Abstract
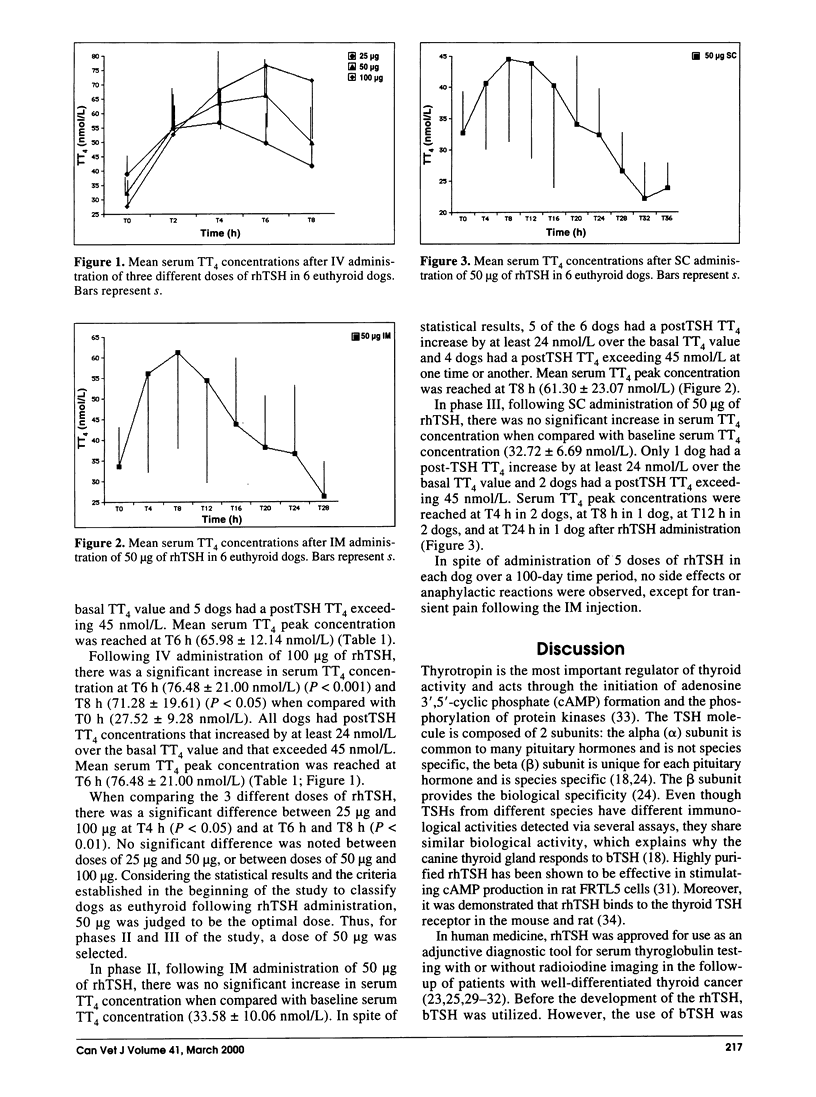
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the effects of the recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone (rhTSH) on serum total thyroxine (TT4) concentration in euthyroid dogs. Six healthy beagle dogs were used in each of the 3 phases of this study. Phase I: thyroid-stimulating hormone response tests were performed by using a total dose of 25 micrograms, 50 micrograms, and 100 micrograms of rhTSH, administered intravenously. Phases II and III: thyroid-stimulating hormone response tests were performed by using 50 micrograms of rhTSH administered by intramuscular and subcutaneous routes, respectively. In each phase and following all the administered doses of rhTSH, an increase in the serum TT4 concentration was noted, although it was not always significant. For phase I, there was a significant increase in serum TT4 concentrations. Based on this study, 50 micrograms was judged to be the optimal intravenous dose of rhTSH. For phases II and III, there was no significant increase in serum TT4 after the administration of rhTSH. Results of this study suggest that rhTSH could be a good substitute for bovine TSH, when used by the intravenous route, for the TSH stimulation test in dogs. Further studies are required to confirm its clinical usefulness.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beale K. M., Helm L. J., Keisling K. Comparison of two doses of aqueous bovine thyrotropin for thyroid function testing in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1990 Oct 1;197(7):865–867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braverman L. E., Pratt B. M., Ebner S., Longcope C. Recombinant human thyrotropin stimulates thyroid function and radioactive iodine uptake in the rhesus monkey. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1992 May;74(5):1135–1139. doi: 10.1210/jcem.74.5.1569160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canonne C., Papandreou M. J., Medri G., Verrier B., Ronin C. Biological and immunochemical characterization of recombinant human thyrotrophin. Glycobiology. 1995 Jul;5(5):473–481. doi: 10.1093/glycob/5.5.473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chastain C. B. Canine hypothyroidism. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1982 Aug 15;181(4):349–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colzani R. M., Alex S., Fang S. L., Braverman L. E., Emerson C. H. The effect of recombinant human thyrotropin (rhTSH) on thyroid function in mice and rats. Thyroid. 1998 Sep;8(9):797–801. doi: 10.1089/thy.1998.8.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. M., Graham P. A., Mooney C. T. Serum thyrotropin concentrations: a new diagnostic test for canine hypothyroidism. Vet Rec. 1996 Jun 15;138(24):594–595. doi: 10.1136/vr.138.24.594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson D. C. Update on diagnosis of canine hypothyroidism. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1994 May;24(3):515–539. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(94)50057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank L. A. Comparison of thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) to thyrotropin (TSH) stimulation for evaluating thyroid function in dogs. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc. 1996 Nov-Dec;32(6):481–487. doi: 10.5326/15473317-32-6-481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasler A., Rohner K. Schwerwiegende Reaktionen nach TSH-Stimulationstest beim Hund. Schweiz Arch Tierheilkd. 1992;134(9):423–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber G. K., Fong P., Concepcion E. S., Davies T. F. Recombinant human thyroid-stimulating hormone: initial bioactivity assessment using human fetal thyroid cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1991 Jun;72(6):1328–1331. doi: 10.1210/jcem-72-6-1328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen A. L., Iversen L., Høier R., Kristensen F., Henriksen P. Evaluation of an immunoradiometric assay for thyrotropin in serum and plasma samples of dogs with primary hypothyroidism. J Comp Pathol. 1996 Apr;114(3):339–346. