Abstract
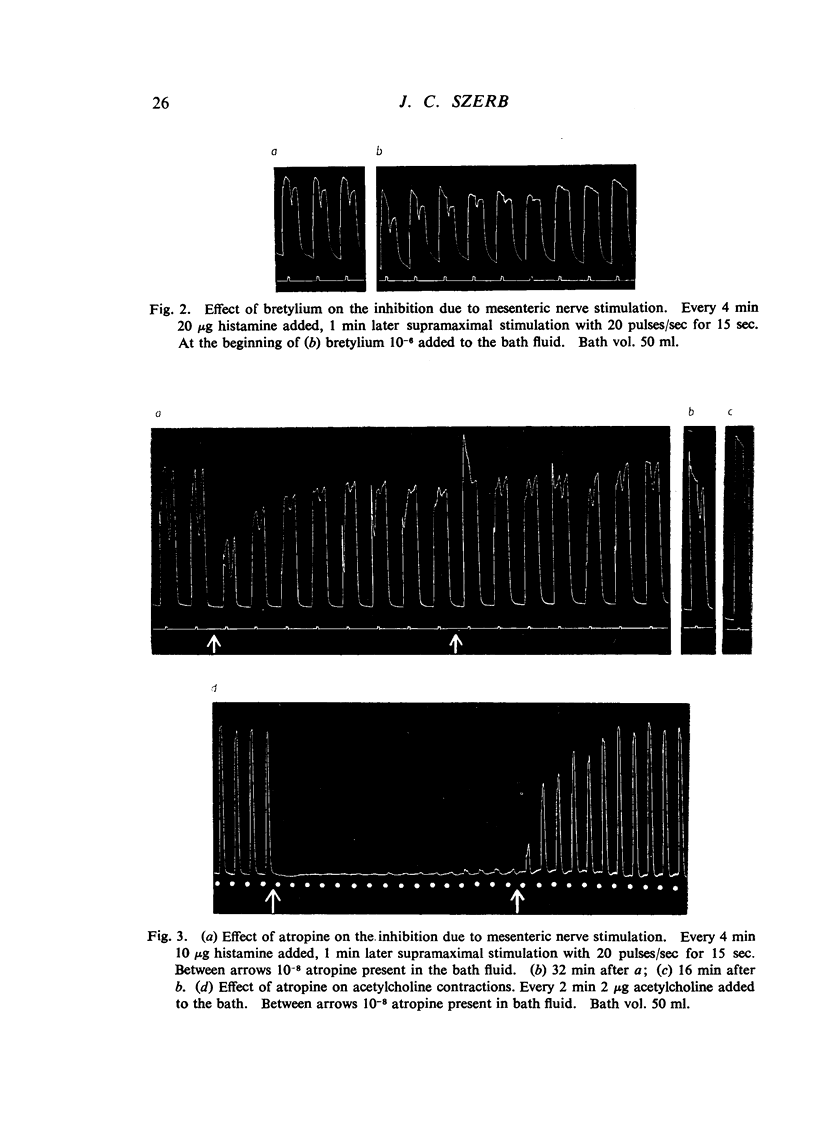
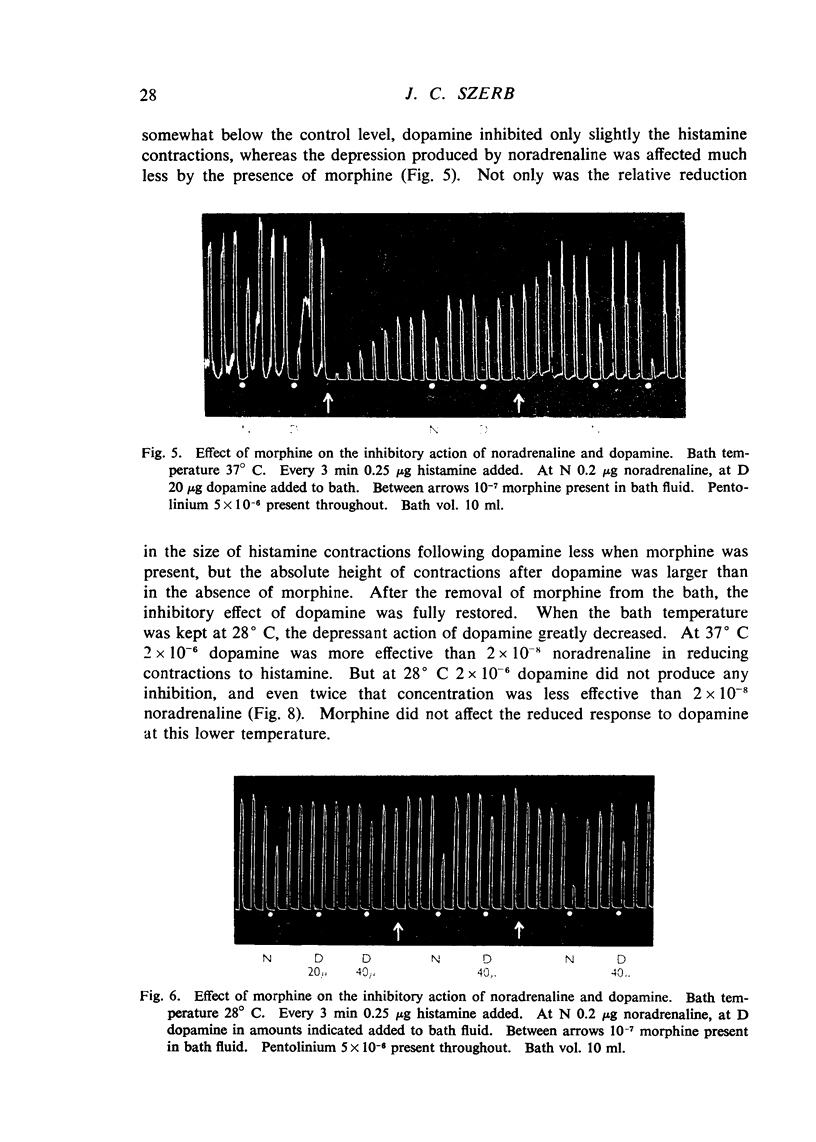
Nerves accompanying the mesenteric blood-vessels of the isolated guinea-pig jejunum were stimulated and changes in the longitudinal muscle coat were recorded. Stimulation of the nerves led to a rapid relaxation if the intestine was contracted by a previous administration of histamine. The relaxation was inhibited by morphine and partially restored by nalorphine. Bretylium and atropine also inhibited the relaxation and cocaine increased it somewhat. Morphine, atropine, and bretylium had no significant effect on the depressant action of noradrenaline on histamine contractions, whereas cocaine slightly enhanced the action of noradrenaline. Morphine, but not the other drugs, prevented the inhibitory action of dopamine.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADLER T. K., ELLIOTT H. W., GEORGE R. Some factors affecting the biological disposition of small doses of morphine in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Aug;120(4):475–487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOURA A. L., GREEN A. F. The actions of bretylium: adrenergic neurone blocking and other effects. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Dec;14:536–548. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb00961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The action of sympathomimetic amines in animals treated with reserpine. J Physiol. 1958 Dec 4;144(2):314–336. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp006104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURN J. H., RAND M. J. The depressor action of dopamine and adrenaline. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Dec;13(4):471–479. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finkleman B. On the nature of inhibition in the intestine. J Physiol. 1930 Sep 18;70(2):145–157. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1930.sp002683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOSTERLITZ H. W., TAYLOR D. W. The effect of morphine on vagal inhibition of the heart. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1959 Jun;14(2):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1959.tb01385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUNRO A. F. Effect of autonomic drugs on the responses of isolated preparations from the guinea-pig intestine to electrical stimulation. J Physiol. 1953 Apr 28;120(1-2):41–52. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ORAHOVATS P. D., WINTER C. A., LEHMAN E. G. Pharmacological studies of mixtures of narcotics and N-allylnormorphine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Oct;112(2):246–251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRENDELENBURG U. The action of morphine on the superior cervical ganglion and on the nictitating membrane of the cat. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):79–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01366.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRENDELENBURG U. The supersensitivity caused by cocaine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1959 Jan;125(1):55–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


