Abstract
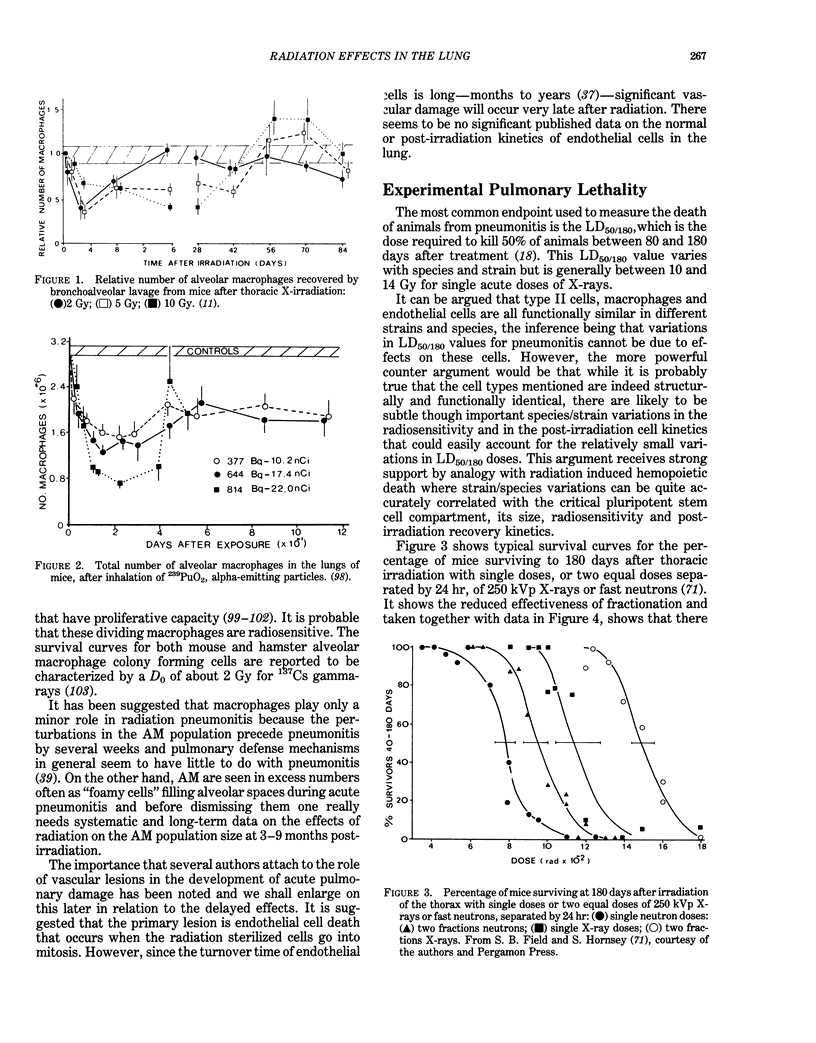
This article outlines the principles of radiobiology that can explain the time of onset, duration, and severity of the complex reactions of the lung to ionizing radiation. These reactions have been assayed biochemically, cell kinetically, physiologically, and pathologically. Clinical and experimental data are used to describe the acute and late reactions of the lung to both external and internal radiation including pneumonitis, fibrosis and carcinogenesis. Acute radiation pneumonitis, which can be fatal, develops in both humans and animals within 6 months of exposure to doses greater than or equal to 8 Gy of low LET radiation. It is divisible into a latent period lasting up to 4 weeks; an exudative phase (3-8 weeks) and with an acute pneumonitic phase between 2 and 6 months. The latter is an inflammatory reaction with intra-alveolar and septal edema accompanied by epithelial and endothelial desquamation. The critical role of type II pneumonocytes is discussed. One favored hypothesis suggests that the primary response of the lung is an increase in microvascular permeability. The plasma proteins overwhelm the lymphatic and other drainage mechanisms and this elicits the secondary response of type II cell hyperplasia. This, in its turn, produces an excess of surfactant that ultimately causes the fall in compliance, abnormal gas exchange values, and even respiratory failure. The inflammatory early reaction may progress to chronic fibrosis. There is much evidence to suggest that pneumonitis is an epithelial reaction and some evidence to suggest that this early damage may not be predictive of late fibrosis. However, despite detailed work on collagen metabolism, the pathogenesis of radiation fibrosis remains unknown. The data on radiation-induced pulmonary cancer, both in man and experimental animals from both external and internal irradiation following the inhalation of both soluble and insoluble alpha and beta emitting radionuclides are reviewed. Emphasis is placed on the data showing that alpha emitters are at least an order of magnitude more hazardous than beta/gamma radiation and on recent data showing that the more homogeneous the irradiation of the lung, the greater is the carcinogenic hazard which contradicts the so-called "hot particle" theory.