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9975(96)80055-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladenson P. W., Braverman L. E., Mazzaferri E. L., Brucker-Davis F., Cooper D. S., Garber J. R., Wondisford F. E., Davies T. F., DeGroot L. J., Daniels G. H. Comparison of administration of recombinant human thyrotropin with withdrawal of thyroid hormone for radioactive iodine scanning in patients with thyroid carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 1997 Sep 25;337(13):888–896. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199709253371304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier C. A., Braverman L. E., Ebner S. A., Veronikis I., Daniels G. H., Ross D. S., Deraska D. J., Davies T. F., Valentine M., DeGroot L. J. Diagnostic use of recombinant human thyrotropin in patients with thyroid carcinoma (phase I/II study). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994 Jan;78(1):188–196. doi: 10.1210/jcem.78.1.8288703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nachreiner R. F., Refsal K. R., Graham P. A., Hauptman J., Watson G. L. Prevalence of autoantibodies to thyroglobulin in dogs with nonthyroidal illness. Am J Vet Res. 1998 Aug;59(8):951–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paradis M., Laperrière E., Larivière N. Effects of administration of a low dose of frozen thyrotropin on serum total thyroxine concentrations in clinically normal dogs. Can Vet J. 1994 Jun;35(6):367–370. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. E., Melián C., Nichols R. Measurement of serum total thyroxine, triiodothyronine, free thyroxine, and thyrotropin concentrations for diagnosis of hypothyroidism in dogs. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1997 Dec 1;211(11):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez L., Braverman L. E., White B., Emerson C. H. Recombinant human thyrotropin is a potent stimulator of thyroid function in normal subjects. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997 Sep;82(9):2836–2839. doi: 10.1210/jcem.82.9.4205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsey I. K., Evans H., Herrtage M. E. Thyroid-stimulating hormone and total thyroxine concentrations in euthyroid, sick euthyroid and hypothyroid dogs. J Small Anim Pract. 1997 Dec;38(12):540–545. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-5827.1997.tb03313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ribela M. T., Bianco A. C., Bartolini P. The use of recombinant human thyrotropin produced by Chinese hamster ovary cells for the preparation of immunoassay reagents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 Jan;81(1):249–256. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.1.8550760. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringel M. D., Ladenson P. W. Diagnostic accuracy of 131I scanning with recombinant human thyrotropin versus thyroid hormone withdrawal in a patient with metastatic thyroid carcinoma and hypopituitarism. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1996 May;81(5):1724–1725. doi: 10.1210/jcem.81.5.8626823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarlett J. M. Epidemiology of thyroid diseases of dogs and cats. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract. 1994 May;24(3):477–486. doi: 10.1016/s0195-5616(94)50053-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Moncrieff J. C., Nelson R. W., Bruner J. M., Williams D. A. Comparison of serum concentrations of thyroid-stimulating hormone in healthy dogs, hypothyroid dogs, and euthyroid dogs with concurrent disease. J Am Vet Med Assoc. 1998 Feb 1;212(3):387–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sparkes A. H., Gruffydd-Jones T. J., Wotton P. R., Gleadhill A., Evans H., Walker M. J. Assessment of dose and time responses to TRH and thyrotropin in healthy dogs. J Small Anim Pract. 1995 Jun;36(6):245–251. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-5827.1995.tb02907.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szkudlinski M. W., Thotakura N. R., Bucci I., Joshi L. R., Tsai A., East-Palmer J., Shiloach J., Weintraub B. D. Purification and characterization of recombinant human thyrotropin (TSH) isoforms produced by Chinese hamster ovary cells: the role of sialylation and sulfation in TSH bioactivity. Endocrinology. 1993 Oct;133(4):1490–1503. doi: 10.1210/endo.133.4.8404588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


