Abstract
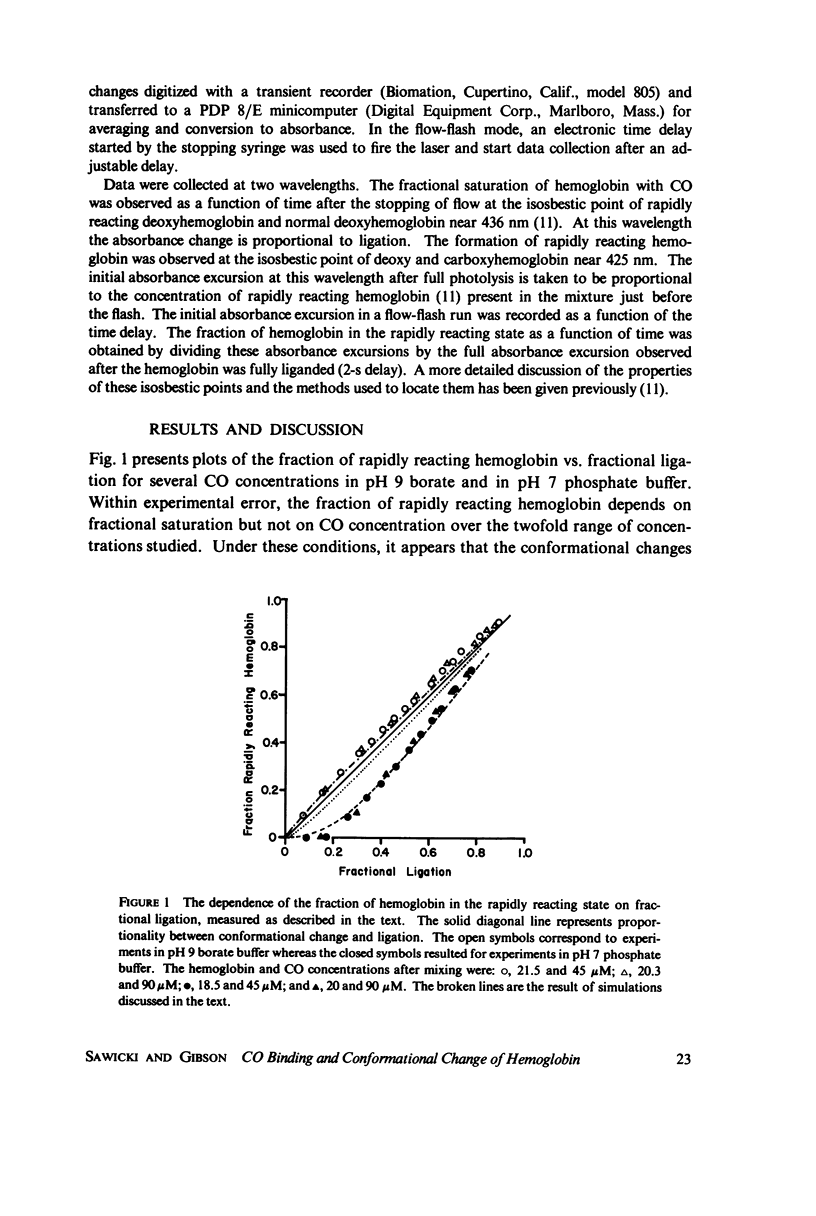
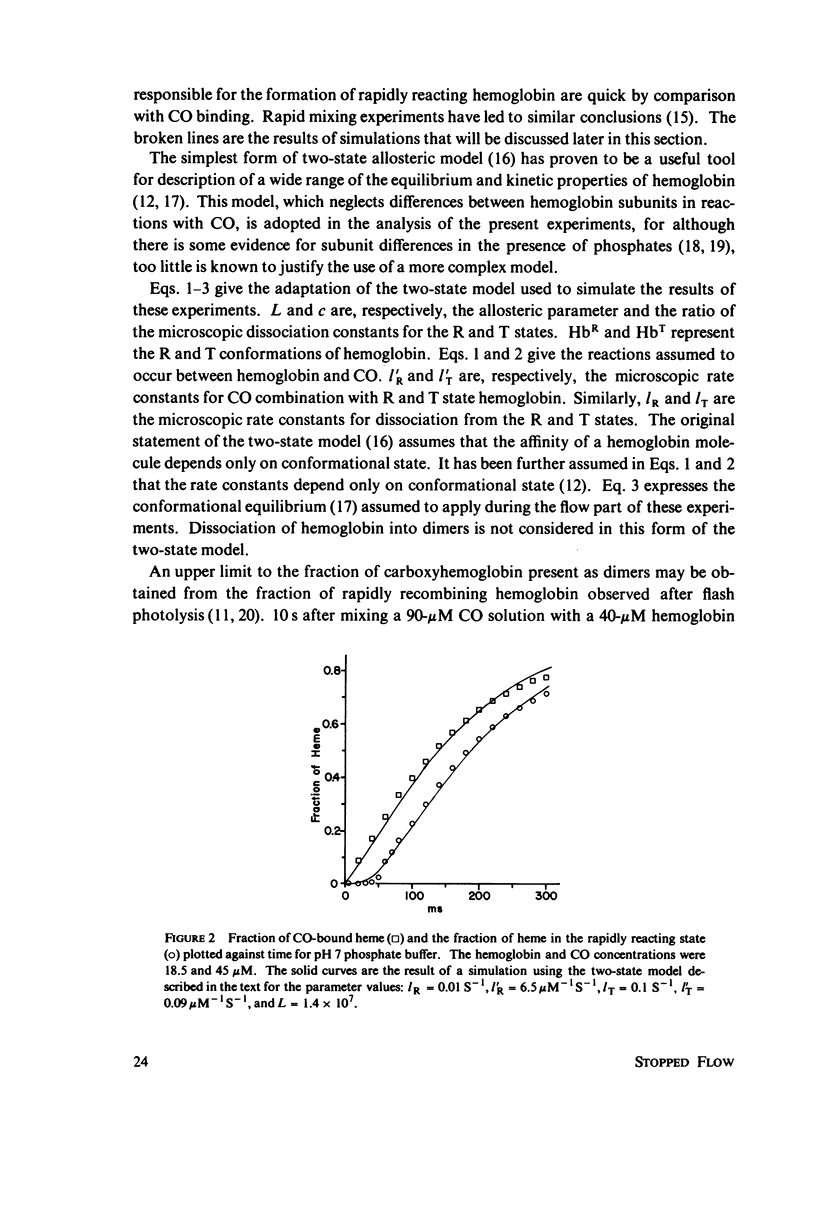
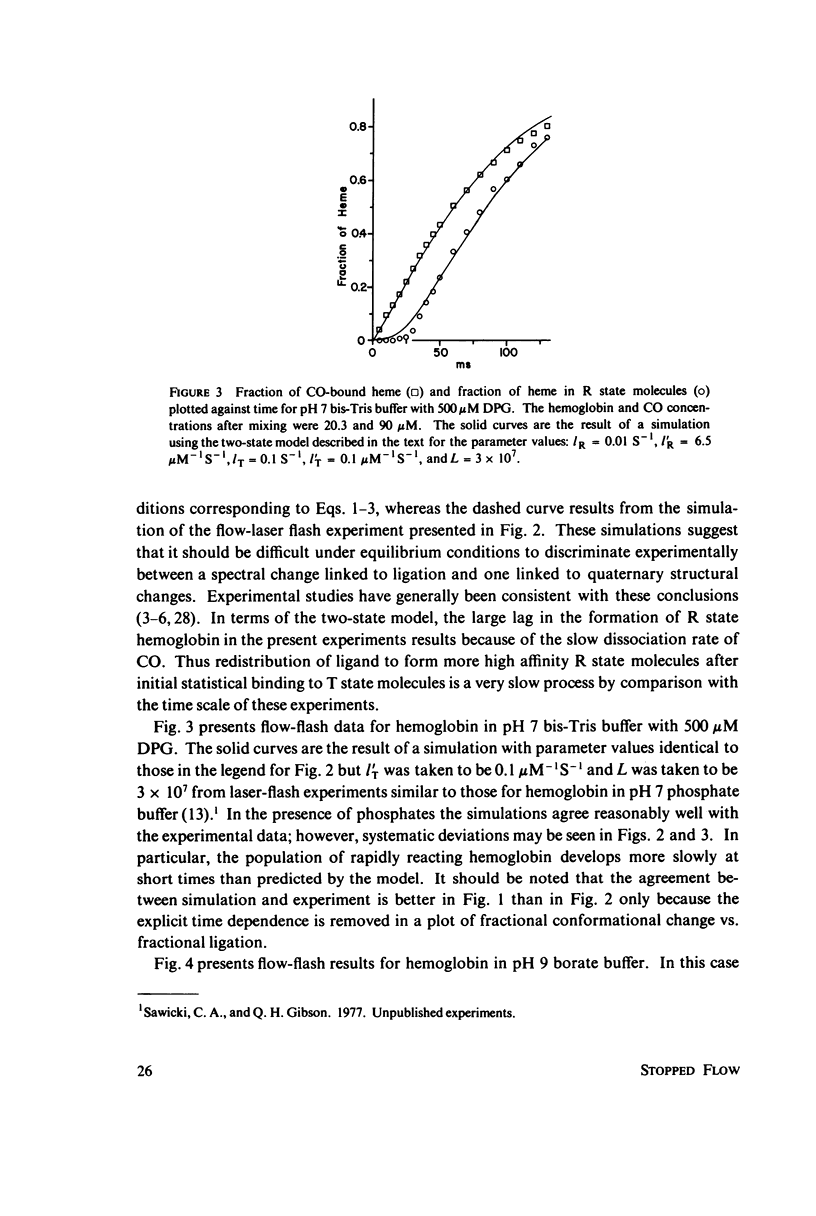
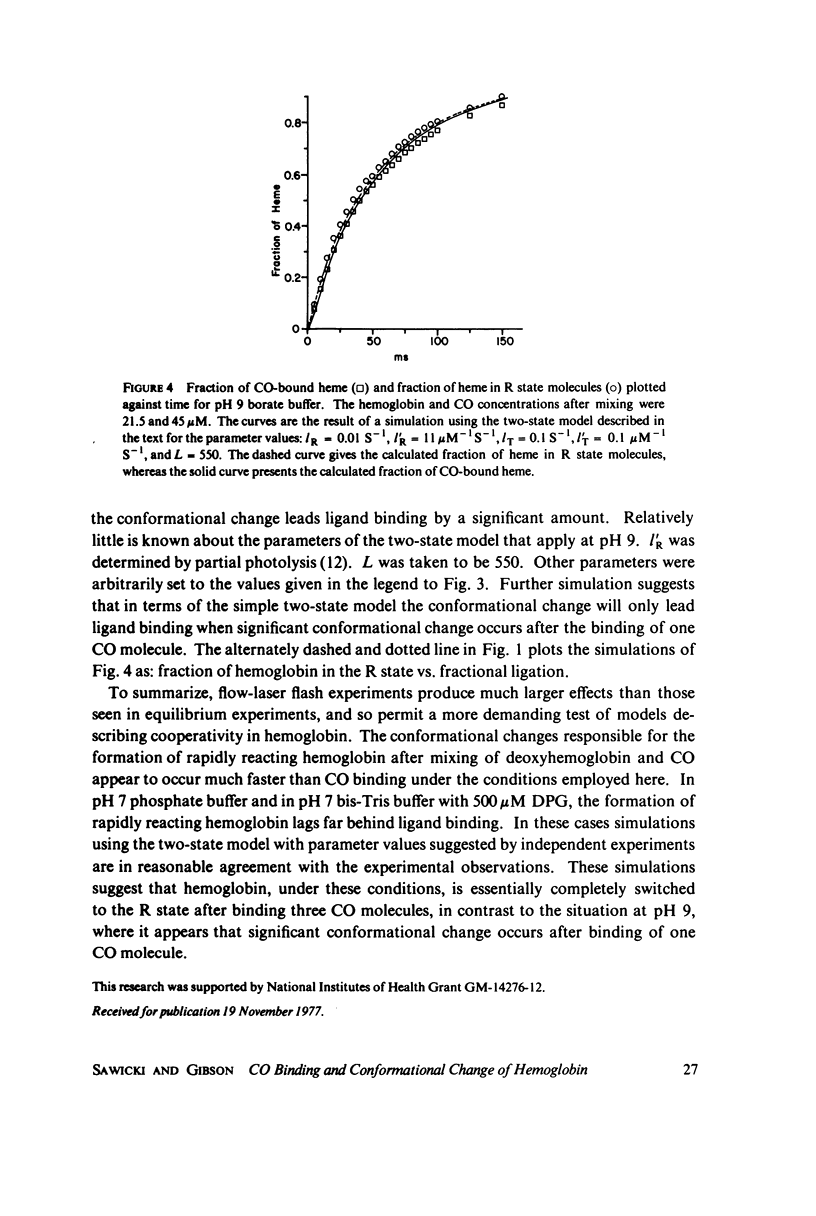
The spectral difference between normal and rapidly reacting deoxyhemoglobin (Sawicki and Gibson (1976), J. Biol Chem. 251:1533-1542) is used to study the relationship between CO binding to hemoglobin and the conformational changes to the rapidly reacting form in a combined flow-laser flash experiment. In both pH 7 phosphate buffer and pH 7 bis(2-hydroxy-ethyl)imino-tris (hydroxymethyl)methane buffer (bis-Tris) with 500 muM 2,3-diphosphoglycerate (DPG), the conformational change lags far behind CO binding; rapidly reacting hemoglobin is not observed until more than 10% of the hemoglobin is liganded. In pH 9 borate buffer the formation of rapidly reacting hemoglobin leads CO binding by a significant amount. A simple two-state allosteric model (Monod et. al. (1965), J. Mol. Biol. 12:88-118) which assumed equivalence of the hemoglobin subunits in their reaction with CO was used to simulate the experimental results. In terms of the model, the conformational change lead observed at pH 9 suggests that significant conformational change has occurred after binding of only one CO molecule per tetramer. In the presence of phosphates good agreement between experimental results and simulations is obtained using parameter values suggested by previous experimental studies. The simulations suggest that the conformational change occurs after binding of three CO molecules.