Full text
PDF





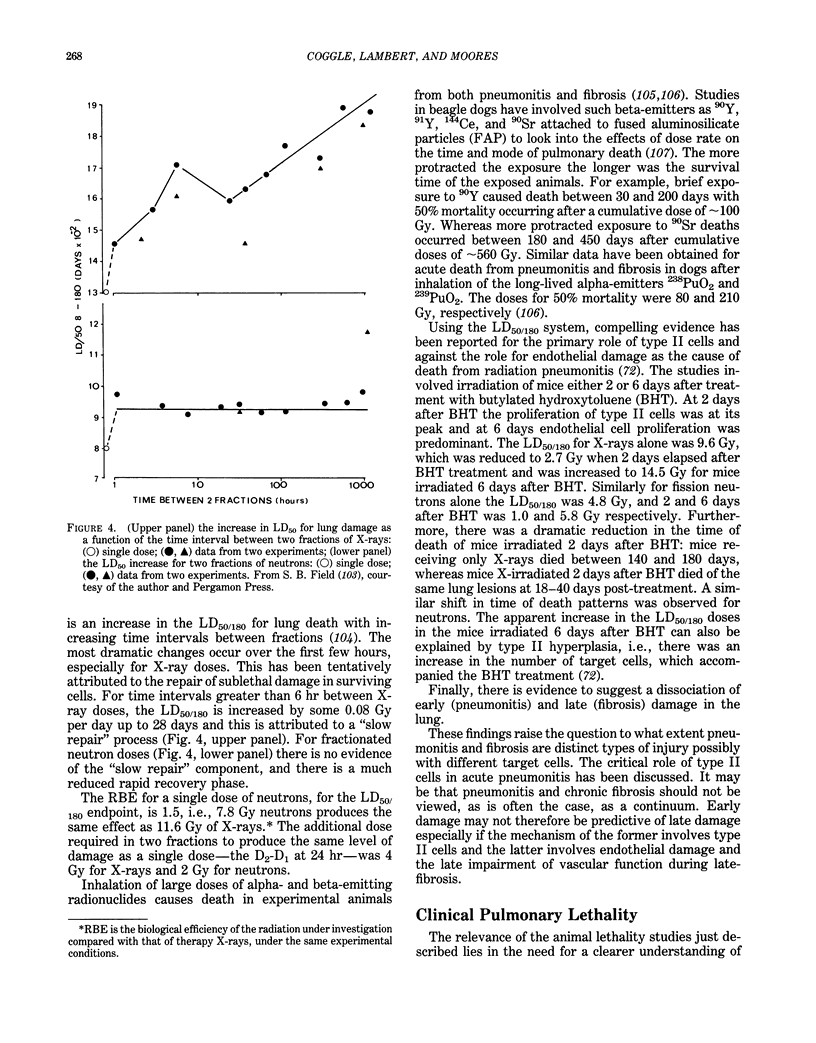




















Images in this article
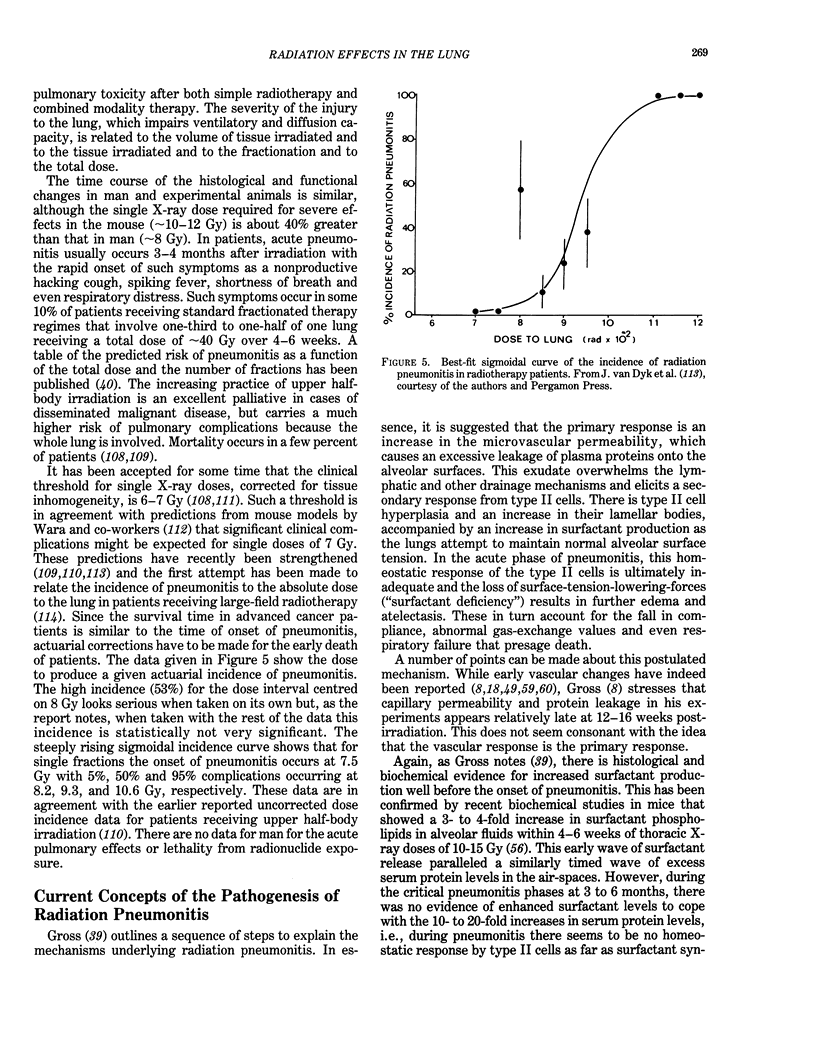
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
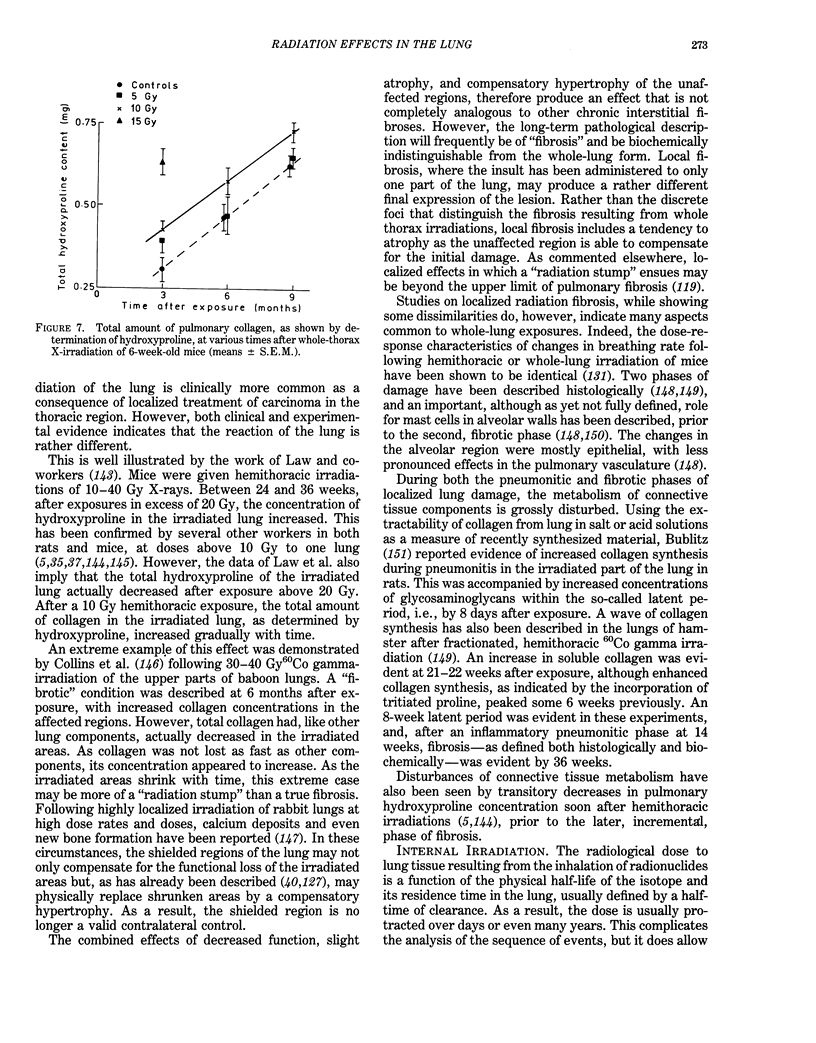
- ALTMANN H. W., HUNSTEIN W., STUTZ E. [On lung changes and lung tumors in rats after irradiation with radioactive strontium (Sr 90)]. Beitr Pathol Anat. 1961;124:145–175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H. Origin of ciliated alveolar epithelial cells in bleomycin-induced lung injury. Am J Pathol. 1977 Jun;87(3):569–580. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adamson I. Y., Bowden D. H., Wyatt J. P. A pathway to pulmonary fibrosis: an ultrastructural study of mouse and rat following radiation to the whole body and hemithorax. Am J Pathol. 1970 Mar;58(3):481–498. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahier R. G., Anderson R. L., Coultas P. G. Responses of mouse lung to irradiation. 1. Alterations in alveolar surfactant after neutrons and X-rays. Radiother Oncol. 1985 Jan;3(1):61–68. doi: 10.1016/s0167-8140(85)80009-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert R. E., Burns F. J., Heimbach R. D. The association between chronic radiation damage of the hair follicles and tumor formation in the rat. Radiat Res. 1967 Mar;30(3):590–599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albert R. E., Burns F. J., Heimbach R. D. The effect of penetration depth of electron radiation on skin tumor formation in the rat. Radiat Res. 1967 Mar;30(3):515–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer V. E., Gillam J. D., Wagoner J. K. Respiratory disease mortality among uranium miners. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;271:280–293. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb23123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer V. E., Saccomanno G., Jones J. H. Frequency of different histologic types of bronchogenic carcinoma as related to radiation exposure. Cancer. 1974 Dec;34(6):2056–2060. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197412)34:6<2056::aid-cncr2820340626>3.0.co;2-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer V. E., Wagoner J. K., Lundin F. E., Jr Uranium mining and cigarette smoking effects on man. J Occup Med. 1973 Mar;15(3):204–211. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archer V. E., Wagoner J. K., Lundin F. E. Lung cancer among uranium miners in the United States. Health Phys. 1973 Oct;25(4):351–371. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197310000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BAIR W. J., WIGGINS A. D., TEMPLE L. A. The effect of inhaled Pu-239-O-2 on the life span of mice. Health Phys. 1962 Dec;8:659–663. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196212000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BLACKETT N. M., ROYLANCE P. J., ADAMS K. STUDIES OF THE CAPACITY OF BONE-MARROW CELLS TO RESTORE ERYTHROPOIESIS IN HEAVILY IRRADIATED RATS. Br J Haematol. 1964 Oct;10:453–467. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1964.tb00722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN S. O. EFFECTS OF CONTINUOUS LOW INTENSITY RADIATION ON SUCCESSIVE GENERATIONS OF THE ALBINO RAT. Genetics. 1964 Nov;50:SUPPL–SUPPL:1113. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballou J. E., Dagle G. E., Morrow W. G. The long-term effects of intratracheally instilled 253EsCl3 in rats. Health Phys. 1975 Aug;29(2):267–272. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197508000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellet-Barthas M., Barthelemy L., Bellet M. Effects of 60Co radiation on the rabbit lung surfactant system. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980 Sep;6(9):1169–1177. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(80)90170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. E., Million R. R., Ackerman L. V. Bilateral radiation penumonitis, a complication of the radiotherapy of bronchogenic carcinoma. (Report and analysis of seven cases with autopsy). Cancer. 1969 May;23(5):1001–1018. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196905)23:5<1001::aid-cncr2820230505>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowden D. H. The alveolar macrophage. Curr Top Pathol. 1971;55:1–36. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65208-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brain J. D., Knudson D. E., Sorokin S. P., Davis M. A. Pulmonary distribution of particles given by intratracheal instillation or by aerosol inhalation. Environ Res. 1976 Feb;11(1):13–33. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(76)90107-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEMBER H. Further studies on lung cancer from Ce144F3. Health Phys. 1963 May;9:539–544. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196305000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEMBER H., HATCH T. F., WATSON J. A., GRUCCI T. Pulmonary effects from radioactive barium sulfate dust. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1955 Dec;12(6):628–634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEMBER H., STEMMER K. LUNG CANCER FROM RADIOACTIVE CERIUM CHLORIDE. Health Phys. 1964 Feb;10:43–48. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196402000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEMBER H., WATSON J. A. Carcinogenic effects of strontium 90 beads implanted in the lungs of rats. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1958 Feb;19(1):36–42. doi: 10.1080/00028895809343538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CEMBER H., WATSON J. A., SPRITZER A. A. Bronchogenic carcinoma from radioactive cerium fluoride. AMA Arch Ind Health. 1959 Jan;19(1):14–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clapp N. K., Darden E. B., Jr, Jernigan M. C. Relative effects of whole-body sublethal doses of 60-MeV protons and 300-kVp X-rays on disease incidences in RF mice. Radiat Res. 1974 Jan;57(1):158–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen B. L. Failures and critique of the BEIR III lung cancer risk estimates. Health Phys. 1982 Mar;42(3):267–284. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198203000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. F., Johanson W. G., Jr, McCullough B., Jones M. A., Waugh H. J., Jr Effects of compensatory lung growth in irradiation-induced regional pulmonary fibrosis in the baboon. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Jun;117(6):1079–1089. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.6.1079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis C. H. A kinetic model for the pathogenesis of radiation lung damage. