Abstract
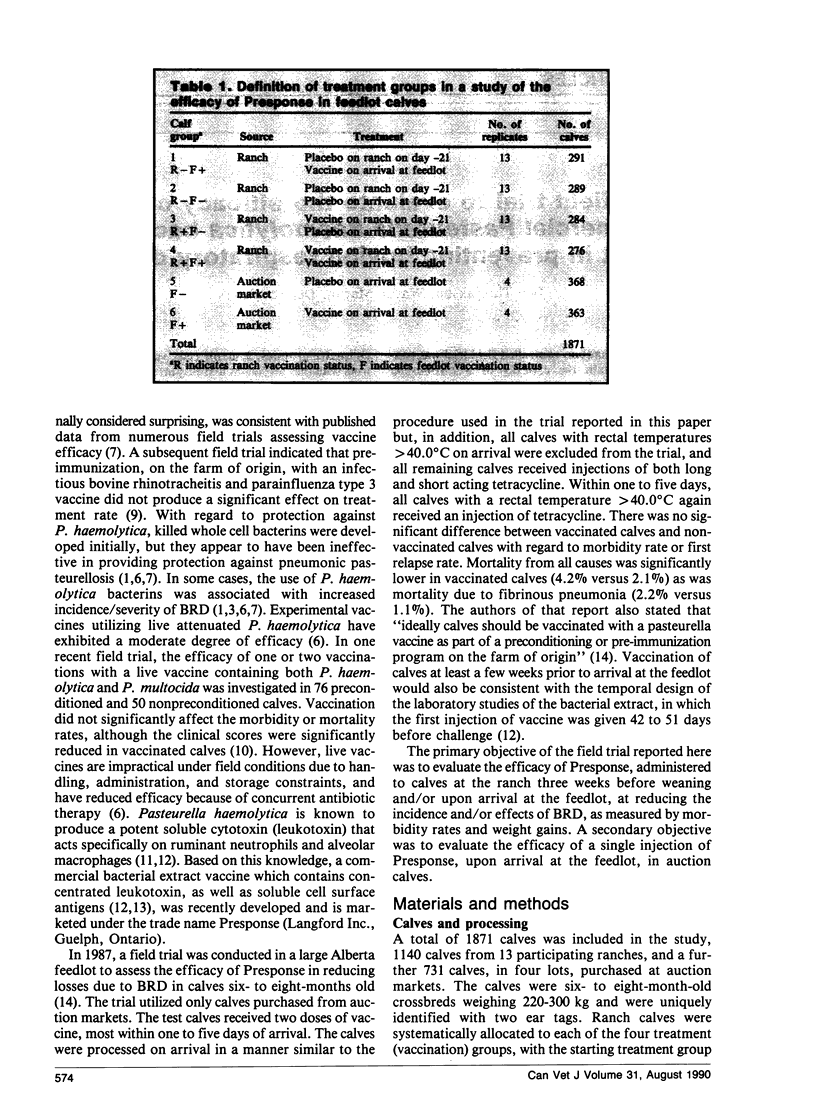
A double blind, random, controlled field trial was conducted to ascertain the efficacy of a Pasteurella haemolytica bacterial extract (Presponse, Langford Inc., Guelph, Ontario) in the prevention of bovine respiratory disease and/or its effects. Calves from 13 ranches (n = 1140 calves) were assigned to one of four groups, namely: vaccinated at the ranch three weeks prior to shipping to the feedlot; vaccinated only on arrival at the feedlot; vaccinated at both locations; or not vaccinated at either location. Four replicates of auction calves (n = 731) were also assigned to either receive or not receive the vaccine on arrival at the feedlot.
