Abstract
Improved understanding of the factors determining the insecticidal activity, the mammalian toxicity, and the stability in air and light of natural and synthetic pyrethroids has led to a series of new compounds with a very favorable combination of properties. Their characteristics include outstanding potency to insects, low toxicity to mammals associated with rapid metabolic breakdown and, in appropriate cases, adequate stability on plant surfaces even in bright sunlight. Initial tests indicate that even the more stable compounds are degraded rapidly in soil, so if the trials at present in progress reveal no toxicological or environmental hazards, within a few years synthetic pyrethroids should be available to control a wide range of domestic, veterinary, horticultural, agricultural, and forest pests at low rates of application.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abernathy C. O., Casida J. E. Pyrethroid insecticides: esterase cleavage in relation to selective toxicity. Science. 1973 Mar 23;179(4079):1235–1236. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4079.1235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
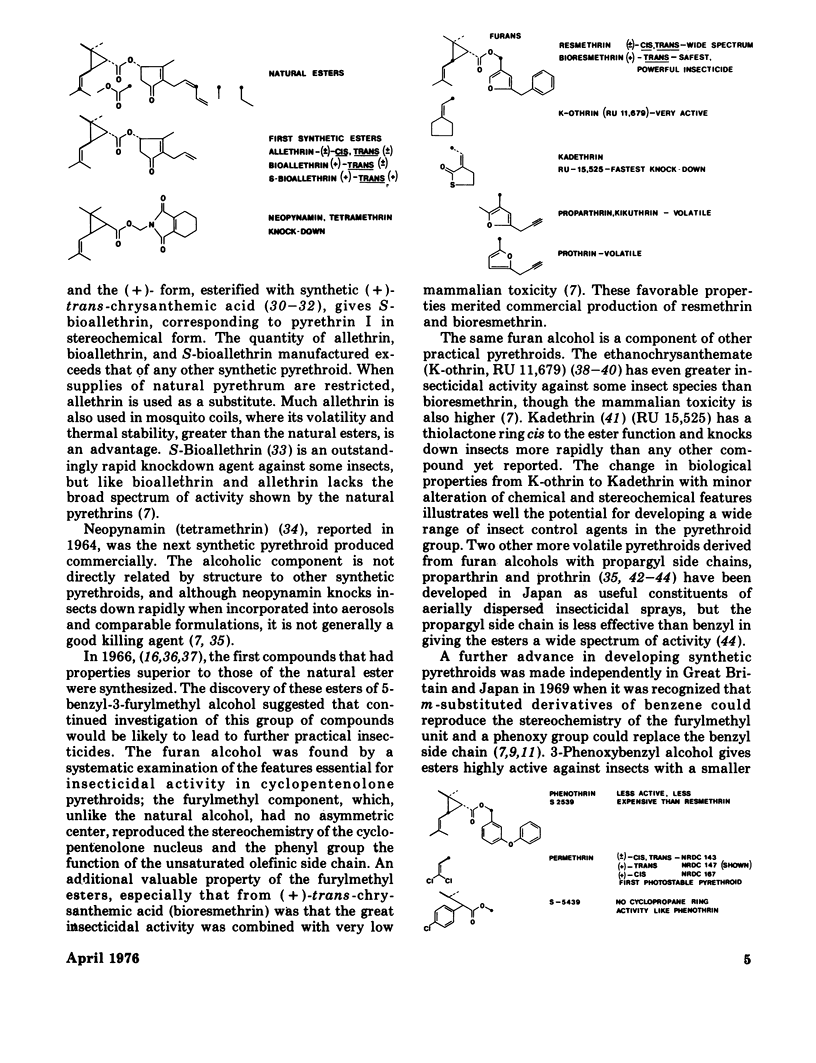
- CROMBIE L., ELLIOTT M. Chemistry of the natural pyrethrins. Fortschr Chem Org Naturst. 1961;19:120–164. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-7156-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
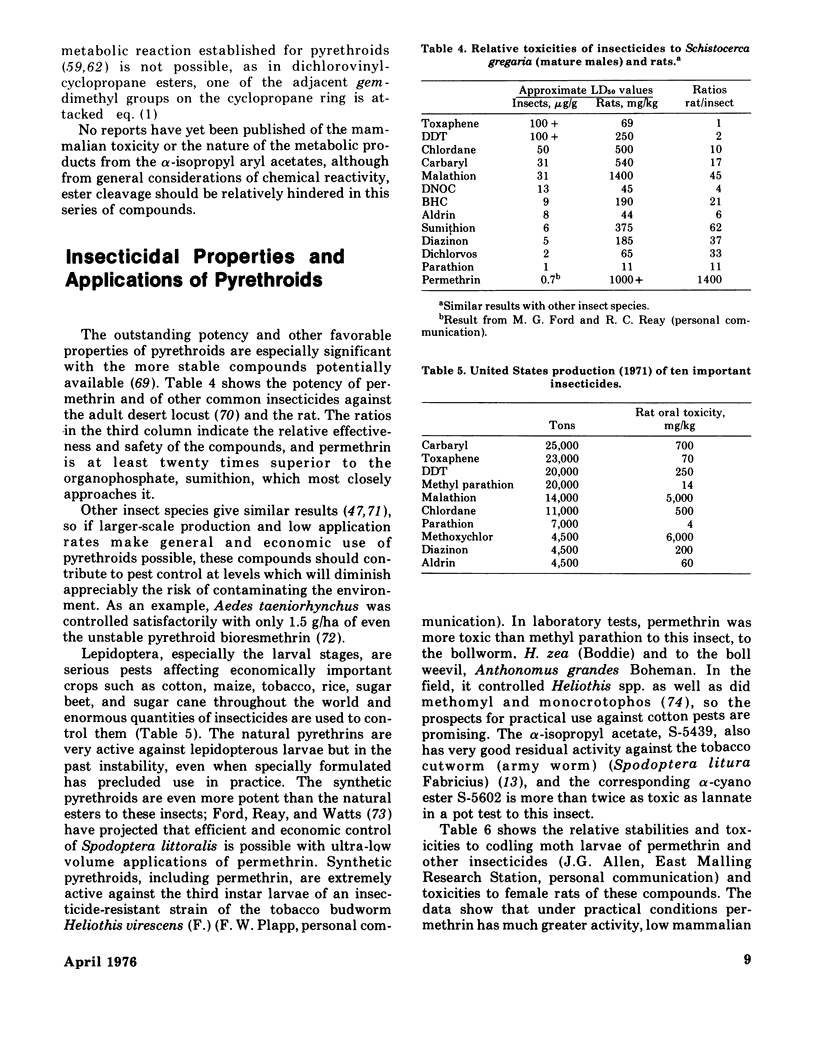
- Casida J. E., Kimmel E. C., Elliott M., Janes N. F. Oxidative metabolism of pyrethrins in mammals. Nature. 1971 Apr 2;230(5292):326–327. doi: 10.1038/230326a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casida J. E. Mixed-function oxidase involvement in the biochemistry of insecticide synergists. J Agric Food Chem. 1970 Sep-Oct;18(5):753–772. doi: 10.1021/jf60171a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J. W., Harding J. A., Wolfenbarger D. A. Activity of a synthetic pyrethroid against cotton insects. J Econ Entomol. 1975 Jun;68(3):373–374. doi: 10.1093/jee/68.3.373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
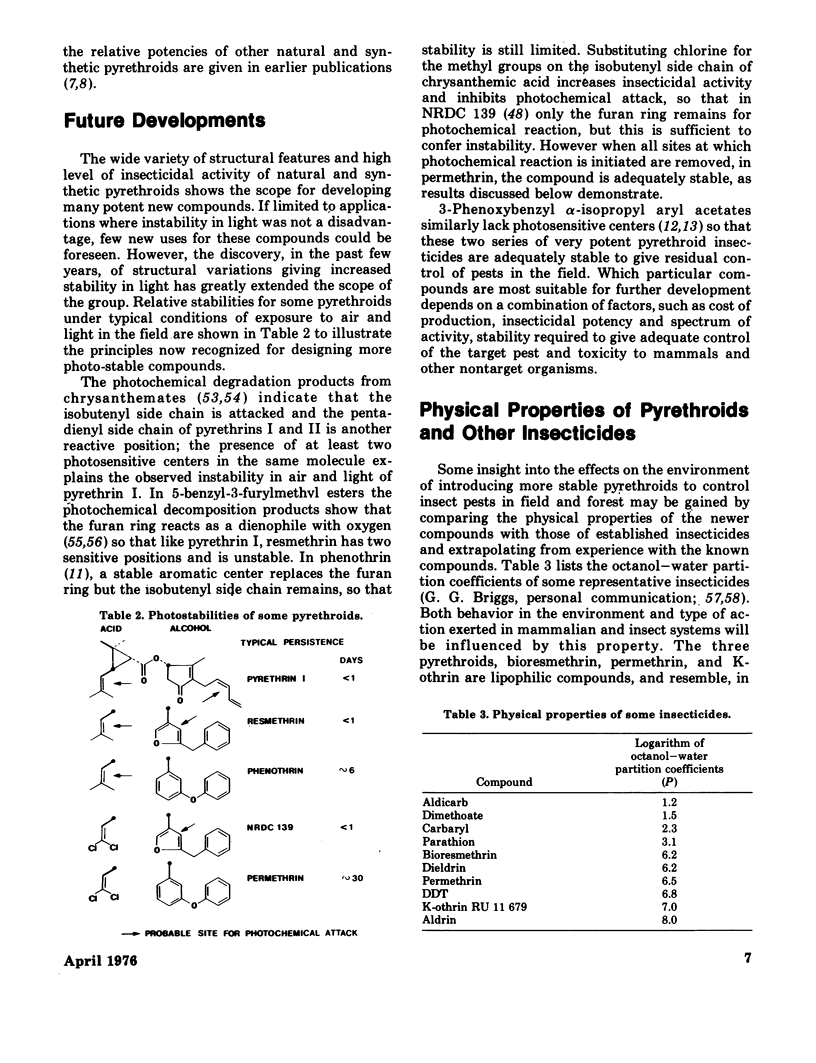