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1982 Sep;42(3):253–263. doi: 10.1080/09553008214551181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis C. H., Steel G. G. Dose-dependence of the time of appearance of lung damage in mice given thoracic irradiation. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1982 Sep;42(3):245–252. doi: 10.1080/09553008214551171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coultas P. G., Ahier R. G., Field S. B. Effects of neutron and X irradiation on cell proliferation in mouse lung. Radiat Res. 1981 Mar;85(3):516–528. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. T., Palmer R. F., Filipy R. E., Dagle G. E., Stuart B. O. Carcinogenic effects of radon daughters, uranium ore dust and cigarette smoke in beagle dogs. Health Phys. 1982 Jan;42(1):33–52. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198201000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DEELEY T. J. The effects of radiation on the lungs in the treatment of carcinoma of the bronchus. Clin Radiol. 1960 Jan;11:33–39. doi: 10.1016/s0009-9260(60)80064-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dancewicz A. M., Mazanowska A., Gerber G. B. Late biochemical changes in the rat lung after hemithoracic irradiation. Radiat Res. 1976 Sep;67(3):482–490. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Villiers A. J., Gross P. Morphologic changes induced in the lungs of hamsters and rats by external radiation (x-rays). A study in experimental carcinogenesis. Cancer. 1966 Oct;19(10):1399–1410. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196610)19:10<1399::aid-cncr2820191011>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean P. N., Langham W. H. Tumorigenicity of small highly radioactive particles. Health Phys. 1969 Jan;16(1):79–84. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196901000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diel J. H., Short R. K. Collagen localization in lung parenchyma irradiated by inhaled 238PuO2 particles. Radiat Res. 1979 Aug;79(2):417–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Divertie M. B., Titus J. L., Shorter R. G. A simple method for the production of experimental squamous cell carcinoma of the lung in rats. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1967 Oct;96(4):820–822. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1967.96.4.820. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Down J. D., Steel G. G. The expression of early and late damage after thoracic irradiation: a comparison between CBA and C57B1 mice. Radiat Res. 1983 Dec;96(3):603–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drózdz M., Kucharz E., Glowacki A., Zylka J. Effect of irradiation on glycosaminoglycans content in rat tissue. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 1981;29(4):514–519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubravsky N. B., Dubrawsky C., Jampolis S., Mason K., Hunter N., Withers H. R. Long-term effects of pulmonary damage in mice on lung weight, compliance, hydroxyproline content and formation of metastases. Br J Radiol. 1981 Dec;54(648):1075–1080. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-54-648-1075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubrawsky C., Dubravsky N. B., Withers H. R. The effect of colchicine on the accumulation of hydroxyproline and on lung compliance after irradiation. Radiat Res. 1978 Jan;73(1):111–120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Bils R. F. Identification of cells labeled with tritiated thymidine in the pulmonary alveolar walls of the mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1969 Sep;100(3):372–378. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1969.100.3.372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Cabral L. J., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Cell division of alveolar macrophages in rat lung following exposure to NO2. Am J Pathol. 1973 Feb;70(2):199–208. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans M. J., Johnson L. V., Stephens R. J., Freeman G. Cell renewal in the lungs of rats exposed to low levels of ozone. Exp Mol Pathol. 1976 Feb;24(1):70–83. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(76)90058-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. B. Early and late normal tissue damage after fast neutrons. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977;3:203–210. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90250-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. B., Hornsey S. Damage to mouse lung with neutrons and x-rays. Eur J Cancer. 1974 Sep;10(9):621–627. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(74)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. B., Hornsey S., Kutsutani Y. Effects of fractionated irradiation on mouse lung and a phenomenon of slow repair. Br J Radiol. 1976 Aug;49(584):700–707. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-49-584-700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field S. B., Hornsey S. Slow repair after x-rays and fast neutrons. Br J Radiol. 1977 Aug;50(596):600–601. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-50-596-600. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowler J. F., Travis E. L. The radiation pneumonitis syndrome in half-body radiation therapy. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1978 Nov-Dec;4(11-12):1111–1113. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(78)90029-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman G. S., Lofgren S. B., Kligerman M. M. Radiation-induced changes in pulmonary perfusion. Radiology. 1974 Aug;112(2):435–437. doi: 10.1148/112.2.435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fryer C. J., Fitzpatrick P. J., Rider W. D., Poon P. Radiation pneumonitis: experience following a large single dose of radiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1978 Nov-Dec;4(11-12):931–936. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(78)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN G. M., KASS E. H. THE ROLE OF THE ALVEOLAR MACROPHAGE IN THE CLEARANCE OF BACTERIA FROM THE LUNG. J Exp Med. 1964 Jan 1;119:167–176. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerber G. B., Dancewicz A. M., Bessemans B., Casale G. Biochemistry of late effects in rat lung after hemithoracic irradiation. Acta Radiol Ther Phys Biol. 1977 Oct;16(5):447–455. doi: 10.3109/02841867709133966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godleski J. J., Brain J. D. The origin of alveolar macrophages in mouse radiation chimeras. J Exp Med. 1972 Sep 1;136(3):630–643. