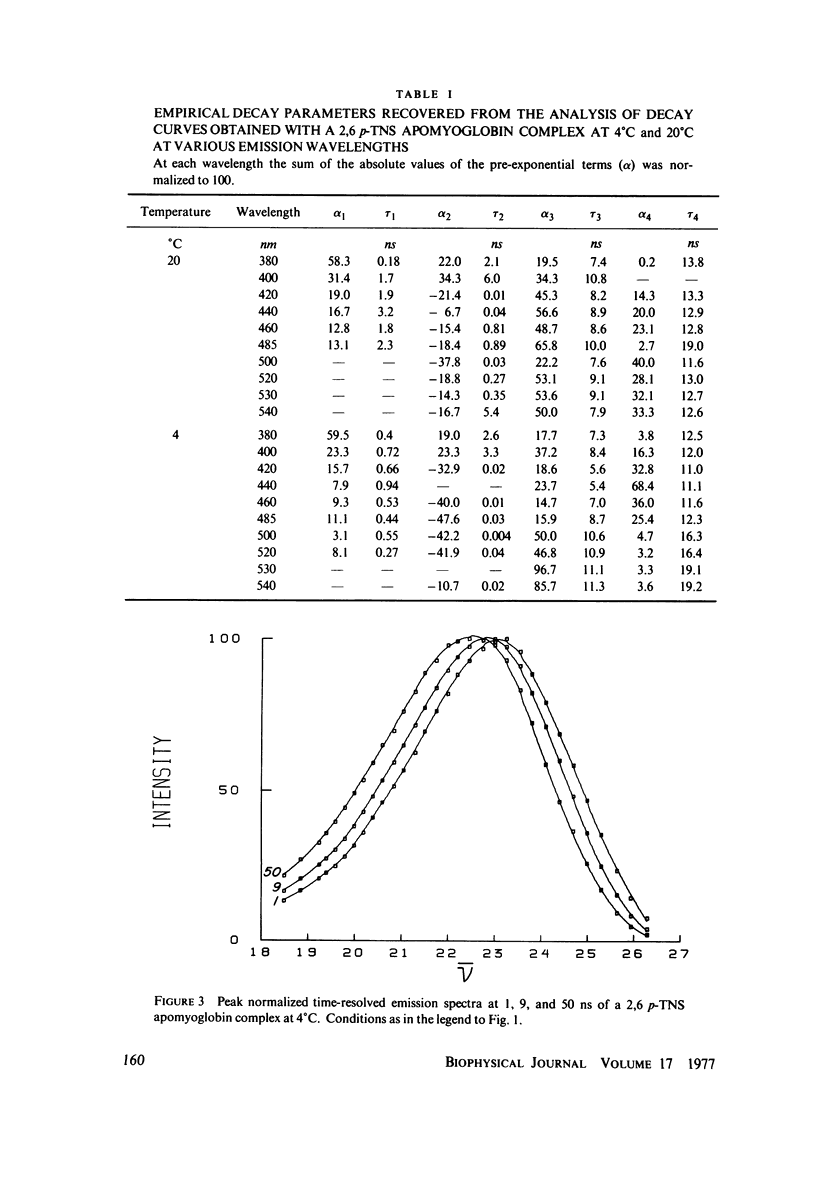
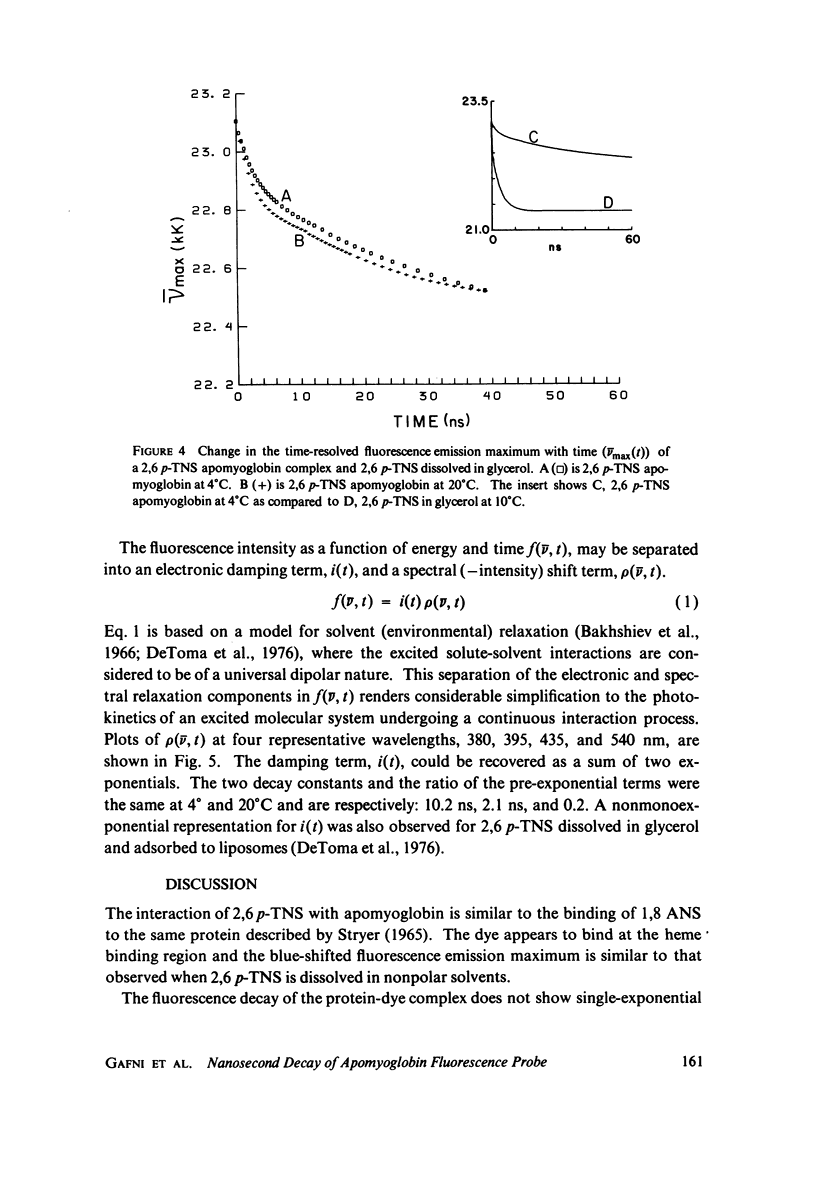
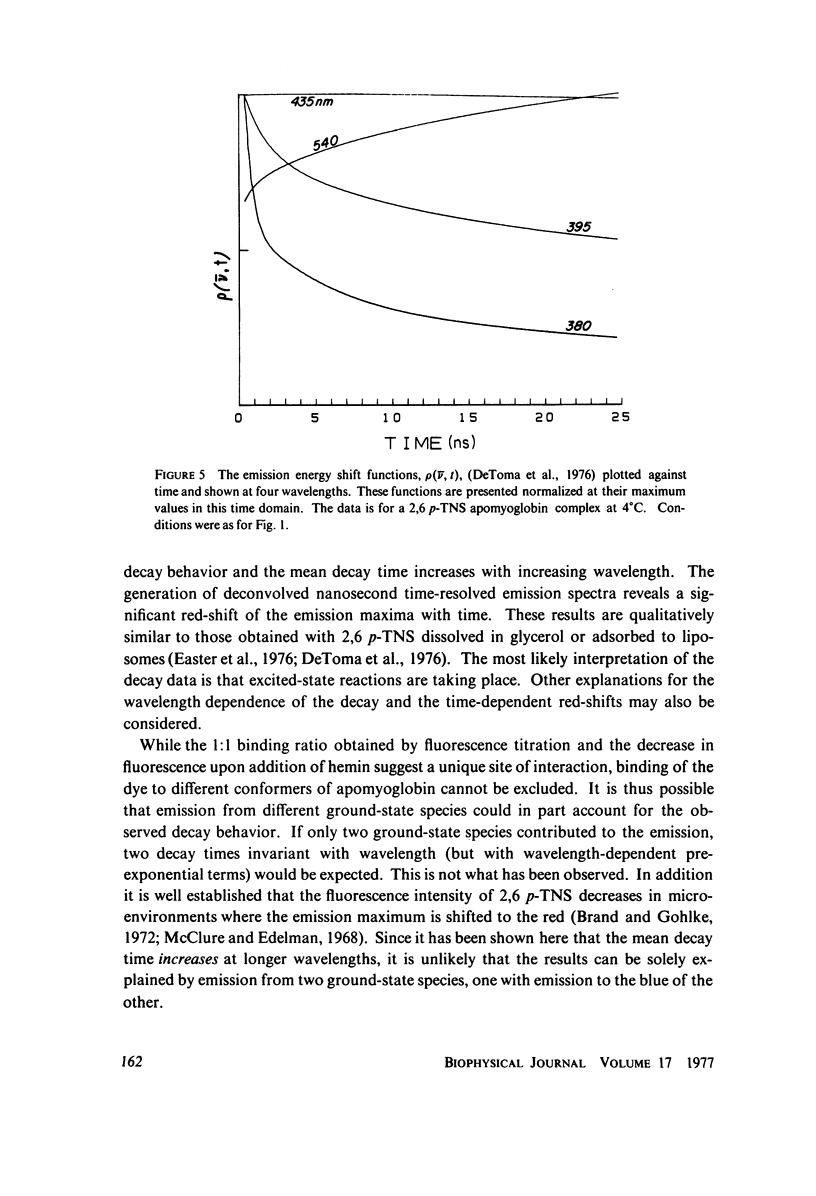
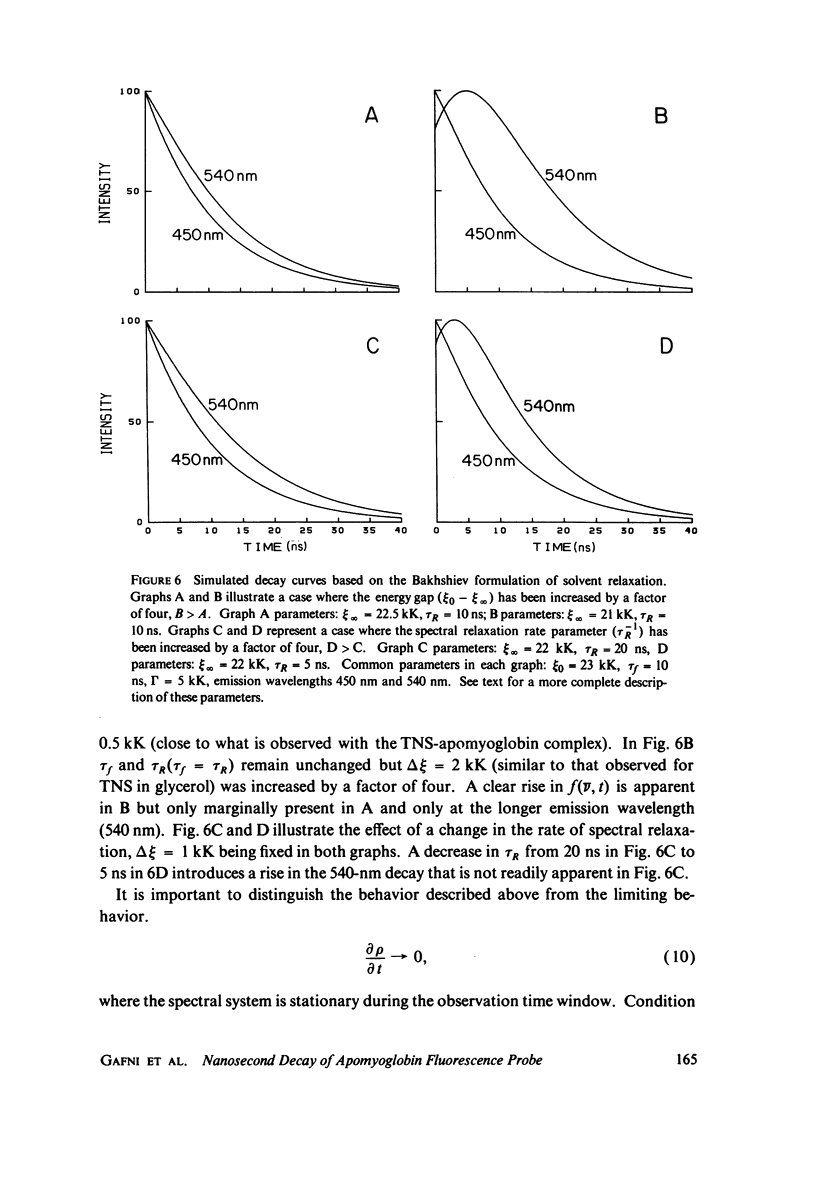
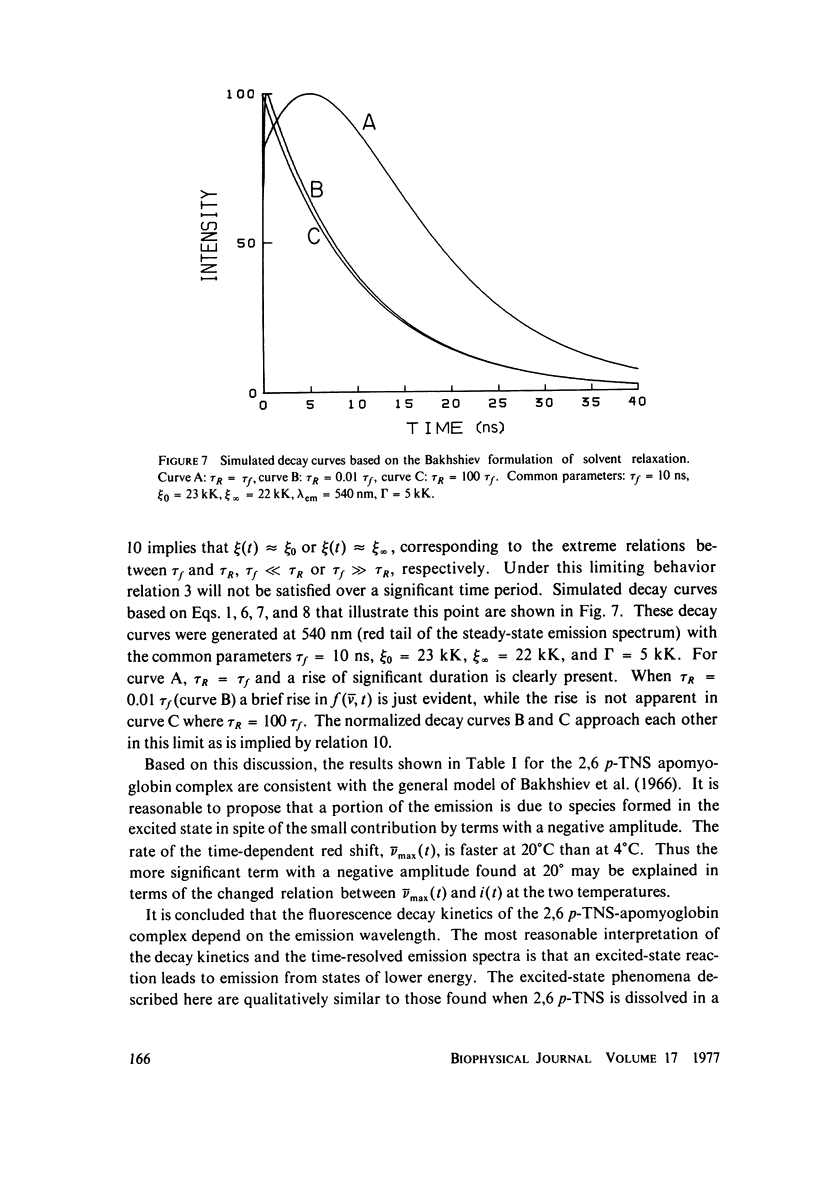
Excited state interactions of N-(p-tolyl)-2-aminonaphthalene-6-sulfonate (2, 6 p-TNS) bound to apomyoglobin were studied by nanosecond time-resolved emission spectroscopy. A dynamic interaction of the excited dye molecule with its binding site, associated with a significant change in the emission energy with time, was observed. The decay kinetics were found to be complex and consistent with the kinetic model for solvent relaxation as proposed by Bakhshiev et al. (Opt. Spectrosc. 21:307. 