- Elliott M., Farnham A. W., Janes N. F., Needham P. H., Pulman D. A. Potent pyrethroid insecticides from modified cyclopropane acids. Nature. 1973 Aug 17;244(5416):456–457. doi: 10.1038/244456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M., Farnham A. W., Janes N. F., Needham P. H., Pulman D. A., Stevenson J. H. A photostable pyrethroid. Nature. 1973 Nov 16;246(5429):169–170. doi: 10.1038/246169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M., Farnham A. W., Janes N. F., Needham P. H., Pulman D. A. Synthetic insecticide with a new order of activity. Nature. 1974 Apr 19;248(5450):710–711. doi: 10.1038/248710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M., Janes N. F., Jeffs K. A., Needham P. H., Sawicki R. M. New pyrethrin-like esters with high insecticidal activity. Nature. 1965 Aug 28;207(5000):938–940. doi: 10.1038/207938a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M., Janes N. F., Kimmel E. C., Casida J. E. Metabolic fate of pyrethrin I, Pyrethrin II, and allethrin administered orally to rats. J Agric Food Chem. 1972 Mar-Apr;20(2):300–313. doi: 10.1021/jf60180a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M., Janes N. F., Pearson B. C. The pyrethrins and related compounds. XII. 5-substituted 3-furoates and 3-thenoates, intermediates for synthesis of insecticidal esters. J Chem Soc Perkin 1. 1971;14:2551–2557. doi: 10.1039/j39710002551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