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.3.630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg V. E., Warren S., Chute R., Besen M. Radiation pneumonitis in single and parabiotic rats. I. Short term effects of supralethal total body irradiation. Lab Invest. 1968 Mar;18(3):215–226. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman S. M., Freeman L. M., Ghossein N. A., Sanfilippo L. J. Effects of thoracic irradiation on pulmonary arterial perfusion in man. Radiology. 1969 Aug;93(2):289–296. doi: 10.1148/93.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Alveolar macrophage number: an index of the effect of radiation on the lungs. Radiat Res. 1977 Nov;72(2):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Alveolar macrophage number: an index of the effect of radiation on the lungs. Radiat Res. 1977 Nov;72(2):325–332. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J., Balis J. V. Functional, biochemical, and morphologic changes in alveolar macrophages following thoracic x-irradiation. Lab Invest. 1978 Oct;39(4):381–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Early physiologic and biochemical effects of thoracic X-irradiation on the pulmonary surfactant system. J Lab Clin Med. 1978 Mar;91(3):537–544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Experimental radiation pneumonitis. III. Phospholipid studies on the lungs. J Lab Clin Med. 1979 Apr;93(4):627–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Experimental radiation pneumonitis. IV. Leakage of circulatory proteins onto the alveolar surface. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Jan;95(1):19–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Pulmonary effects of radiation therapy. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Jan;86(1):81–92. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-86-1-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. Radiation pneumonitis in mice. Some effects of corticosteroids on mortality and pulmonary physiology. J Clin Invest. 1980 Sep;66(3):504–510. doi: 10.1172/JCI109881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross N. J. The pathogenesis of radiation-induced lung damage. Lung. 1981;159(3):115–125. doi: 10.1007/BF02713907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross P., Pfitzer E. A., Watson J., De Treville R. T., Kaschak M., Tolker E. B., Babyak M. A. Experimental carcinogenesis. Bronchial intramural adenocarcinomas in rats from x-ray irradiation of the chest. Cancer. 1969 May;23(5):1046–1060. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(196905)23:5<1046::aid-cncr2820230509>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn F. F., Goldstein E., Dungworth D. L. Effect of whole-body x-irradiation on pulmonary bactericidal function. Radiat Res. 1971 Aug;47(2):461–471. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall E. J. Radiation dose-rate: a factor of importance in radiobiology and radiotherapy. Br J Radiol. 1972 Feb;45(530):81–97. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-45-530-81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R. F., Muggenburg B. A., Mauderly J. L., Tuttle W. A. Early damage indicators in the lung. II. Time sequence of protein accumulation and lipid loss in the airways of beagle dogs with beta irradiation of the lung. Radiat Res. 1978 Oct;76(1):145–158. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heppleston A. G., Styles J. A. Activity of a macrophage factor in collagen formation by silica. Nature. 1967 Apr 29;214(5087):521–522. doi: 10.1038/214521a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horácek J., Placek V., Sevc J. Histologic types of bronchogenic cancer in relation to different conditions of radiation exposure. Cancer. 1977 Aug;40(2):832–835. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197708)40:2<832::aid-cncr2820400235>3.0.co;2-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENNNINGS F. L., ARDEN A. Development of radiation pneumonitis. Time and dose factors. Arch Pathol. 1962 Oct;74:351–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Sagerman R. H., Dombrowski C. S. Ischemia of the lung due to ionizing radiation: quantitative studies. J Nucl Med. 1970 Aug;11(8):491–495. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. M., Sagerman R. H., Jacox H. W. Changes in pulmonary arterial perfusion due to intrathoracic neoplasia and irradiation of the lung. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1968 Mar;102(3):637–644. doi: 10.2214/ajr.102.3.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KREYBERG L. Histological lung cancer types. A morphological and biological correlation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand Suppl. 1962;Suppl 157:1–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlinsky J. B. Glycosaminoglycans in emphysematous and fibrotic hamster lungs. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jan;125(1):85–88. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.1.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlinsky J. B., Goldstein R. H. Fibrotic lung disease--a perspective. J Lab Clin Med. 1980 Dec;96(6):939–942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman S. L. Autoradiographic study of type II-cell hyperplasia in lungs of mice chronicall exposed to urethane. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1976 Sep;9(5):489–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1976.tb01299.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kauffman S. L., Burri P. H., Weibel E. R. The postnatal growth of the rat lung. II. Autoradiography. Anat Rec. 1974 Sep;180(1):63–76. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091800108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim M., Goldstein E., Lewis J. P., Lippert W., Warshauer D. Murine pulmonary alveolar macrophages: rates of bacterial ingestion, inactivation, and destruction. J Infect Dis. 1976 Mar;133(3):310–320. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.3.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk J. M., Heard B. E., Kerr I., Turner-Warwick M., Laurent G. J. Quantitation of types I and III collagen in biopsy lung samples from patients with cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Coll Relat Res. 1984 May;4(3):169–182. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korsower J. M., Skovron M. L., Ghossein N. A., Goldman H. S. Acute changes in pulmonary arterial perfusion following irradiation. Radiology. 1971 Sep;100(3):691–693. doi: 10.1148/100.3.691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshurnikova N. A., Aristov V. P., Lemberg V. K., Mushkacheva G. S., Poplyko M. G., Tseveleva I. A. Mechanism of development of plutonium-induced pulmonary sclerosis. Health Phys. 1972 Jun;22(6):753–754. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197206000-00033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurohara S. S., Casarett G. W. Effects of single thoracic x-ray exposure in rats. Radiat Res. 1972 Nov;52(2):263–290. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKIN S., KUSCHNER M., ALTSHULER B., NELSON N. TISSUE REACTIONS AND DOSE RELATIONSHIPS IN RATS FOLLOWING INTRAPULMONARY BETA RADIATION. Health Phys. 1964 Dec;10:1229–1233. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196412000-00044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LASKIN S., KUSCHNER M., NELSON N., ALTSHULER B., HARLEY J. H., DANIELS M. CARCINOMA OF THE LUNG IN RATS EXPOSED TO THE BETA-RADIATION OF INTRABRONCHIAL RUTHENIUM PELLETS. I. DOSERESPONSE RELATIONSHIPS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Aug;31:219–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., Cockerill P., McAnulty R. J., Hastings J. R. A simplified method for quantitation of the relative amounts of type I and type III collagen in small tissue samples. Anal Biochem. 1981 May 15;113(2):301–312. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90081-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J., McAnulty R. J., Corrin B., Cockerill P. Biochemical and histological changes in pulmonary fibrosis induced in rabbits with intratracheal bleomycin. Eur J Clin Invest. 1981 Dec;11(6):441–448. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2362.1981.tb02011.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent G. J. Rates of collagen synthesis in lung, skin and muscle obtained in vivo by a simplified method using [3H]proline. Biochem J. 1982 Sep 15;206(3):535–544. doi: 10.1042/bj2060535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law M. P., Hornsey S., Field S. B. Collagen content of lungs of mice after x-ray irradiation. Radiat Res. 1976 Jan;65(1):60–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy E. P., Liebner E. J., Jensik R. J. The ultrastructure of canine alveoli after supervoltage irradiation of the thorax. I. Lesions of the latent period. Lab Invest. 1966 Oct;15(10):1544–1558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. S., Kuhn C., 3rd, Chen D. M. Effects of hydrocortisone acetate on pulmonary alveolar macrophage colony-forming cells. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1982 Jun;125(6):712–715. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1982.125.6.712. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little J. B., O'Toole W. F. Respiratory tract tumors in hamsters induced by benzo(a)pyrene and 210Po alpha-radiation. Cancer Res. 1974 Nov;34(11):3026–3039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren D. L., Hahn F. F. Suppression of the pulmonary clearance of Staphylococcus aureus in mice that had inhaled either 144CeO2 or 239PuO2. Radiat Res. 1979 Feb;77(2):361–376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundgren D. L., McClellan R. O., Thomas R. L., Hahn F. F., Sanchez A. Toxicity of inhaled 144CeO2 in mice. Radiat Res. 1974 Jun;58(3):448–461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin F. E., Jr Lloyd JW, Smith EM, Archer VE, Holaday DA: Mortality of uranium miners in relation to radiation exposure, hard-rock mining and cigarette smoking--1950 through September 1967. Health Phys. 1969 May;16(5):571–578. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196905000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundin F. E., Jr Lloyd JW, Smith EM, Archer VE, Holaday DA: Mortality of uranium miners in relation to radiation exposure, hard-rock mining and cigarette smoking--1950 through September 1967. Health Phys. 1969 May;16(5):571–578. doi: 10.1097/00004032-196905000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madrazo A., Suzuki Y., Churg J. Radiation pneumonitis. Ultrastructural changes in the pulmonary alveoli following high doses of radiation. Arch Pathol. 1973 Oct;96(4):262–268. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisin J. R. The influence of radiation on blood vessels and circulation. Chapter 3. Ultrastructure of the vessel wall. Curr Top Radiat Res Q. 1974 Jun;10(1):29–57. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maisin J. R. The ultrastructure of the lung of mice exposed to a supra-lethal dose of ionizing radiation on the thorax. Radiat Res. 1970 Nov;44(2):545–564. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauderly J. L., Pickrell J. A., Hobbs C. H., Benjamin S. A., Hahn F. F., Jones R. K., Barnes J. E. The effects of inhaled 90Y fused clay aerosol on pulmonary function and related parameters of the beagle dog. Radiat Res. 1973 Oct;56(1):83–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metivier H., Masse R., Legendre N., Lafuma J. Pulmonary connective tissue modifications induced by internal alpha irradiation. I. Effect of time and dose on alterations following inhalation of plutonium-239 dioxide aerosol in rat. Radiat Res. 1978 Aug;75(2):385–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metivier H., Masse R., Nolibé D., Lafuma J. 239PuO2 aerosol inhalation with emphasis on pulmonary connective tissue modifications. Inhaled Part. 1975 Sep;4(Pt 2):583–595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metivier H., Nolibe D., Masse R., Lafuma J. Cancers provoqués chez le singe babouin (Papio papio) par inhalation de PuO2. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1972 Dec 18;275(25):3069–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. R., Ullrich R. L. Effects of X rays and fission neutrons on an induced proliferative response in lung type 2 epithelial cells. Radiat Res. 1981 Feb;85(2):380–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer K. R., Witschi H., Ullrich R. L. Proliferative responses of type 2 lung epithelial cells after X rays and fission neutrons. Radiat Res. 1980 Jun;82(3):559–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyer O. T., Dannenberg A. M., Jr Radiation, infection, and macrophage function. II. Effect of whole body radiation on the number of pulmonary alveolar macrophages and their levels of hydrolytic enzymes. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1970 Jan;7(1):79–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson S. M., Schreiner B. F., Jr Cardiopulmonary effects of upper-body x-irradiation in the dog. Radiat Res. 1971 Jul;47(1):168–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalowski A. Effects of radiation on normal tissues: hypothetical mechanisms and limitations of in situ assays of clonogenicity. Radiat Environ Biophys. 