1966). The behavior of 2, 6 p-TNS bound to apomyoglobin was found to be qualitatively similar to that of the dye dissolved in a viscous solvent such as glycerol or adsorbed to egg lecithin vesicles. The detailed information obtained by following the changes in emission spectra of fluorescent probes on the nanosecond time scale leads to a better understanding of their interactions with biological systems.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. R., Brunori M., Weber G. Fluorescence studies of Aplysia and sperm whale apomyoglobins. Biochemistry. 1970 Nov 24;9(24):4723–4729. doi: 10.1021/bi00826a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand L., Gohlke J. R. Fluorescence probes for structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:843–868. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.004211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand L., Gohlke J. R., Rao D. S. Evidence for binding of rose bengal and anilinonaphthalenesulfonates at the active site regions of liver alcohol dehydrogenase. Biochemistry. 1967 Nov;6(11):3510–3518. doi: 10.1021/bi00863a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Toma R. P., Easter J. H., Brand L. Dynamic interactions of fluorescence probes with the solvent environment. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Aug 4;98(16):5001–5007. doi: 10.1021/ja00432a048. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gafni A., Modlin R. L., Brand L. Analysis of fluorescence decay curves by means of the Laplace transformation. Biophys J. 1975 Mar;15(3):263–280. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85817-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene F. C. Neutral and Cationic Sulfonamido Derivatives of the Fluorescent Probe 2-p-Toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate. Properties and Mechanistic implications. Biochemistry. 1975 Feb 25;14(4):747–753. doi: 10.1021/bi00675a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinvald A., Steinberg I. Z. On the analysis of fluorescence decay kinetics by the method of least-squares. Anal Biochem. 1974 Jun;59(2):583–598. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90312-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClure W. O., Edelman G. M. Fluorescent probes for conformational states of proteins. I. Mechanism of fluorescence of 2-p-toluidinylnaphthalene-6-sulfonate, a hydrophobic probe. Biochemistry. 1966 Jun;5(6):1908–1919. doi: 10.1021/bi00870a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penzer G. R. 1-anilinonaphthalene-8-sulphonate. The dependence of emission spectra on molecular conformation studied by fluorescence and proton-magnetic resonance. Eur J Biochem. 1972 Feb 15;25(2):218–228. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01687.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L. The interaction of a naphthalene dye with apomyoglobin and apohemoglobin. A fluorescent probe of non-polar binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):482–495. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80111-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. C., Brand L. Quantitative estimation of protein binding site polarity. Fluorescence of N-arylaminonaphthalenesulfonates. Biochemistry. 1968 Oct;7(10):3381–3390. doi: 10.1021/bi00850a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


