Abstract
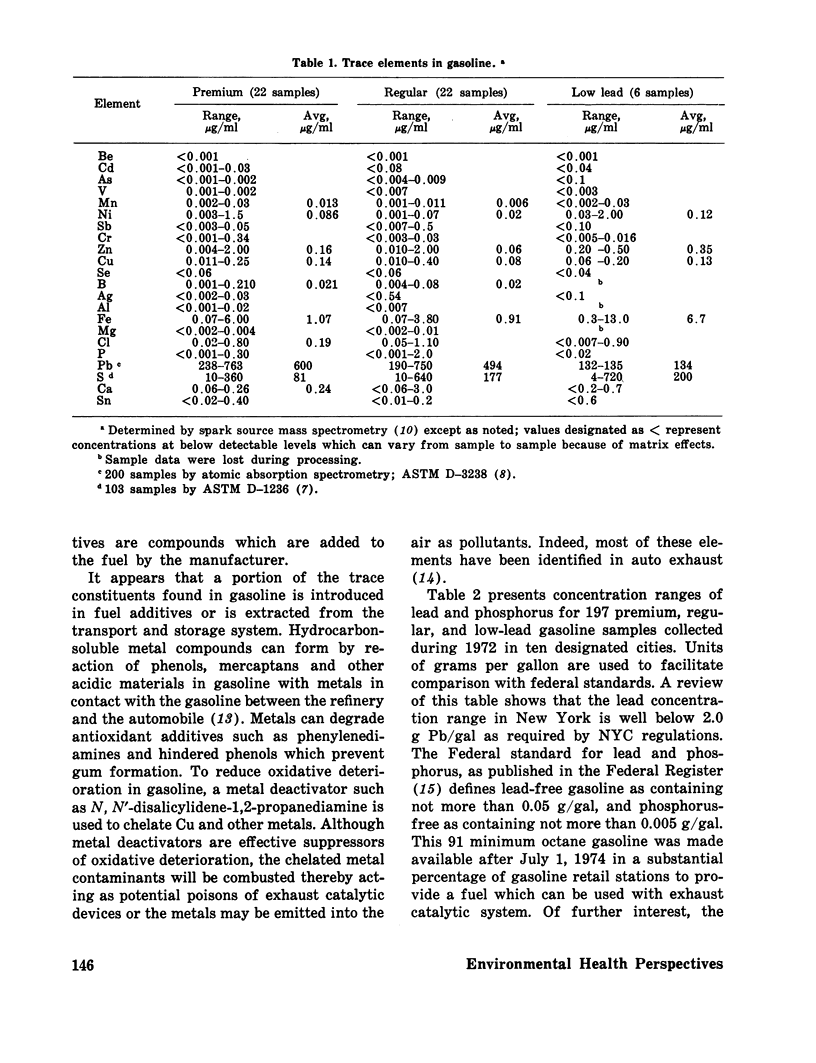
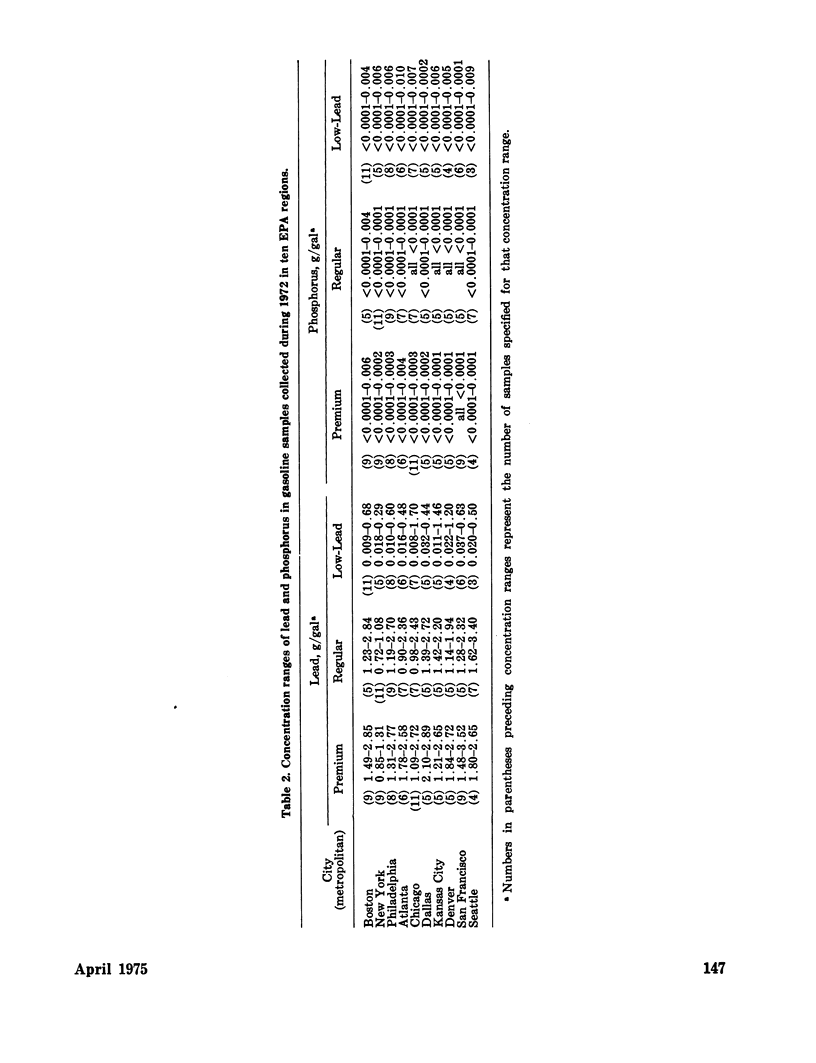
A National Fuels Surveillance Network has been established to collect gasoline and other fuels through the 10 regional offices of the Environmental Protection Agency. Physical, chemical, and trace element analytical determinations are made on the collected fuel samples to detect components which may present an air pollution hazard or poison exhaust catalytic control devices. A summary of trace elemental constituents in over 50 gasoline samples and 18 commercially marketed consumer purchased gasoline additives is presented. Quantities of Mn, Ni, Cr, Zn, Cu, Fe, Sb, B, Mg, Pb, and S were found in most regular and premium gasoline. Environmental implications of trace constituents in gasoline are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balgord W. D. Fine particles produced from automotive emissions-control catalysts. Science. 1973 Jun 15;180(4091):1168–1169. doi: 10.1126/science.180.4091.1168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORROW P. E. EVALUATION OF INHALATION HAZARDS BASED UPON THE RESPIRABLE DUST CONCEPT AND THE PHILOSOPHY AND APPLICATION OF SELECTIVE SAMPLING. Am Ind Hyg Assoc J. 1964 May-Jun;25:213–236. doi: 10.1080/00028896409342581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Lehmden D. J., Jungers R. H., Lee R. E., Jr Determination of trace elements in coal, fly ash, fuel oil, and gasoline--a preliminary comparison of selected analytical techniques. Anal Chem. 1974 Feb;46(2):239–245. doi: 10.1021/ac60338a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


