Abstract
Ultraviolet irradiation of Escherichia coli cells with a low level of 5-bromouracil incorporated produces DNA double-strand breaks by single photochemical events, one such break per 100 single-strand breaks, the latter assayed in alkali-denatured DNA. About 2.5--4 double-strand breaks are produced per "lethal hit," compared with about 6 double-strand breaks per lethal hit induced by gamma rays. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that an unrepaired DNA double-strand break is a major lethal event in both cases. The increase in sensitivity to ultraviolet (measured by colony-forming ability) seems linear in the number of bromouracils incorporated (0--20% of the thymines), and the linear relationship is much the same for incorporation in one or in both strands of the DNA double helix.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beattie K. L. Breakage of parental DNA strands in Haemophilus influenzae by 313 nm radiation after replication in the presence of 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Biophys J. 1972 Nov;12(11):1573–1582. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(72)86183-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blair D. G., Sherratt D. J., Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Isolation of supercoiled colicinogenic factor E 1 DNA sensitive to ribonuclease and alkali. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Sep;69(9):2518–2522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.9.2518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonura T., Smith K. C. Enzymatic production of deoxyribonucleic acid double-strand breaks after ultraviolet irradiation of Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):511–517. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.511-517.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonura T., Smith K. C., Kaplan H. S. Enzymatic induction of DNA double-strand breaks in gamma-irradiated Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4265–4269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S. Unique double-stranded fragments of bacteriophage T5 DNA resulting from preferential shear-induced breakage at nicks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 May;71(5):2108–2112. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.5.2108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hotz G., Mauser R., Walser R. Infectious DNA from coliphage TI. 3. The occurrence of single-strand breaks in stored, thermally-treated, and U.V.-irradiated molecules. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(6):519–536. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550711. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F., Krasin F. Dependence of the sedimentation of high molecular weight DNA on centrifuge speed. Biophys Chem. 1976 Dec;6(1):23–29. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80058-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchinson F. The lesions produced by ultraviolet light in DNA containing 5-bromouracil. Q Rev Biophys. 1973 May;6(2):201–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krasin F., Hutchinson F. Repair of DNA double-strand breaks in Escherichia coli, which requires recA function and the presence of a duplicate genome. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 15;116(1):81–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90120-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