1981;19(3):157–172. doi: 10.1007/BF01324183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moores S. R., Talbot R. J., Evans N., Lambert B. E. Macrophage depletion of mouse lung following inhalation of 239PuO2. Radiat Res. 1986 Mar;105(3):387–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosavi H., McDonald S., Rubin P., Cooper R., Stuard I. D., Penney D. Early radiation dose-response in lung: an ultrastructural study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977 Sep-Oct;2(9-10):921–931. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan A., Moores S. R., Holmes A., Evans J. C., Evans N. H., Black A. The effect of quartz, administered by intratracheal instillation, on the rat lung. I. The cellular response. Environ Res. 1980 Jun;22(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90113-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NOWELL P. C., COLE L. J. Late effects of fast neutrons versus x-rays in mice: nephrosclerosis, tumors, longevity. Radiat Res. 1959 Oct;11:545–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naimark A., Newman D., Bowden D. H. Effect of radiation on lecithin metabolism, surface activity, and compliance of rat lung. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1970 Oct;48(10):685–694. doi: 10.1139/y70-101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pagani J. J., Libshitz H. I. CT manifestations of radiation-induced change in chest tissue. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1982 Apr;6(2):243–248. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198204000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. F., Bair W. J., Busch R. H. Progress in beagle dog studies with transuranium elements at Battelle-Northwest. Health Phys. 1972 Jun;22(6):803–810. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197206000-00041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Park J. F., Lund J. E., Ragan H. A., Hackett P. L., Frazier M. E. Bone tumors induced by inhalation of 238PuO2 in dogs. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1976;(54):17–35. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-80997-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris T. M., Knight J. G., Hess C. E., Constable W. C. Severe radiation pneumonitis precipitated by withdrawal of corticosteroids: a diagnostic and therapeutic dilemma. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1979 Feb;132(2):284–286. doi: 10.2214/ajr.132.2.284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patrick G. The retention of uranium dioxide particles in the trachea of the rat. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1979 Jun;35(6):571–576. doi: 10.1080/09553007914550681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peel D. M., Coggle J. E. The effect of X irradiation on alveolar macrophages in mice. Radiat Res. 1980 Jan;81(1):10–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penney D. P., Rubin P. Specific early fine structural changes in the lung irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977 Nov-Dec;2(11-12):1123–1132. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90119-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perraud R., Chameaud J., Masse R., Lafuma J. Cancers pulmonaires expérimentaux chez le rat après inhalation de radon associé à des poussières non radioactives. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1970 May 25;270(21):2594–2595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. L. An ultrastructural study of the development of radiation injury in the lung. Radiology. 1966 Jul;87(1):49–54. doi: 10.1148/87.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips T. L., Wharam M. D., Margolis L. W. Modification of radiation injury to normal tissues by chemotherapeutic agents. Cancer. 1975 Jun;35(6):1678–1684. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197506)35:6<1678::aid-cncr2820350629>3.0.co;2-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell J. A., Harris D. V., Benjamin S. A., Cuddihy R. G., Peleger R. C., Mauderly J. L. Pulmonary collagen metabolism after lung injury from inhaled 90Y in fused clay particles. Exp Mol Pathol. 1976 Aug;25(1):70–81. doi: 10.1016/0014-4800(76)90018-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell J. A., Harris D. V., Hahn F. F., Belasich J. J., Jones R. K. Biological alterations resulting from chronic lung irradiation. III. Effect of partial 30Co thoracic irradiation upon pulmonary collagen metabolism and fractionation in syrian hamsters. Radiat Res. 1975 Apr;62(1):133–144. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell J. A., Harris D. V., Mauderly J. L., Hahn F. F. Altered collagen metabolism in radiation-induced interstitial pulmonary fibrosis. Chest. 1976 Feb;69(2 Suppl):311–316. doi: 10.1378/chest.69.2.311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell J. A., Harris D. V., Pfleger R. C., Benjamin S. A., Belasich J. J., Jones R. K., McClellan R. O. Biological alterations resulting from chronic wing irradation. II. Connective tissue alterations following inhalation of 144Ce fused clay aerosol in beagle dogs. Radiat Res. 1975 Aug;63(2):299–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pickrell J. A., Schnizlein C. T., Hahn F. F., Snipes M. B., Jones R. K. Radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis: study of changes in collagen constituents in different lung regions of beagle dogs after inhalation of beta-emitting radionuclides. Radiat Res. 1978 May;74(2):363–377. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prato F. S., Kurdyak R., Saibil E. A., Rider W. D., Aspin N. Regional and total lung function in patients following pulmonary irradiation. Invest Radiol. 1977 May-Jun;12(3):224–237. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197705000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prato F. S., Kurdyak R., Saibil E. A., Rider W. D., Aspin N. Regional and total lung function in patients following pulmonary irradiation. Invest Radiol. 1977 May-Jun;12(3):224–237. doi: 10.1097/00004424-197705000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasey J. S., Nelson N. J. Repair of potentially lethal damage following irradiation with X rays or cyclotron neutrons: response of the EMT-6/uw tumor system treated under various growth conditions in vitro and in vivo. Radiat Res. 1981 Jan;85(1):69–84. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond C. R., Langham J., Stone R. S. Biological response to small discrete highly radioactive sources. II. Morphogenesis of microlesions in rat lungs from intravenously injected 238 PuO 2 microspheres. Health Phys. 1970 Apr;18(4):401–408. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197004000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richmond C. R. Plutonium--health implications for man. The importance of non-uniform dose-distribution in an organ. Health Phys. 1975 Oct;29(4):525–537. