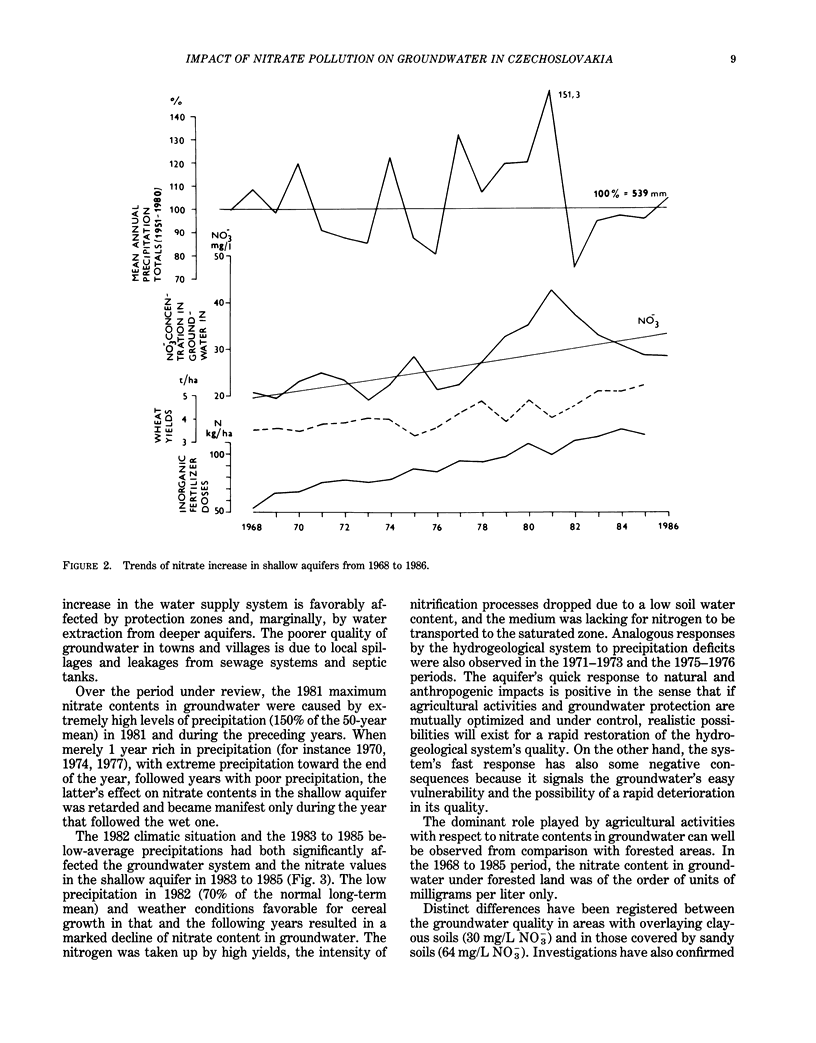
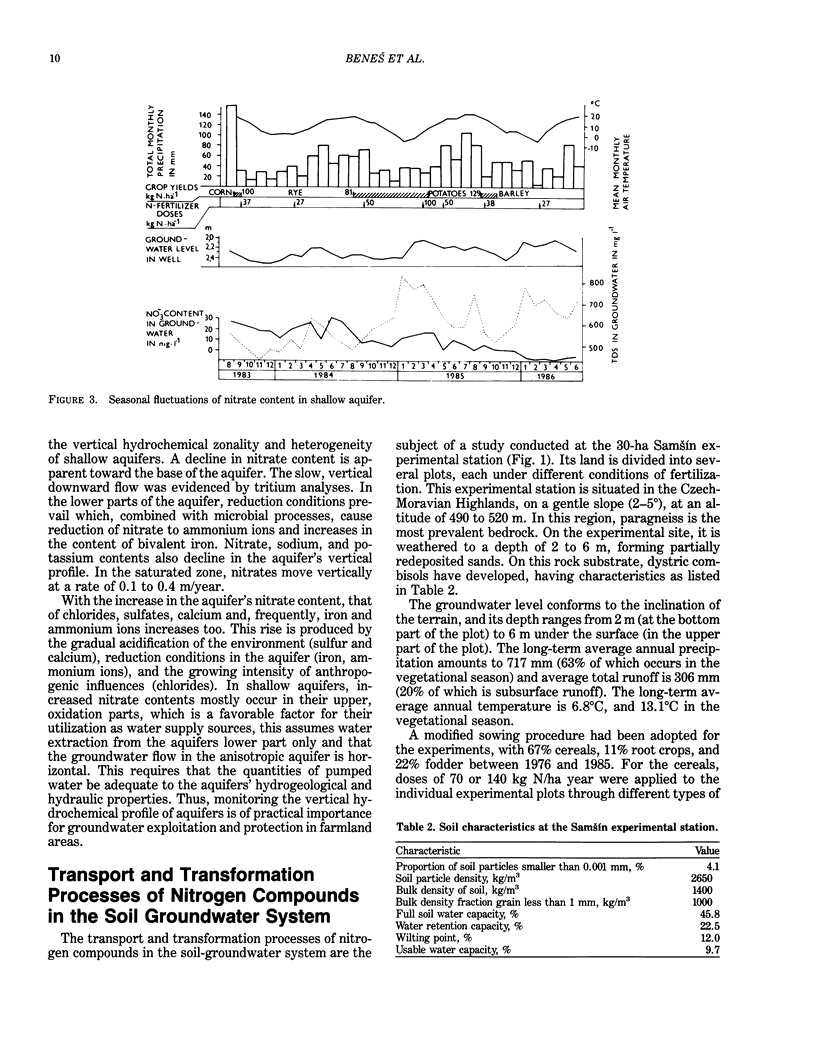
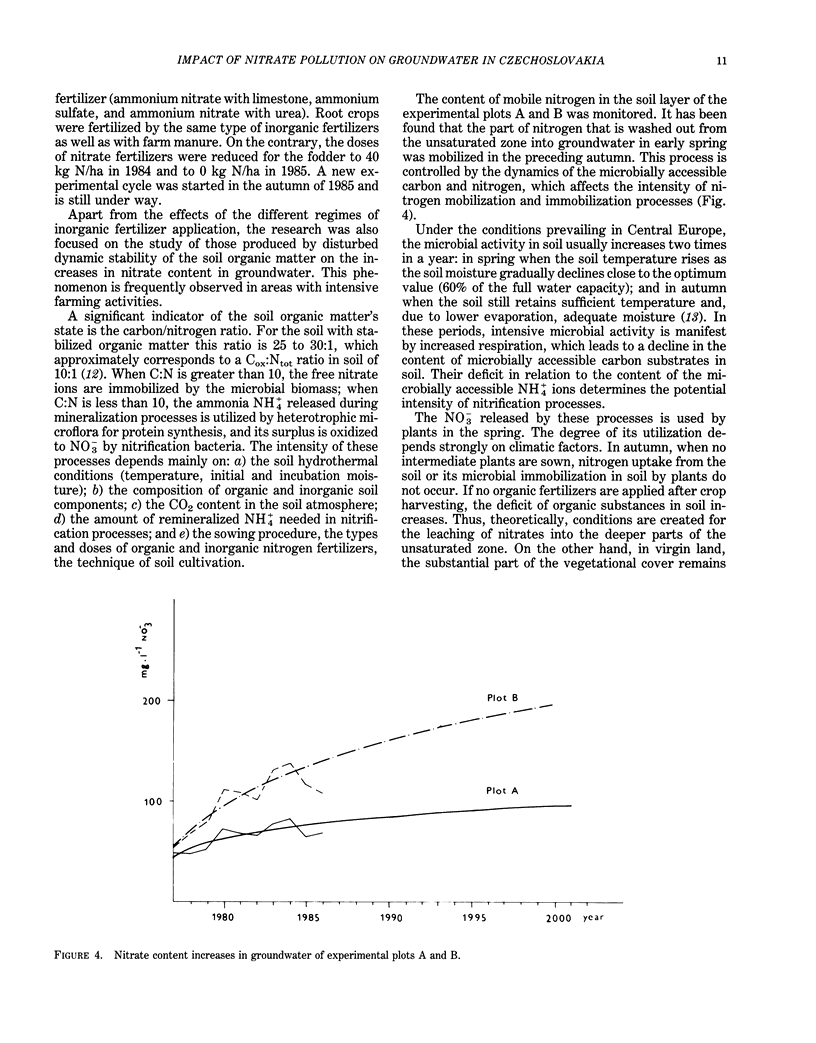
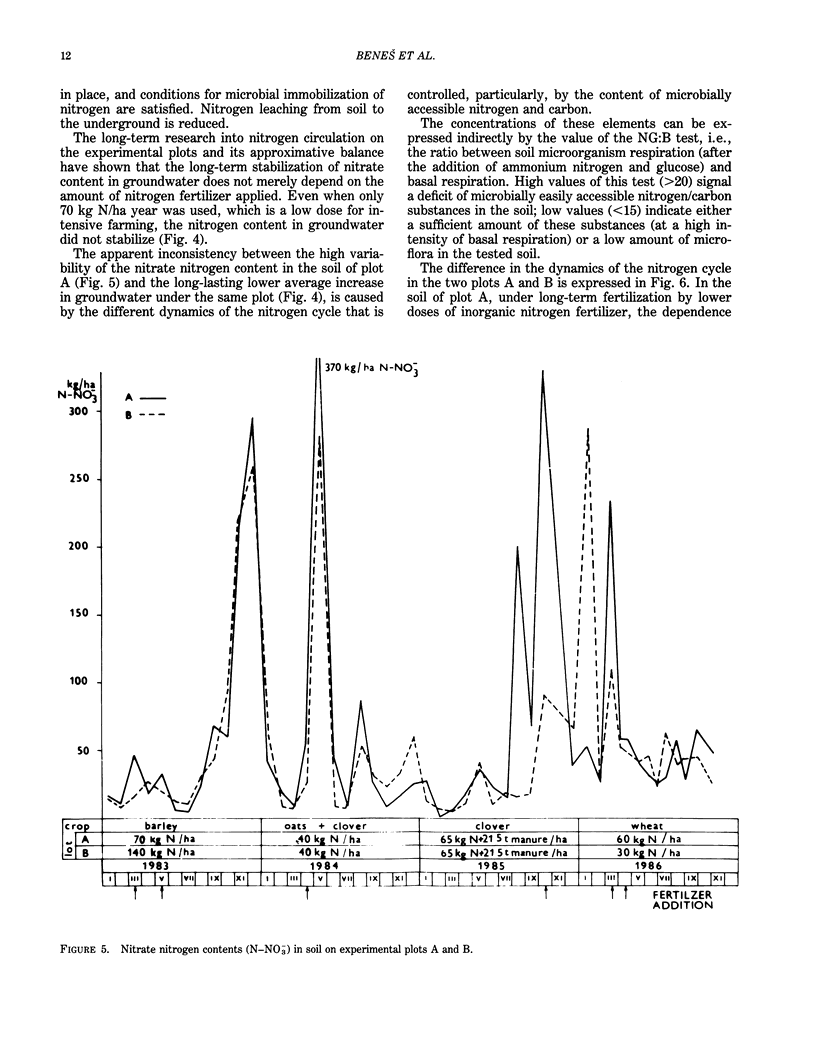
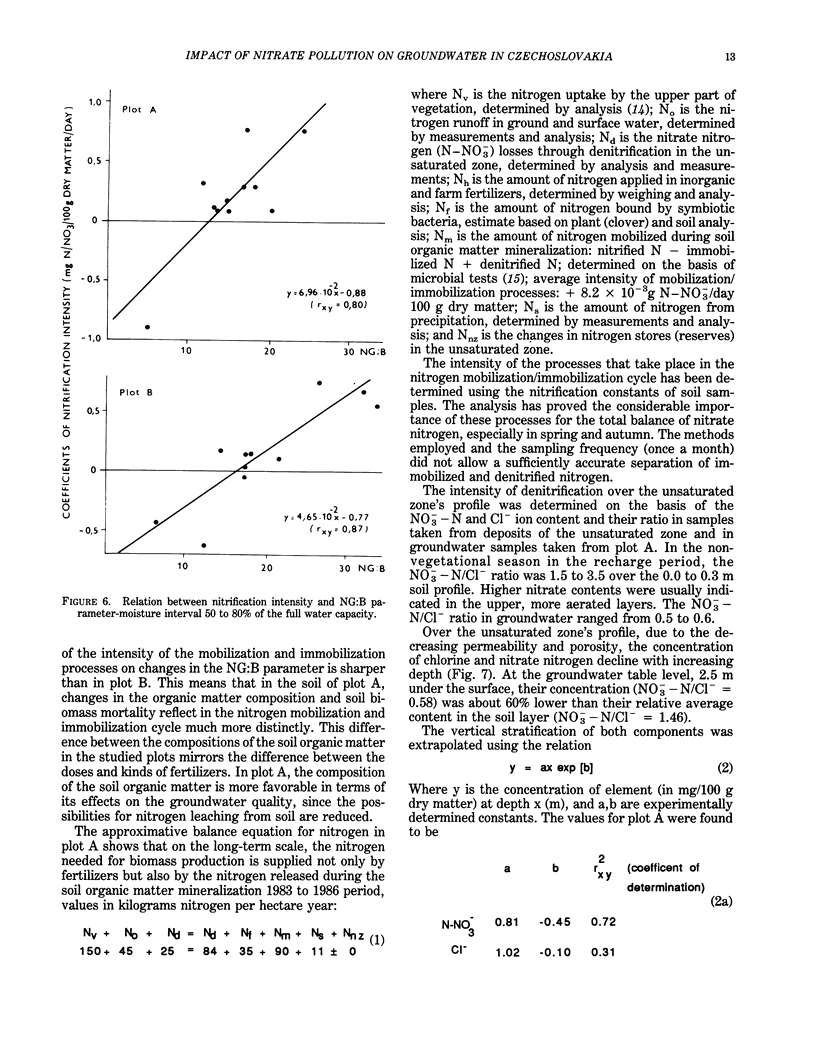
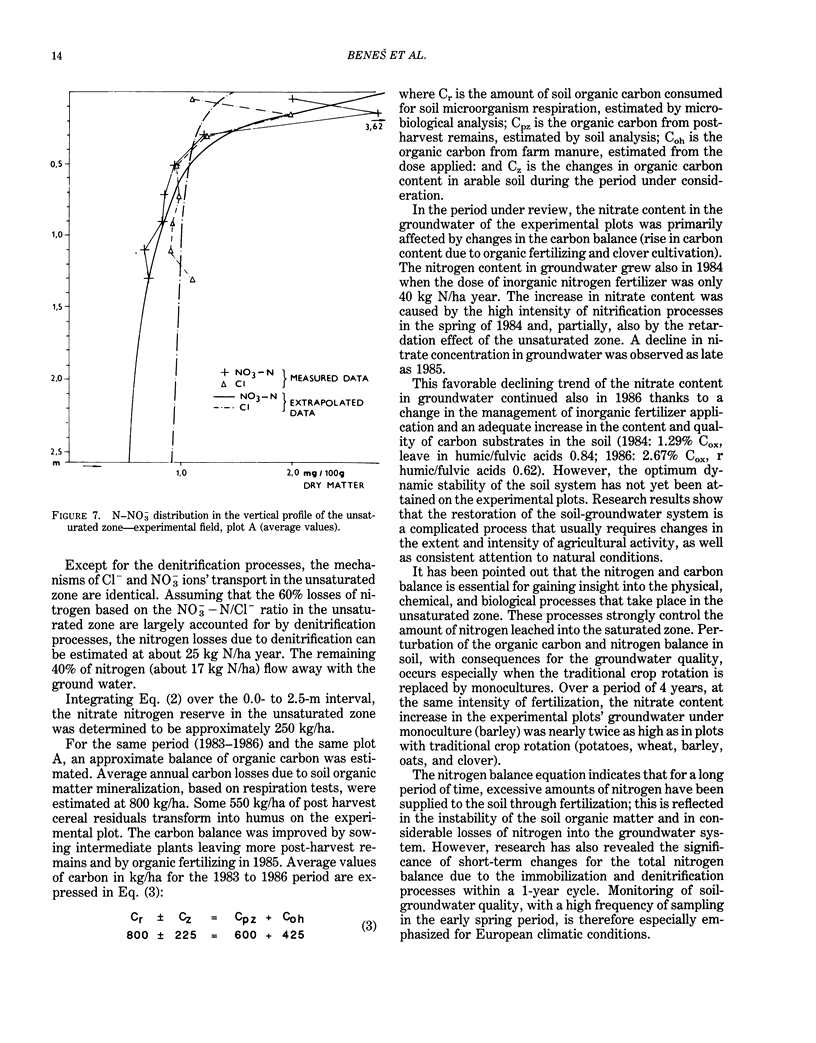
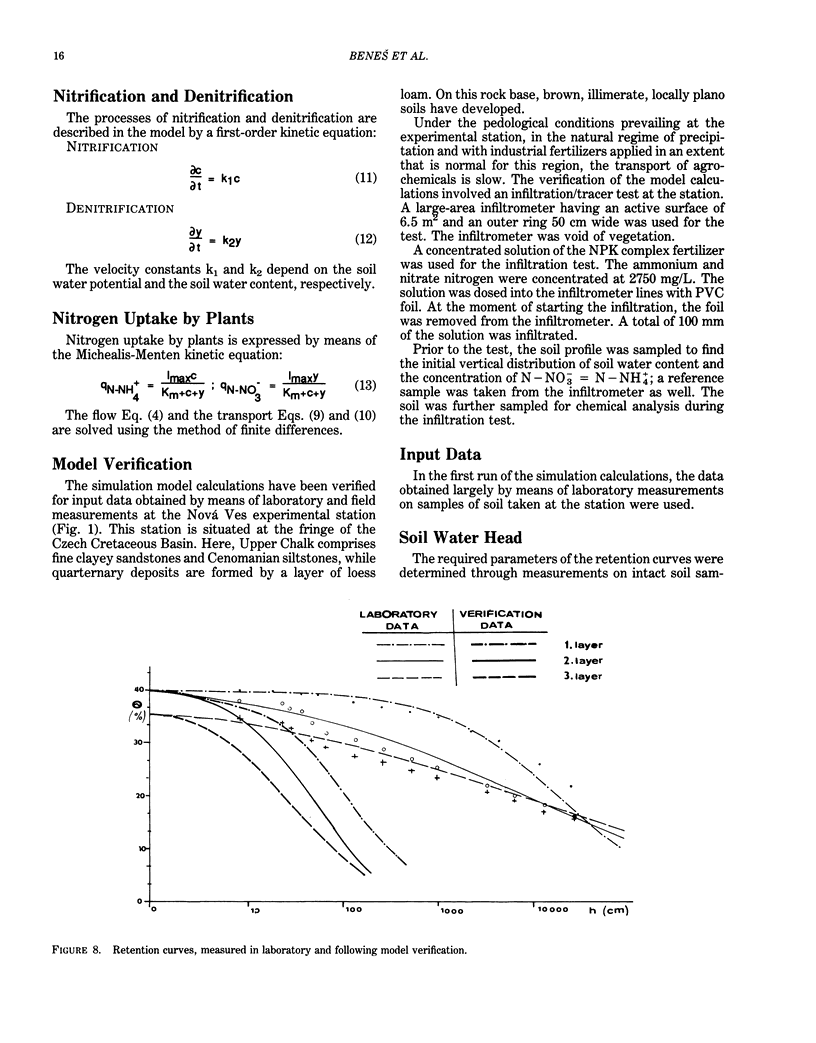