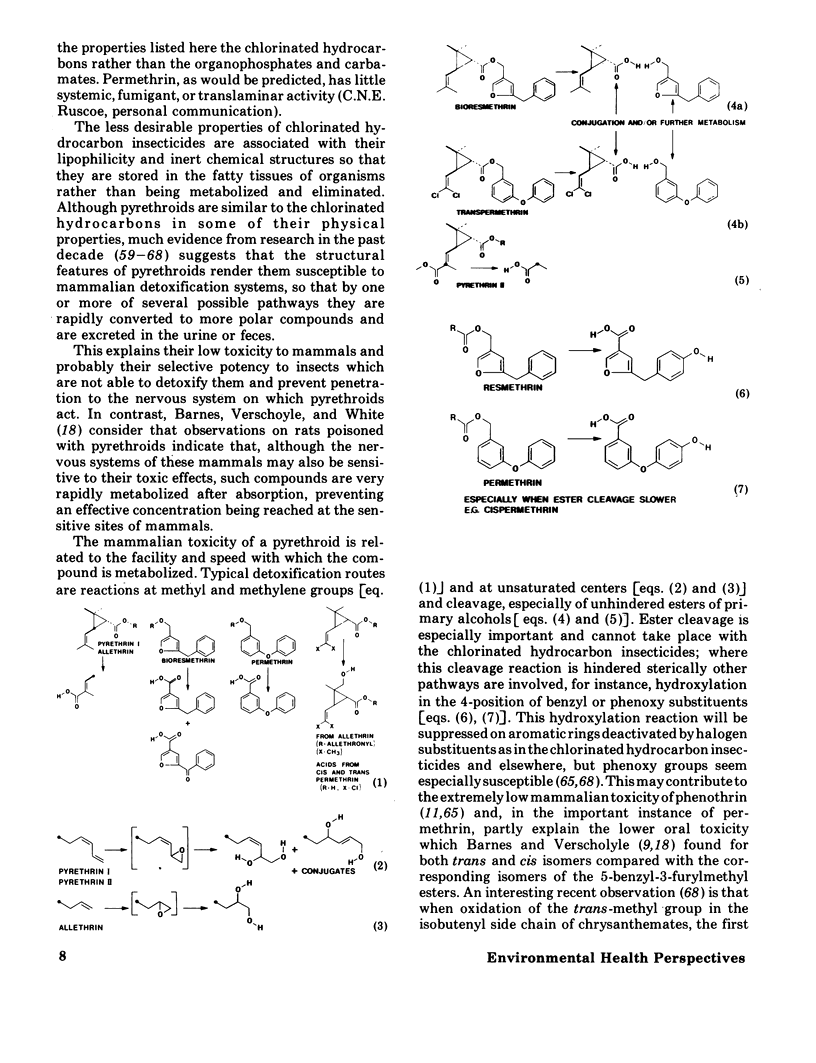
- Elliott M. Structural requirements for pyrethrin-like activity. Chem Ind. 1969 Jun 14;24:776–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elliott M. The relationship between the structure and the activity of pyrethroids. Bull World Health Organ. 1971;44(1-3):315–324. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyamoto J. Degradation, metabolism and toxicity of synthetic pyrethroids. Environ Health Perspect. 1976 Apr;14:15–28. doi: 10.1289/ehp.761415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Gaughan L. C., Casida J. E. Metabolism of (+)-trans- and (+)-cis-resmethrin in rats. J Agric Food Chem. 1975 Jan-Feb;23(1):106–115. doi: 10.1021/jf60197a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Gaughan L. C., Casida J. E. Photodecomposition of resmethrin and related pyrethroids. J Agric Food Chem. 1974 Mar-Apr;22(2):212–220. doi: 10.1021/jf60192a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