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197510000-00009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossi H. H. The effects of small doses of ionizing radiation. Fundamental biophysical characteristics. Radiat Res. 1977 Jul;71(1):1–8. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STONE D. J., SCHWARTZ M. J., GREEN R. A. Fatal pulmonary insufficiency due to radiation effect upon the lung. Am J Med. 1956 Aug;21(2):211–226. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(56)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salazar O. M., Rubin P., Keller B., Scarantino C. Systemic (half-body) radiation therapy: response and toxicity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1978 Nov-Dec;4(11-12):937–950. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(78)90003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. L., Dagle G. E., Cannon W. C., Craig D. K., Powers G. J., Meier D. M. Inhalation carcinogenesis of high-fired 239PuO2 in rats. Radiat Res. 1976 Nov;68(2):349–360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. L., Dagle G. E., Cannon W. C., Powers G. J., Meier D. M. Inhalation carcinogenesis of high-fired 238PuO2 in rats. Radiat Res. 1977 Sep;71(3):528–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. L. Deposition patterns and the toxicity of transuranium elements in lung. Health Phys. 1972 Jun;22(6):607–615. doi: 10.1097/00004032-197206000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. L. Inhalation toxicology of 238PuO2 and 239PuO2 in Syrian golden hamsters. Radiat Res. 1977 May;70(2):334–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. L., Jr Carcinogenicity of inhaled plutonium-238 in the rat. Radiat Res. 1973 Dec;56(3):540–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders C. L., Mahaffey J. A. Inhalation carcinogenesis of repeated exposures to high-fired 239PuO2 in rats. Health Phys. 1981 Oct;41(4):629–644. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198110000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Dixon F. J. The effect of in vivo irradiation on macrophage function. J Immunol. 1973 Mar;110(3):848–854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidtke J. R., Dixon F. J. The functional capacity of x-irradiated macrophages. J Immunol. 1972 Jun;108(6):1624–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott B. R. Proposed estimates of te probability of inducing pulmonary injury sufficient to cause death from radiation pneumonitis and pulmonary fibrosis after briefly inhaling a mixture of insoluble beta-emitting particles. Health Phys. 1980 Apr;38(4):635–642. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198004000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Hutcheson E. T., Kang A. H. Collagen polymorphism in idiopathic chronic pulmonary fibrosis. J Clin Invest. 1976 Jun;57(6):1498–1507. doi: 10.1172/JCI108420. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Rodnan G. Investigation of type I and type III collagens of the lung in progressive systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum. 1981 Apr;24(4):625–631. doi: 10.1002/art.1780240410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharplin J., Franko A. J. Irradiation of mouse lungs causes a dose-dependent increase in lung weight. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982 Jun;8(6):1065–1069. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(82)90179-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shrivastava P. N., Hans L., Concannon J. P. Changes in pulmonary compliance and production of fibrosis in x-irradiated lungs of rats. Radiology. 1974 Aug;112(2):439–440. doi: 10.1148/112.2.439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemann D. W., Hill R. P., Penney D. P. Early and late pulmonary toxicity in mice evaluated 180 and 420 days following localized lung irradiation. Radiat Res. 1982 Feb;89(2):396–407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slauson D. O., Hahn F. F., Benjamin S. A., Chiffelle T. L., Jones R. K. Inflammatory sequences in acute pulmonary radiation injury. Am J Pathol. 1976 Mar;82(3):549–572. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. G., Doll R. Mortality among patients with ankylosing spondylitis after a single treatment course with x rays. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Feb 13;284(6314):449–460. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6314.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith P. G., Doll R. Mortality from cancer and all causes among British radiologists. Br J Radiol. 1981 Mar;54(639):187–194. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-54-639-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider G. L., Celli B. R., Goldstein R. H., O'Brien J. J., Lucey E. C. Chronic interstitial pulmonary fibrosis produced in hamsters by endotracheal bleomycin. Lung volumes, volume-pressure relations, carbon monoxide uptake, and arterial blood gas studied. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1978 Feb;117(2):289–297. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1978.117.2.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Surina A. G. Zavisimost' izmeneniia soderzhaniia oksiprolina i lipidov v legkikh krys ot kolichestva vvedennogo plutoniia. Radiobiologiia. 1976 May-Jun;16(3):344–347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMPLE L. A., MARKS S., BAIR W. J. Tumours in mice after pulmonary deposition of radioactive particles. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1960 Apr;2:143–156. doi: 10.1080/09553006014550161. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarling J. D., Coggle J. E. Evidence for the pulmonary origin of alveolar macrophages. Cell Tissue Kinet. 1982 Nov;15(6):577–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1982.tb01064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarling J. D., Coggle J. E. The absence of effect on pulmonary alveolar macrophage numbers during prolonged periods of monocytopenia. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1982 Mar;31(3):221–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teates C. D. The effects of unilateral thoracic irradiation on pulmonary blood flow. Am J Roentgenol Radium Ther Nucl Med. 1968 Apr;102(4):875–882. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E., Storb R., Clift R. A., Fefer A., Johnson F. L., Neiman P. E., Lerner K. G., Glucksberg H., Buckner C. D. Bone-marrow transplantation (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975 Apr 17;292(16):832–843. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197504172921605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas R. L., Scott J. K., Chiffelle T. L. Metabolism and toxicity of inhaled 144 Ce in rats. Radiat Res. 1972 Mar;49(3):598–610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis E. L., Down J. D., Holmes S. J., Hobson B. Radiation pneumonitis and fibrosis in mouse lung assayed by respiratory frequency and histology. Radiat Res. 1980 Oct;84(1):133–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis E. L., Down J. D. Repair in mouse lung after split doses of X rays. Radiat Res. 1981 Jul;87(1):166–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis E. L., Harley R. A., Fenn J. O., Klobukowski C. J., Hargrove H. B. Pathologic changes in the lung following single and multi-fraction irradiation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1977 May-Jun;2(5-6):475–490. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(77)90159-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis E. L. The sequence of histological changes in mouse lungs after single doses of x-rays. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1980 Mar;6(3):345–347. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(80)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travis E. L., Vojnovic B., Davies E. E., Hirst D. G. A plethysmographic method for measuring function in locally irradiated mouse lung. Br J Radiol. 1979 Jan;52(613):67–74. doi: 10.1259/0007-1285-52-613-67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseveleva I. A. Biosintez kollagena v legkikh krys pri radiatsionnom porazhenii. Vopr Med Khim. 1974 Nov-Dec;20(6):640–643. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseveleva I. A., Libinzon R. E., Mushkacheva G. S., Rysina T. N., Surina A. G. Biokhimicheskie izmeneniia legkikh krolikov posle ingaliatsii plutoniia. Radiobiologiia. 1968 Jul-Aug;8(4):535–541. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseveleva I. A. Obmen glikozaminoglikanov (kislykh mukopolisakharidov) v legkikh krolikov pri porazhenii plutoniem. Vopr Med Khim. 1970 Jul-Aug;16(4):399–405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tseveleva I. A. Vliianie radiatsionnogo porazheniia legkikh na obmen glikozaminoglikanov. Vopr Med Khim. 1974 Mar-Apr;20(2):127–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsurufuji S., Ohuchi K. X-irradiation and ageing as reflected in the accumulation and insolubilization of collagen. Exp Gerontol. 1968 Dec;3(4):309–315. doi: 10.1016/0531-5565(68)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UPTON A. C., FURTH J., CHRISTENBERRY K. W. Late effects of thermal neutron irradiation in mice. Cancer Res. 1954 Oct;14(9):682–690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UPTON A. C., KIMBALL A. W., FURTH J., CHRISTENBERRY K. W., BENEDICT W. H. Some delayed effects of atom-bomb radiations in mice. Cancer Res. 1960 Sep;20(8):1–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich R. L. Effects of split doses of x rays or neutrons on lung tumor formation in RFM mice. Radiat Res. 1980 Jul;83(1):138–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich R. L., Jernigan M. C., Adams L. M. Induction of lung tumors in RFM mice after localized exposures to X rays or neutrons. Radiat Res. 1979 Dec;80(3):464–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich R. L., Jernigan M. C., Cosgrove G. E., Satterfield L. C., Bowles N. D., Storer J. B. The influence of dose and dose rate on the incidence of neoplastic disease in RFM mice after neutron irradiation. Radiat Res. 1976 Oct;68(1):115–131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich R. L., Meyer K. R. The influence of butylated hydroxytoluene-induced cell proliferation on mouse lung damage after x rays or fission neutrons. Radiat Res. 1982 Feb;89(2):428–432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich R. L., Storer J. B. Influence of gamma irradiation on the development of neoplastic disease in mice. III. Dose-rate effects. Radiat Res. 1979 Nov;80(2):325–342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Upton A. C., Randolph M. L., Conklin J. W., Kastenbaum M. A., Slater M., Melville G. S., Jr, Conte F. P., Sproul J. A., Jr Late effects of fast neutrons and gamma-rays in mice as influenced by the dose rate of irradiation: induction of neoplasia. Radiat Res. 1970 Mar;41(3):467–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Dyk J., Keane T. J., Kan S., Rider W. D., Fryer C. J. Radiation pneumonitis following large single dose irradiation: a re-evaluation based on absolute dose to lung. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1981 Apr;7(4):461–467. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(81)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velo G. P., Spector W. G. The origin and turnover of alveolar macrophages in experimental pneumonia. J Pathol. 1973 Jan;109(1):7–19. doi: 10.1002/path.1711090103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wara W. M., Phillips T. L., Margolis L. W., Smith V. Radiation pneumonitis: a new approach to the derivation of time-dose factors. Cancer. 1973 Sep;32(3):547–552. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197309)32:3<547::aid-cncr2820320306>3.0.co;2-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward W. F., Shih-Hoellwarth A., Tuttle R. D. Collagen accumulation in irradiated rat lung: modification by D-penicillamine. Radiology. 1983 Feb;146(2):533–537. doi: 10.1148/radiology.146.2.6849102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren S., Gates O. Cancers induced in different species by continuous gamma-radiation. Arch Environ Health. 1968 Nov;17(5):697–704. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1968.10665308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Watanabe K., Oishi T., Aiba M., Kageyama K. Mast cells in the rat alveolar septa undergoing fibrosis after ionizing irradiation. Ultrastructural and histochemical studies. Lab Invest. 1974 Nov;31(5):555–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss W., Boucot K. R., Seidman H., Carnahan W. J. Risk of lung cancer according to histologic type and cigarette dosage. JAMA. 1972 Nov 13;222(7):799–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright E. S., Couves C. M. Radiation-induced carcinoma of the lung--the St. Lawrence tragedy. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1977 Oct;74(4):495–498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuhas J. M., Walker A. E. Exposure-response curve for radiation-induced lung tumors in the mouse. Radiat Res. 1973 May;54(2):261–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Bekkum D. W., Bentvelzen P. The concept of gene transfer-misrepair mechanism of radiation carcinogenesis may challenge the linear extrapolation model of risk estimation for low radiation doses. Health Phys. 1982 Aug;43(2):231–237. doi: 10.1097/00004032-198208000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