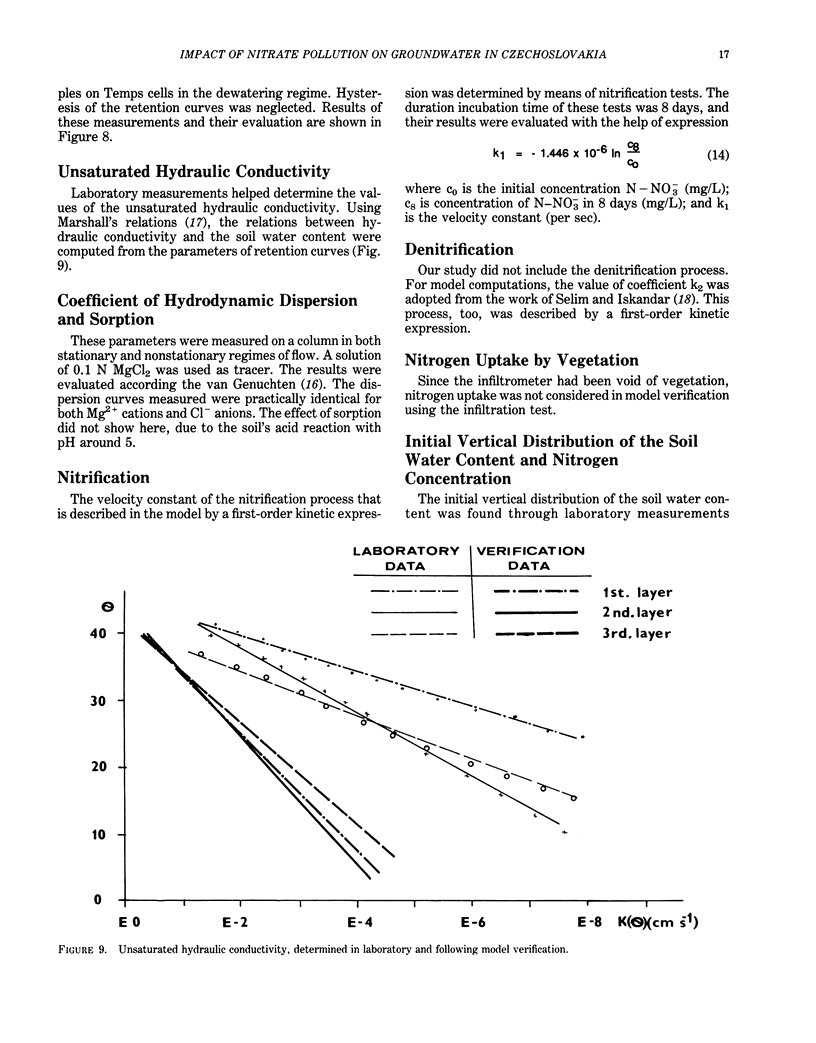
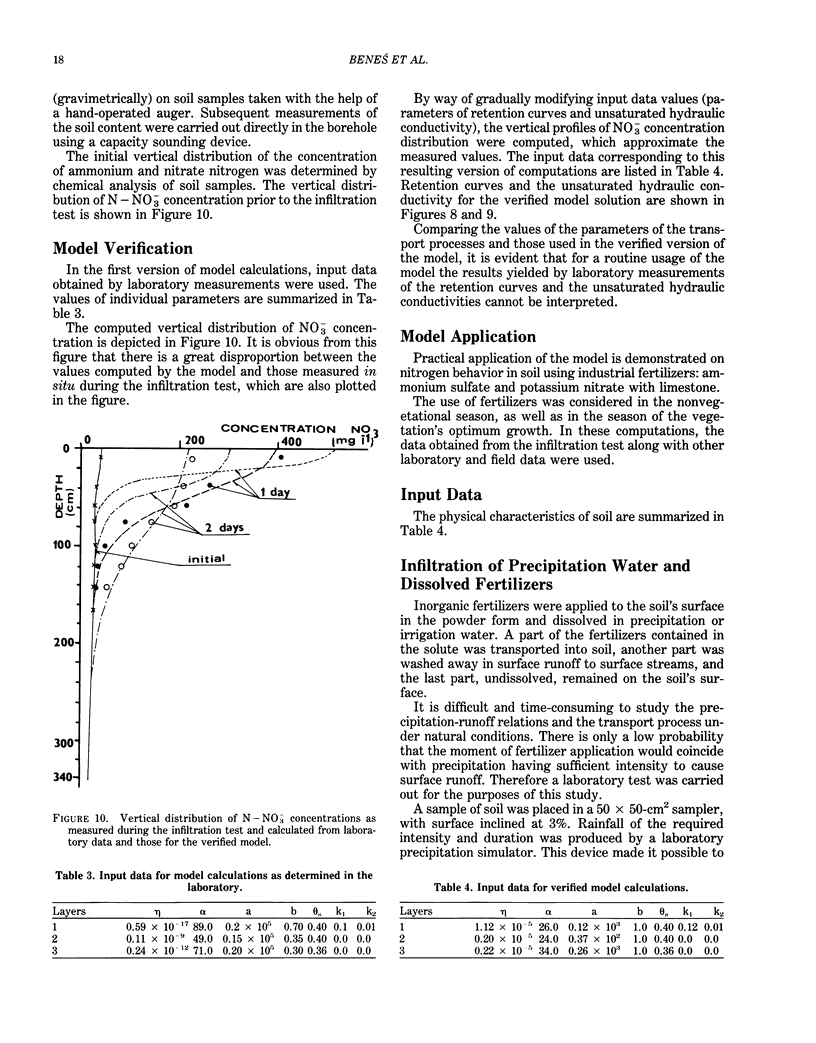
Abstract
In several regions of Czechoslovakia with intensive agricultural production, the correlation between the amount of nitrogen fertilizer applied and the nitrate content in groundwater has been recognized. Nitrate pollution of groundwater is considered to be the most serious source of nonpoint pollution in Czechoslovakia. A program of research into the effects of farming activities on groundwater quality in Czechoslovakia is under way on experimental fields (20 to 30 hectares) and, simultaneously, in regions in which shallow, vulnerable aquifers occur. The importance of the soil organic matter's stability for maintaining the groundwater quality is emphasized. Research based on nitrogen and organic carbon balance has shown that the restoration of a soil-groundwater system is a complicated process that usually requires changes in the extent and intensity of agricultural activities and consistent attention to the effects produced by natural conditions. Regional investigation of the impact of farming on shallow aquifers in the fluvial deposits of the Elbe River in Bohemia has proved the hydrochemical instability and vertical hydrochemical heterogeneity of these aquifers. The WASTEN deterministic model was used for modeling the transport and transformation of various types of inorganic fertilizers. The input data is based on laboratory and field measurements. Special topics are the verification of model calculations and the time and spatial variability of input data with respect to the unsaturated zone. The research results are being used for making regional and national agro-groundwater managerial schemes more precise, as well as for decision-making.
Full text
PDF