Abstract
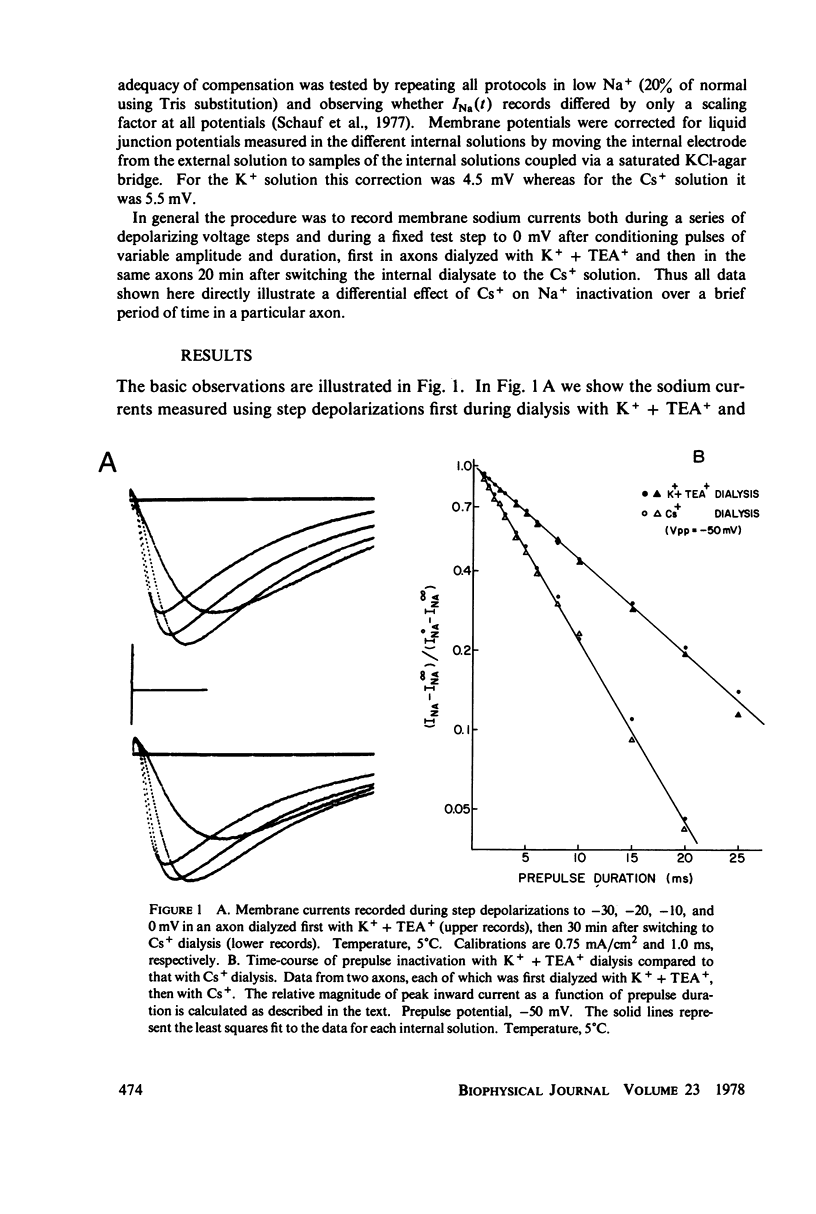
When Myxicola giant axons are internally dialyzed with Cs+ as the sole cation, the time-course of prepulse inactivation is selectively accelerated compared to its rate with K+ dialysis in the same axons. This decrease in tauph occurs without any change in the magnitude or time-course of INa during step depolarizations and results in tauph/taush ratios near unity over most of the potential range in Cs+ dialyzed axons.