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antonini E., Chiancone E., Brunori M. Studies on the relations between molecular and functional properties of hemoglobin. VI. Observations on the kinetics of hemoglobin reactions in concentrated salt solutions. J Biol Chem. 1967 Oct 10;242(19):4360–4366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman P. F. A study of conformational changes in two beta-93 modified hemoglobin A's using a triphosphate spin label. Biochemistry. 1977 Feb 8;16(3):345–351. doi: 10.1021/bi00622a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J., Rehmar M. J., Olson J. S., Gibson Q. H. Functional aspects of the subunit association-dissociation equilibria of hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 10;245(17):4372–4381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson Q. H., Milnes L. Apparatus for rapid and sensitive spectrophotometry. Biochem J. 1964 Apr;91(1):161–171. doi: 10.1042/bj0910161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson Q. H., Parkhurst L. J. Kinetic evidence for a tetrameric functional unit in hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 25;243(20):5521–5524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray R. D., Gibson Q. H. The binding of carbon monoxide to and chains in tetrameric mammalian hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 25;246(16):5176–5178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J., Ogawa S., Shulman R. G. The rate of carbon monoxide binding to hemoglobin Kansas. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Dec 18;49(6):1480–1484. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90506-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J., Shulman R. G., Ogawa S. An allosteric model of hemoglobin. I. Kinetics. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huestis W. H., Raftery M. A. 31 P-NMR studies of the release of diphospholygeric acid on carbon monoxide binding to hemoglobin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 17;49(2):428–433. