Abstract
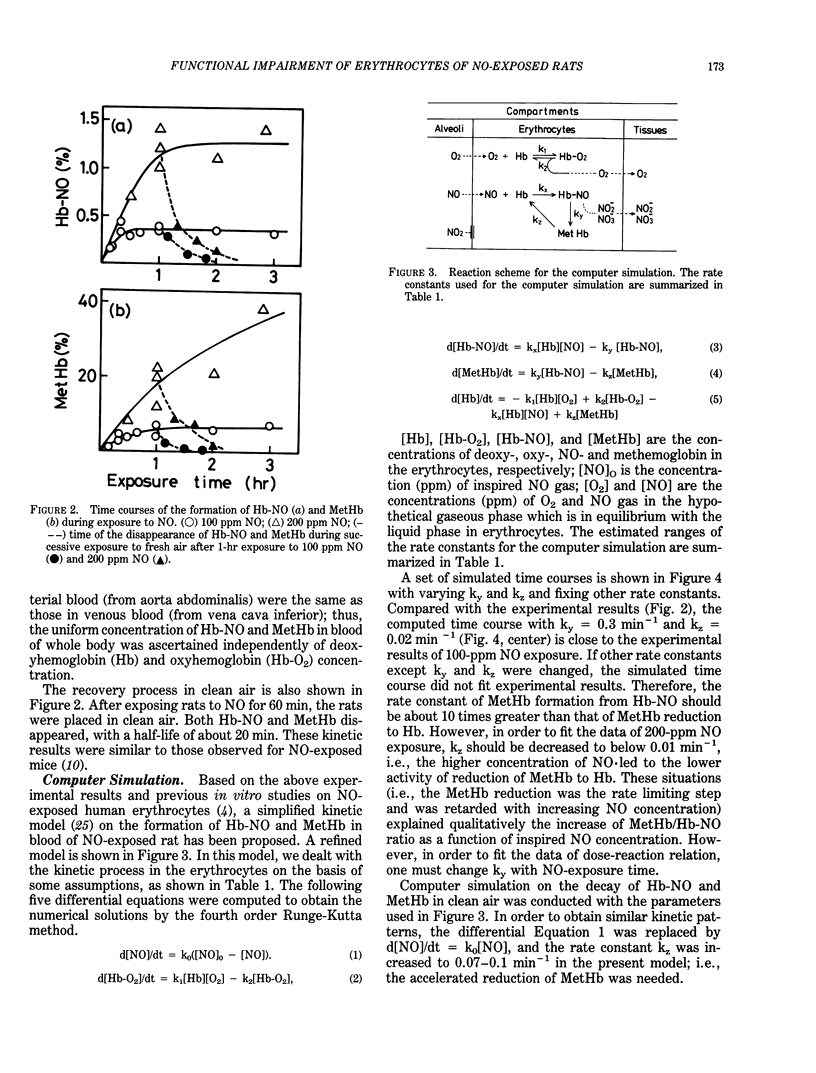
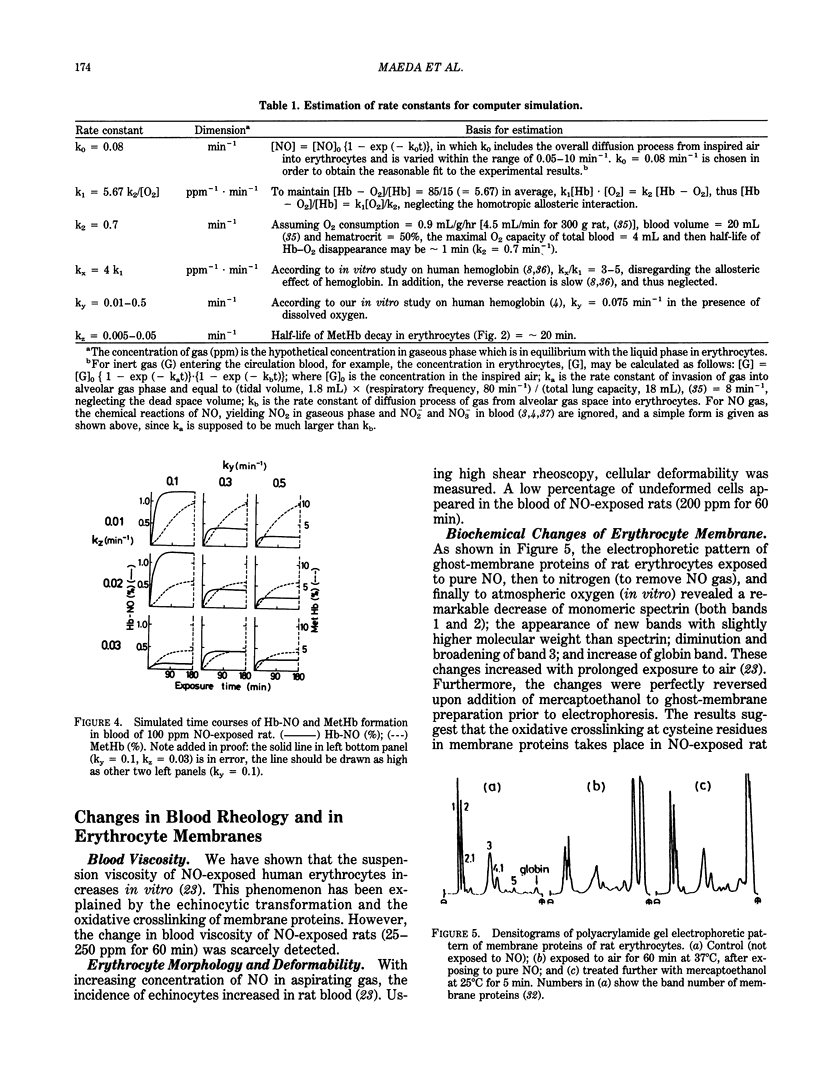
In acute in vivo exposure of rats to 25 to 250 ppm nitric oxide (NO) by use of a small exposure chamber for a single rat, the kinetic parameters of nitrosylhemoglobin (Hb-NO) and methemoglobin (MetHb) formation were estimated (with the aid of computer simulation) on the basis of experimental data. The biochemical and rheological injuries of erythrocytes were also examined. The time course of Hb-NO and MetHb formation in blood was compared with that simulated by a simplified kinetic model. The rate of MetHb formation from Hb-NO was much faster than MetHb reduction to ferrous form and dissociation of Hb-NO; thus, MetHb content was always greater than Hb-NO content. The activity of MetHb reduction decreased on exposure to a high concentration of NO, but the activity was recovered when rats were placed in clean air. Rheologically, the blood viscosity was scarcely altered, but a few undeformed cells were detected at high shear stress. Morphologically, echinocytic transformation was observed to some extent. Biochemically, the crosslinking of membrane proteins and the alteration of acyl chain composition of membrane phospholipids were not detected in the in vivo exposure, though the in vitro exposure of rat erythrocytes to high concentrations of NO revealed remarkable oxidative crosslinking among membrane proteins and hemoglobin. In conclusion, both for persistent methemoglobinemia and for membrane damage, the maintenance of reductive activity in erythrocytes is the most important determinant factor for the protection of NO-induced oxidative injury.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alloisio N., Michelon D., Bannier E., Revol A., Beuzard Y., Delaunay J. Alterations of red cell membrane proteins and hemoglobin under natural and experimental oxidant stress. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 7;691(2):300–308. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(82)90419-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayres S. M., Evans R., Licht D., Griesbach J., Reimold F., Ferrand E. F., Criscitiello A. Health effects of exposure to high concentrations of automotive emissions. Studies in bridge and tunnel workers in New York City. Arch Environ Health. 1973 Sep;27(3):168–178. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1973.10666347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Case G. D., Dixon J. S., Schooley J. C. Interactions of blood metalloproteins with nitrogen oxides and oxidant air pollutants. Environ Res. 1979 Oct;20(1):43–65. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(79)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassoly R., Gibson Q. Conformation, co-operativity and ligand binding in human hemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jan 25;91(3):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flynn T. P., Allen D. W., Johnson G. J., White J. G. Oxidant damage of the lipids and proteins of the erythrocyte membranes in unstable hemoglobin disease. Evidence for the role of lipid peroxidation. J Clin Invest. 1983 May;71(5):1215–1223. doi: 10.1172/JCI110870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman B. A., Crapo J. D. Biology of disease: free radicals and tissue injury. Lab Invest. 