Full text
PDF
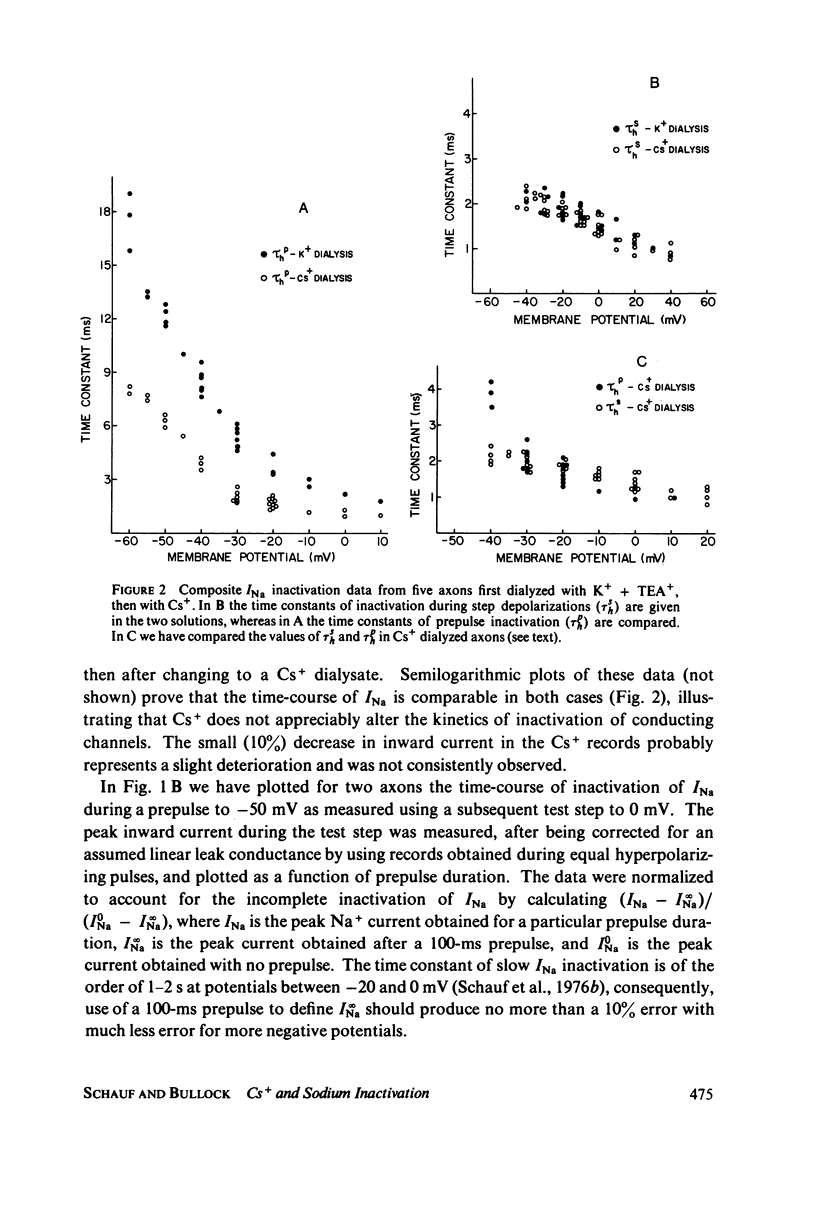


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bezanilla F., Armstrong C. M. Inactivation of the sodium channel. I. Sodium current experiments. J Gen Physiol. 1977 Nov;70(5):549–566. doi: 10.1085/jgp.70.5.549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bullock J. O., Schauf C. L. Combined voltage-clamp and dialysis of Myxicola axons: behaviour of membrane asymmetry currents. J Physiol. 1978 May;278:309–324. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1978.sp012306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman L., Schauf C. L. Quantitative description of sodium and potassium currents and computed action potentials in Myxicola giant axons. J Gen Physiol. 1973 Mar;61(3):361–384. doi: 10.1085/jgp.61.3.361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore J. W., Cox E. B. A kinetic model for the sodium conductance system in squid axon. Biophys J. 1976 Feb;16(2 Pt 1):171–192. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(76)85673-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford G. S., Pooler J. P. Selective modification of sodium channel gating in lobster axons by 2, 4, 6-trinitrophenol: Evidence for two inactivation mechanisms. J Gen Physiol. 1975 Dec;66(6):765–779. doi: 10.1085/jgp.66.6.765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Bullock J. O., Pencek T. L. Characteristics of sodium tail currents in Myxicola axons. Comparison with membrane asymmetry currents. Biophys J. 1977 Jul;19(1):7–28. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(77)85559-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Davis F. A. Further studies of activation-inactivation coupling in Myxicola axons. Insensitivity to changes in calcium concentration. Biophys J. 1975 Nov;15(11):1111–1116. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85887-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Pencek T. L., Davis F. A. Activation-inactivation coupling in Myxicola giant axons injected with tetraethylammonium. Biophys J. 1976 Sep;16(9):985–989. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85749-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauf C. L., Pencek T. L., Davis F. A. Slow sodium inactivation in Myxicola axons. Evidence for a second inactive state. Biophys J. 1976 Jul;16(7):771–778. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(76)85727-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