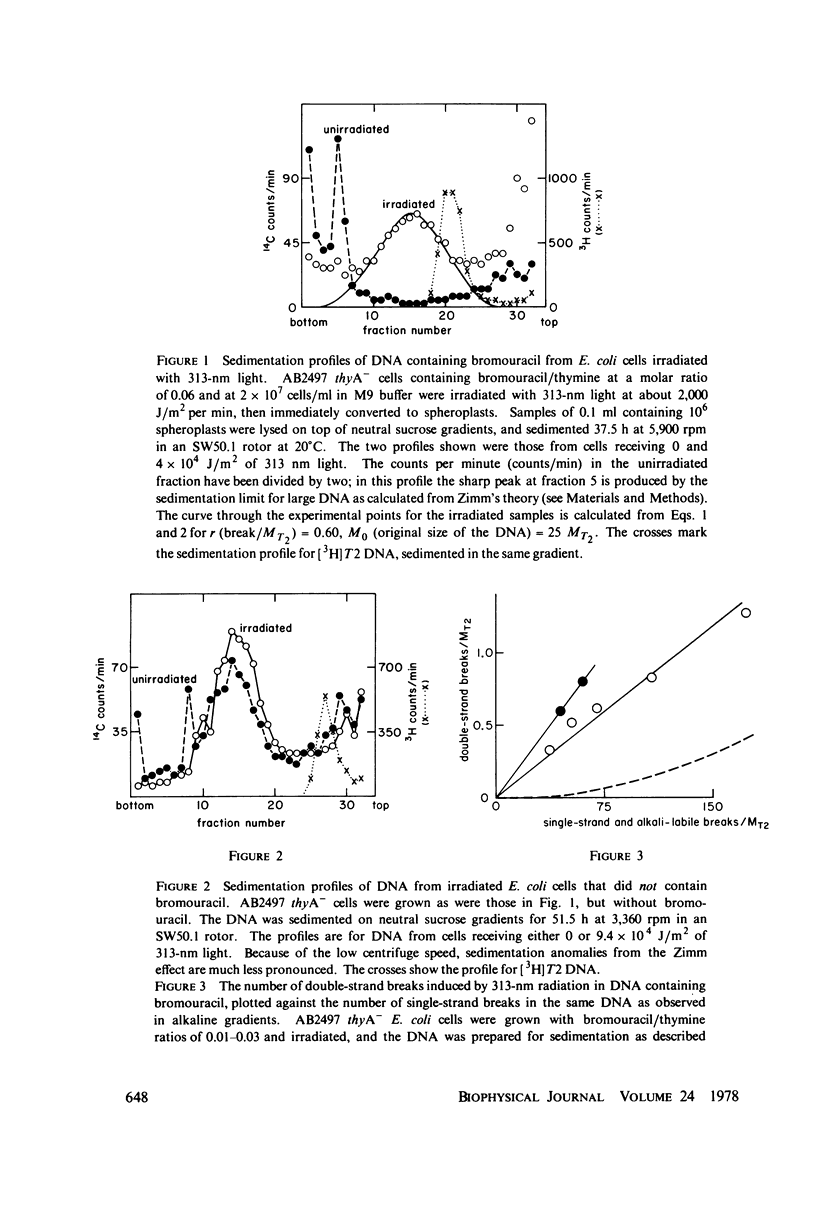
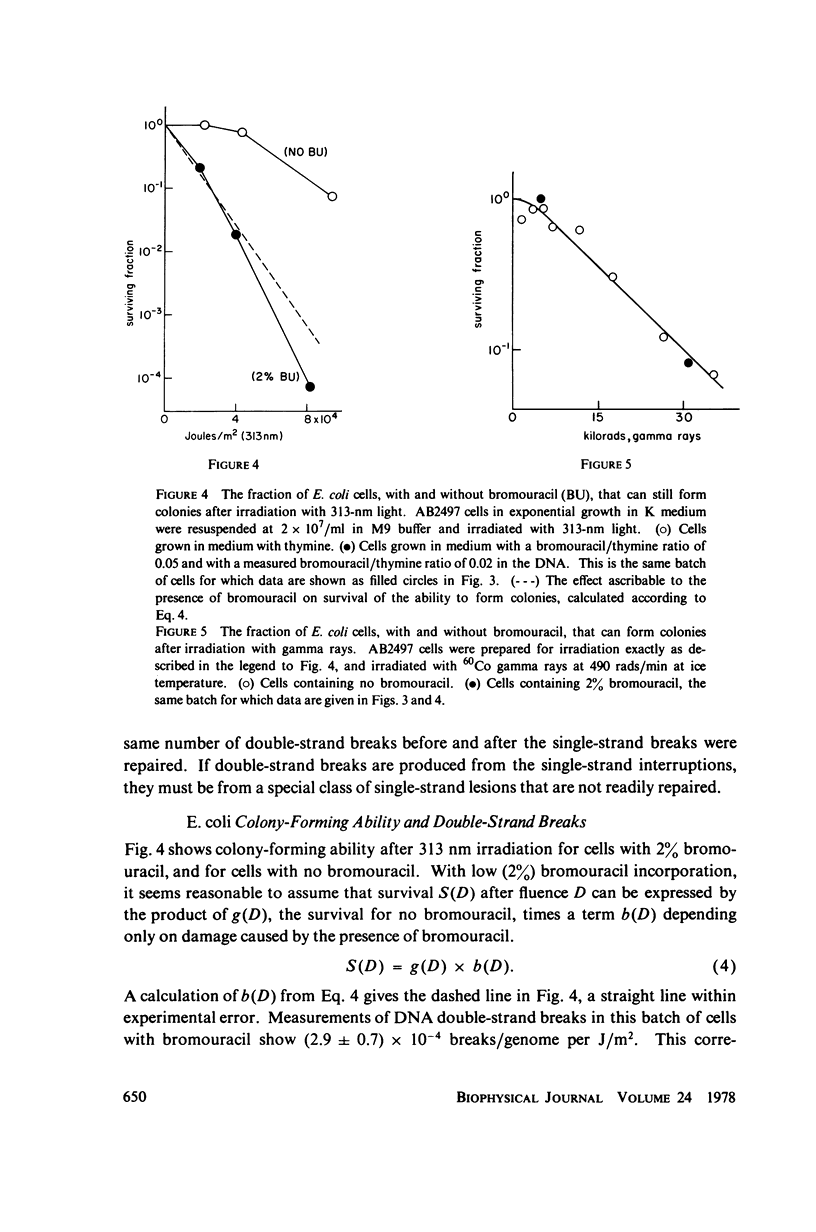
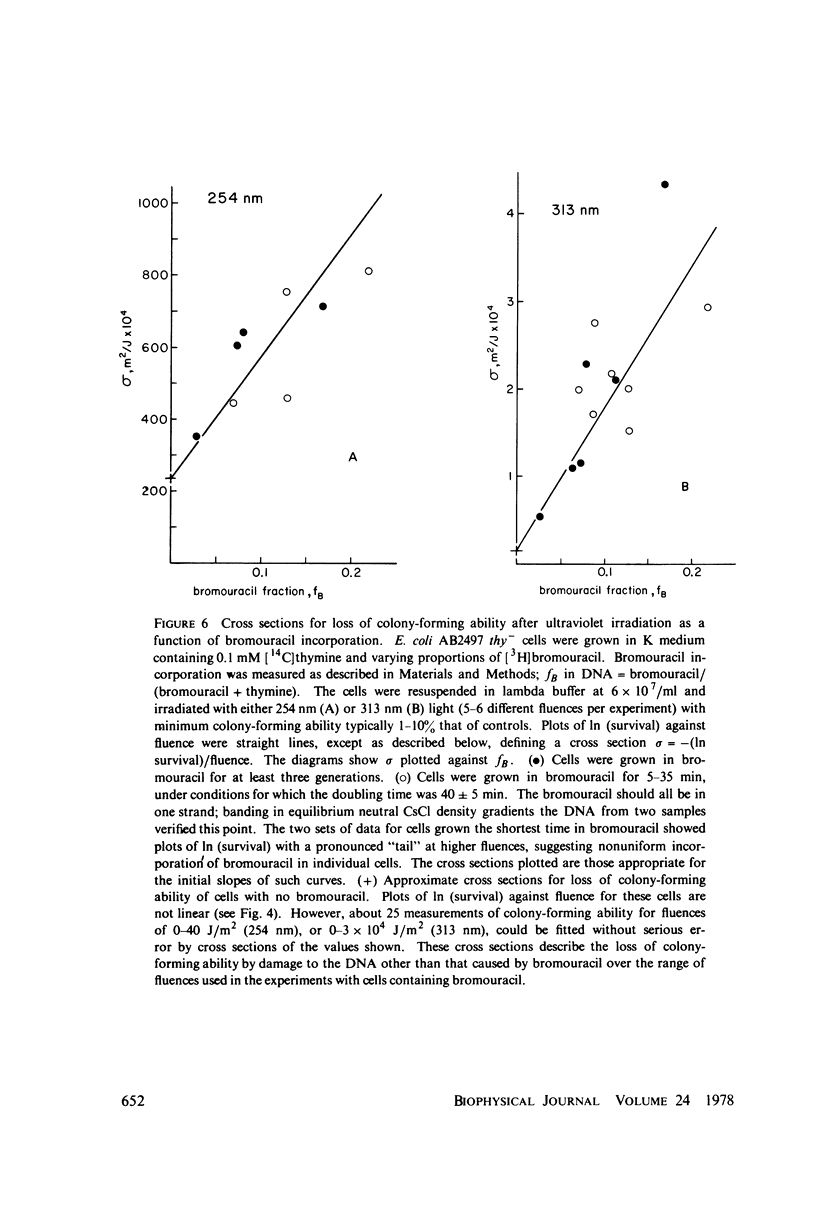
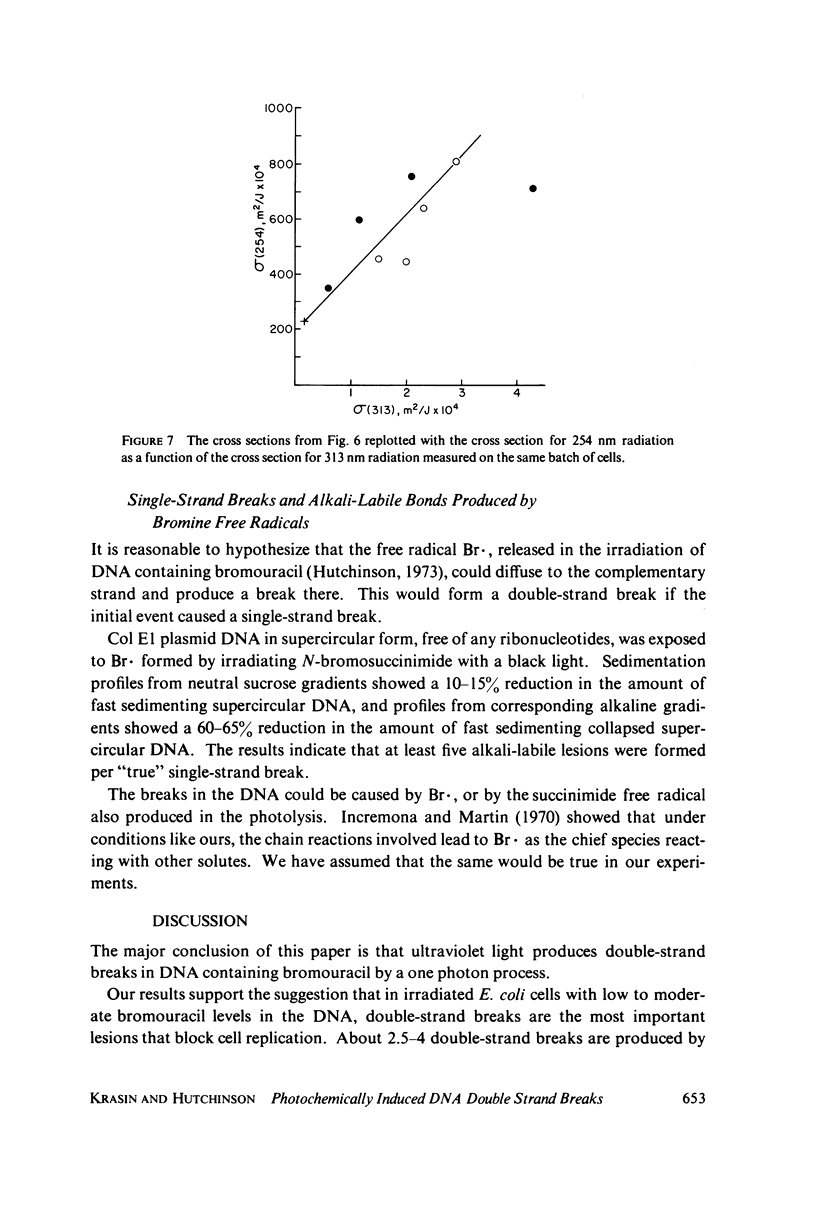
- Krasin F., Hutchinson F. Strand breaks and alkali-labile bonds induced by ultraviolet light in DNA with 5-bromouracil in vivo. Biophys J. 1978 Dec;24(3):657–664. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(78)85411-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupersztoch-Portroy Y. M., Helinski D. R. Breaks induced in supercoiled colicinogenic factor E1 DNA as a result of the decay of incorporated tritium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 20;374(3):316–323. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90252-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhnlein W., Mönkehaus F. Experimentelle Hinweise auf intramolekulare Energieleitung in der hydrbiden DNA von Bacillus subtilis nach Bestrahlung mit langwelligem UV-Licht. Z Naturforsch B. 1972 Jun;27(6):708–713. doi: 10.1515/znb-1972-0624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmann A. R. Postreplication repair of DNA in ultraviolet-irradiated mammalian cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 May 28;66(3):319–337. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ley R. D. Postreplication repair in an excision-defective mutant of Escherichia coli: ultraviolet light-induced incorporation of bromodeoxyuridine into parental DNA. Photochem Photobiol. 1973 Aug;18(2):87–95. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1973.tb06397.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lion M. B. Search for a mechanism for the increased sensitivity of 5-bromouracil-substituted DNA to ultraviolet radiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Feb 26;155(2):505–520. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(68)90195-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radloff R., Bauer W., Vinograd J. A dye-buoyant-density method for the detection and isolation of closed circular duplex DNA: the closed circular DNA in HeLa cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 May;57(5):1514–1521. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.5.1514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roufa D. J. 5-bromodeoxyuridine-DNA strand symmetry and the repair of photolytic breaks in Chinese hamster cell chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3905–3909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smets L. A., Cornelis J. J. Repairable and irrepairable damage in 5-bromouracil-substituted DNA exposed to ultra-violet radiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1971;19(5):445–457. doi: 10.1080/09553007114550581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimm B. H. Anomalies in sedimentation. IV. Decrease in sedimentation coefficients of chains at high fields. Biophys Chem. 1974 Apr;1(4):279–291. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(74)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimm B. H., Schumaker V. N., Zimm C. B. Anomalies in sedimentation. V. Chains at high fields, practical consequences. Biophys Chem. 1976 Jul;5(1-2):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(76)80039-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