1982 Nov;47(5):412–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GIBSON Q. H., ROUGHTON F. J. The kinetics and equilibria of the reactions of nitric oxide with sheep haemoglobin. J Physiol. 1957 May 23;136(3):507–524. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jain S. K., Hochstein P. Polymerization of membrane components in aging red blood cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jan 15;92(1):247–254. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)91545-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon H., Kataoka N. Electron paramagnetic resonance of nitric oxide--protoheme complexes with some nitrogenous base. Model systems of nitric oxide hemoproteins. Biochemistry. 1969 Dec;8(12):4757–4762. doi: 10.1021/bi00840a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon K., Maeda N., Sekiya M., Shiga T., Suda T. A method for studying oxygen diffusion barrier in erythrocytes: effects of haemoglobin content and membrane cholesterol. J Physiol. 1980 Dec;309:569–590. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1980.sp013528. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon K., Maeda N., Shiga T. Effect of nitric oxide on the oxygen transport of human erythrocytes. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1977 May;2(5):1109–1113. doi: 10.1080/15287397709529508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon K., Maeda N., Shiga T. Functional impairments of human red cells, induced by dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate. Pflugers Arch. 1982 Oct 1;394(4):279–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00583691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon K., Maeda N., Shiga T. The influence of deformation of transformed erythrocytes during flow on the rate of oxygen release. J Physiol. 1983 Jun;339:573–584. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1983.sp014734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kon K., Maeda N., Suda T., Sekiya M., Shiga T. Protective effect of alpha-tocopherol on the morphological and rheological changes of rat red cells. Acta Haematol. 1983;69(2):111–116. doi: 10.1159/000206864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Imaizumi K., Imai K., Tyuma I. Stoichiometry of the reaction of oxyhemoglobin with nitrite. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Nov 23;581(1):184–188. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90235-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Imaizumi K., Tyuma I. Mechanism of autocatalytic oxidation of oxyhemoglobin by nitrite. An intermediate detected by electron spin resonance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Apr 3;702(2):237–241. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Tyuma I. Production of superoxide anion by N,N-bis(2-hydroxyethyl)-iminotris(hydroxymethyl)methane buffer during oxidation of oxyhemoglobin by nitrite and effect of inositol hexaphosphate on the oxidation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Dec 20;709(2):187–193. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(82)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuma F. Properties of methemoglobin reductase and kinetic study of methemoglobin reduction. J Biol Chem. 1981 Jun 10;256(11):5518–5523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuma F., Prough R. A., Masters B. S. Studies on methemoglobin reductase. Immunochemical similarity of soluble methemoglobin reductase and cytochrome b5 of human erythrocytes with NADH-cytochrome b5 reductase and cytochrome b5 of rat liver microsomes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Feb;172(2):600–607. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda N., Kon K., Imaizumi K., Sekiya M., Shiga T. Alteration of rheological properties of human erythrocytes by crosslinking of membrane proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Oct 26;735(1):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(83)90265-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohandas N., Chasis J. A., Shohet S. B. The influence of membrane skeleton on red cell deformability, membrane material properties, and shape. Semin Hematol. 1983 Jul;20(3):225–242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore E. G., Gibson Q. H. Cooperativity in the dissociation of nitric oxide from hemoglobin. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 10;251(9):2788–2794. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrow P. E. Toxicological data on NOx: an overview. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1984;13(2-3):205–227. doi: 10.1080/15287398409530494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda H., Kusumoto S., Nakajima T. Nitrosyl-hemoglobin formation in the blood of animals exposed to nitric oxide. Arch Environ Health. 1975 Sep;30(9):453–456. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1975.10666749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda H., Nogami H., Kusumoto S., Nakajima T., Kurata A. Lifetime exposure to 2.4 ppm nitric oxide in mice. Environ Res. 1980 Jun;22(1):254–263. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(80)90137-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda H., Nogami H., Nakajima T. Reaction of hemoglobin with nitric oxide and nitrogen dioxide in mice. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1980 May;6(3):673–678. doi: 10.1080/15287398009529884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANCIER K. M., FREEMAN G., MILLS J. S. Electron spin resonance of nitric oxide- hemoglobin complexes in solution. Science. 1962 Sep 7;137(3532):752–754. doi: 10.1126/science.137.3532.752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sauberman N., Fortier N. L., Joshi W., Piotrowski J., Snyder L. M. Spectrin-haemoglobin crosslinkages associated with in vitro oxidant hypersensitivity in pathologic and artificially dehydrated red cells. Br J Haematol. 1983 May;54(1):15–28. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02063.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid-Schoenbein H., Wells R., Schildkraut R. Microscopy and viscometry of blood flowing under uniform shear rate (rheoscopy). J Appl Physiol. 1969 May;26(5):674–678. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1969.26.5.674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga T., Hwang K. J., Tyuma I. An electron paramagnetic resonance study of nitric oxide hemoglobin derivatives. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jan;123(1):203–205. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90121-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga T., Hwang K. J., Tyuma I. Electron paramagnetic resonance studies of nitric oxide hemoglobin derivatives. I. Human hemoglobin subunits. Biochemistry. 1969 Jan;8(1):378–383. doi: 10.1021/bi00829a052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga T., Imaizumi K. Electron spin resonance study on peroxidase- and oxidase-reactions of horse radish peroxidase and methemoglobin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1975 Apr;167(2):469–479. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(75)90489-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga T., Imaizumi K. Generation of phenoxy radicals by methemoglobin-hydrogen peroxide studies by electron paramagnetic resonance. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Feb;154(2):540–547. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiga T., Sekiya M., Maeda N., Kon K., Okazaki M. Cell age-dependent changes in deformability and calcium accumulation of human erythrocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Apr 11;814(2):289–299. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(85)90447-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. M., Fortier N. L., Trainor J., Jacobs J., Leb L., Lubin B., Chiu D., Shohet S., Mohandas N. Effect of hydrogen peroxide exposure on normal human erythrocyte deformability, morphology, surface characteristics, and spectrin-hemoglobin cross-linking. J Clin Invest. 1985 Nov;76(5):1971–1977. doi: 10.1172/JCI112196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder L. M., Leb L., Piotrowski J., Sauberman N., Liu S. C., Fortier N. L. Irreversible spectrin-haemoglobin crosslinking in vivo: a marker for red cell senescence. Br J Haematol. 1983 Mar;53(3):379–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1983.tb02038.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suda T., Maeda N., Shimizu D., Kamitsubo E., Shiga T. Decreased viscosity of human erythrocyte suspension due to drug-induced spherostomatocytosis. Biorheology. 1982;19(4):555–565. doi: 10.3233/bir-1982-19407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita Y., Nomura S., Yoneyama Y. Purification of reduced pyridine nucleotide dehydrogenase from human erythrocytes and methemoglobin reduction by the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):6072–6078. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoda A., Yubisui T., Tsuji A., Yoneyama Y. Kinetic studies on methemoglobin reduction by human red cell NADH cytochrome b5 reductase. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):3119–3123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ways P., Hanahan D. J. Characterization and quantification of red cell lipids in normal man. J Lipid Res. 1964 Jul;5(3):318–328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Kasama K., Kitabatake M., Imai M. Biotransformation of nitric oxide, nitrite and nitrate. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1983;52(2):103–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00405415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Kasama K., Kitabatake M., Okuda M., Imai M. Metabolic fate of nitric oxide. Int Arch Occup Environ Health. 1980;46(1):71–77. doi: 10.1007/BF00377461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