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ip S. H., Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on subunit assembly in human hemoglobin. Temperature dependence of the dimer-tetramer association constants for oxygenated and unliganded hemoglobins. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):82–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOELS N., PUGH L. G. The carbon monoxide dissociation curve of human blood. J Physiol. 1958 Jun 18;142(1):63–77. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson M. E., Ho C. Effects of ligands and organic phosphates on functional properties of human adult hemoglobin. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 27;13(18):3653–3661. doi: 10.1021/bi00715a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellett G. L., Gutfreund H. Reactions of haemoglobin dimers after ligand dissociation. Nature. 1970 Aug 29;227(5261):921–926. doi: 10.1038/227921a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacQuarrie R., Gibson Q. H. Ligand binding and release of an analogue of 2,3-diphosphoglycerate from human hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1972 Sep 25;247(18):5686–5694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moffat J. K. Spin-labelled haemoglobins: a structural interpretation of electron paramagnetic resonance spectra based on X-ray analysis. J Mol Biol. 1971 Jan 28;55(2):135–146. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90187-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., McConnell H. M. Mechanism of cooperative oxygen binding to hemoglobin (spin-labeled triphosphate-concerted transition model-hemoglobin chesapeake). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):335–339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., McConnell H. M. The binding of a spin-labeled triphosphate to hemoglobin. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:325–336. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa S., McConnell H. M. Spin-label study of hemoglobin conformations in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jul;58(1):19–26. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki C. A., Gibson Q. H. Properties of the T state of human oxyhemoglobin studies by laser photolysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Nov 10;252(21):7538–7547. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki C. A., Gibson Q. H. Quaternary conformational changes in human hemoglobin studied by laser photolysis of carboxyhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 25;251(6):1533–1542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawicki C. A., Gibson Q. H. Quaternary conformational changes in human oxyhemoglobin studied by laser photolysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Aug 25;252(16):5783–5788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma V. S., Schmidt M. R., Ranney H. M. Dissociation of CO from carboxyhemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jul 25;251(14):4267–4272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. G., Hopfield J. J., Ogawa S. Allosteric interpretation of haemoglobin properties. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 Jul;8(3):325–420. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon S. R., Cantor C. R. Measurement of ligand-induced conformational changes in hemoglobin by circular dichroism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 May;63(1):205–212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