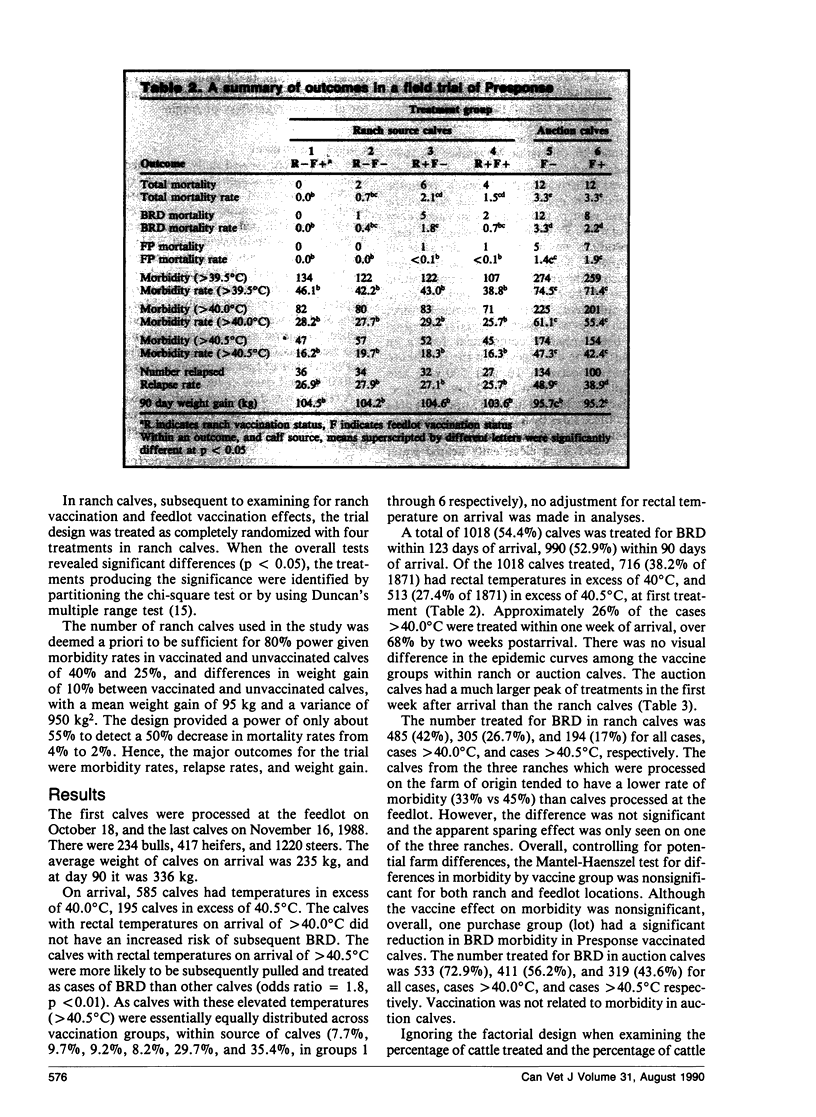
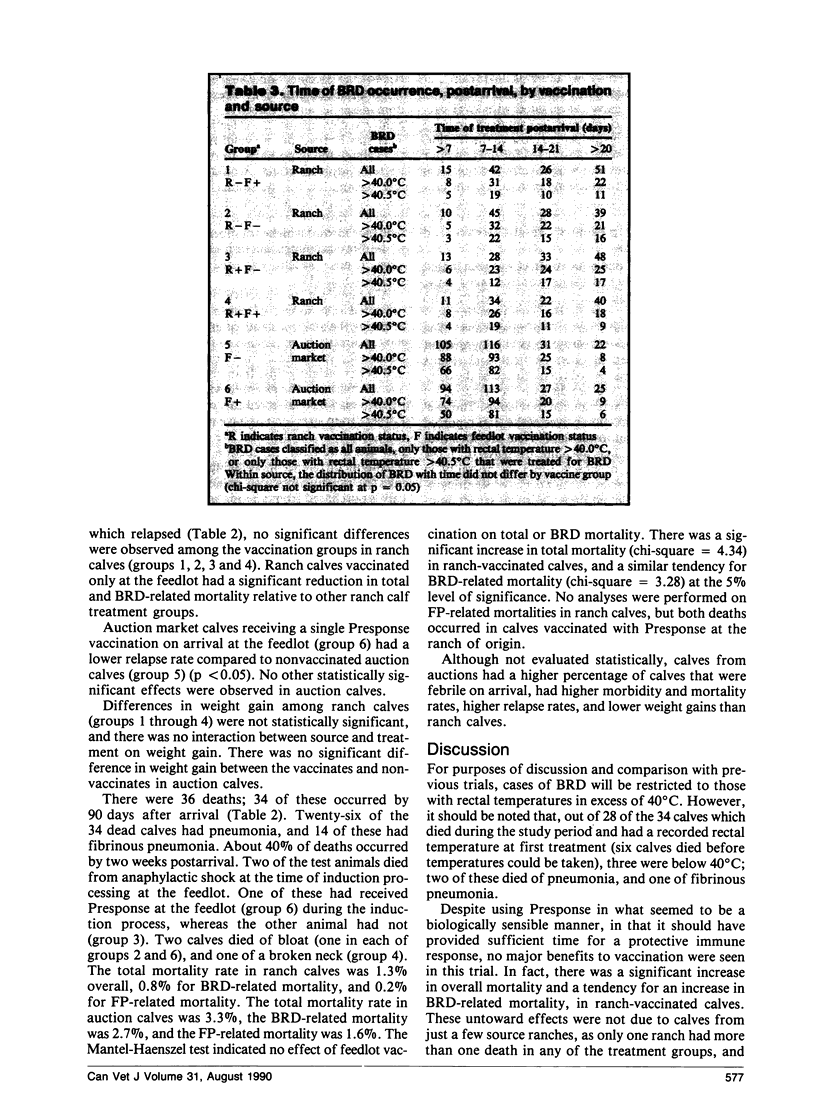
The vaccine did not effect a change in morbidity rates or weight gain. Total mortality rates were increased significantly, and mortality rates from respiratory disease tended to be increased in ranch calves that were vaccinated with Presponse at the ranch. In auction calves, the relapse rates were significantly lower in vaccinated calves. There was a tendency towards a reduction of respiratory disease-related mortality, however there appeared to be no sparing against death from fibrinous pneumonia in auction calves.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bateman K. G. Efficacy of a pasteurella haemolytica vaccine/bacterial extract in the prevention of bovine respiratory disease in recently shipped feedlot calves. Can Vet J. 1988 Oct;29(10):838–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadel W. L., Chengappa M. M., Herren C. E. Field-trial evaluation of a Pasteurella vaccine in preconditioned and nonpreconditioned lightweight calves. Am J Vet Res. 1985 Sep;46(9):1944–1948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Bateman K. G., Shewen P. E., Rosendal S., Bohac J. E. The frequency, distribution and effects of antibodies, to seven putative respiratory pathogens, on respiratory disease and weight gain in feedlot calves in Ontario. Can J Vet Res. 1989 Jul;53(3):355–362. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Johnson J. A., Curtis R. A. Factors associated with morbidity and mortality in feedlot calves: the Bruce County beef project, year two. Can J Comp Med. 1981 Apr;45(2):103–112. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W., Meek A. H., Davis D. G., Thomson R. G., Johnson J. A., Lopez A., Stephens L., Curtis R. A., Prescott J. F., Rosendal S. Factors associated with mortality in feedlot cattle: the Bruce County Beef Cattle Project. Can J Comp Med. 1980 Jan;44(1):1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin S. W. Vaccination: Is it Effective in Preventing Respiratory Disease or Influencing Weight Gains in Feedlot Calves? Can Vet J. 1983 Jan;24(1):10–19. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Willson P., Curtis R., Allen B., Acres S. A field trial, of preshipment vaccination, with intranasal infectious bovine rhinotracheitis-parainfluenza-3 vaccines. Can J Comp Med. 1983 Jul;47(3):245–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Cytotoxin of Pasteurella haemolytica acting on bovine leukocytes. Infect Immun. 1982 Jan;35(1):91–94. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.1.91-94.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shewen P. E., Wilkie B. N. Vaccination of calves with leukotoxic culture supernatant from Pasteurella haemolytica. Can J Vet Res. 1988 Jan;52(1):30–36. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates W. D. A review of infectious bovine rhinotracheitis, shipping fever pneumonia and viral-bacterial synergism in respiratory disease of cattle. Can J Comp Med. 1982 Jul;46(3):225–263. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


