Abstract
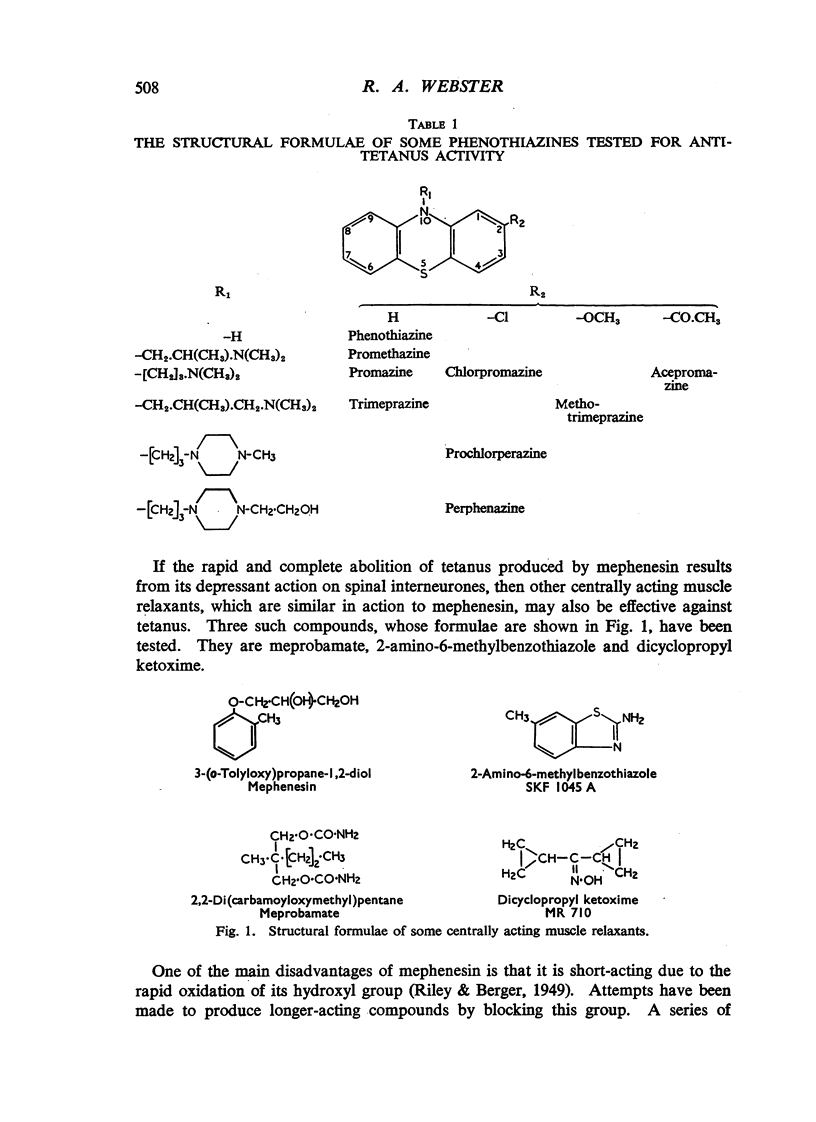
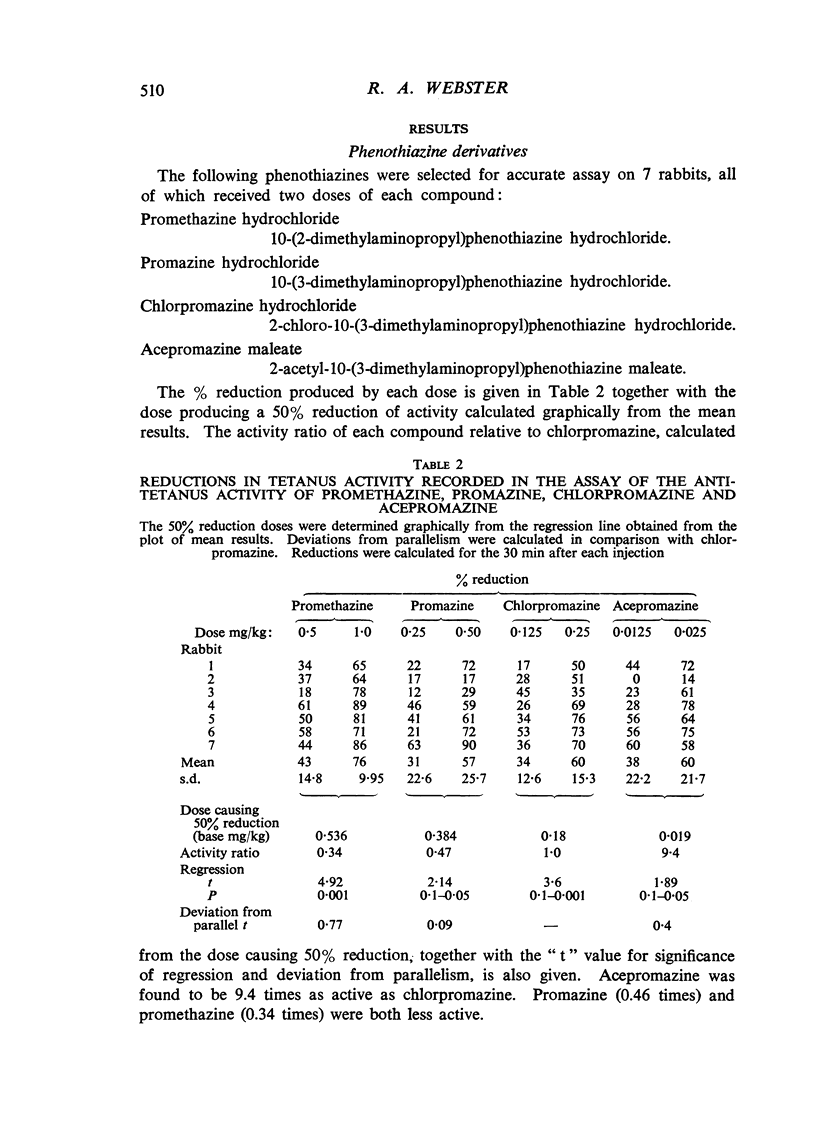
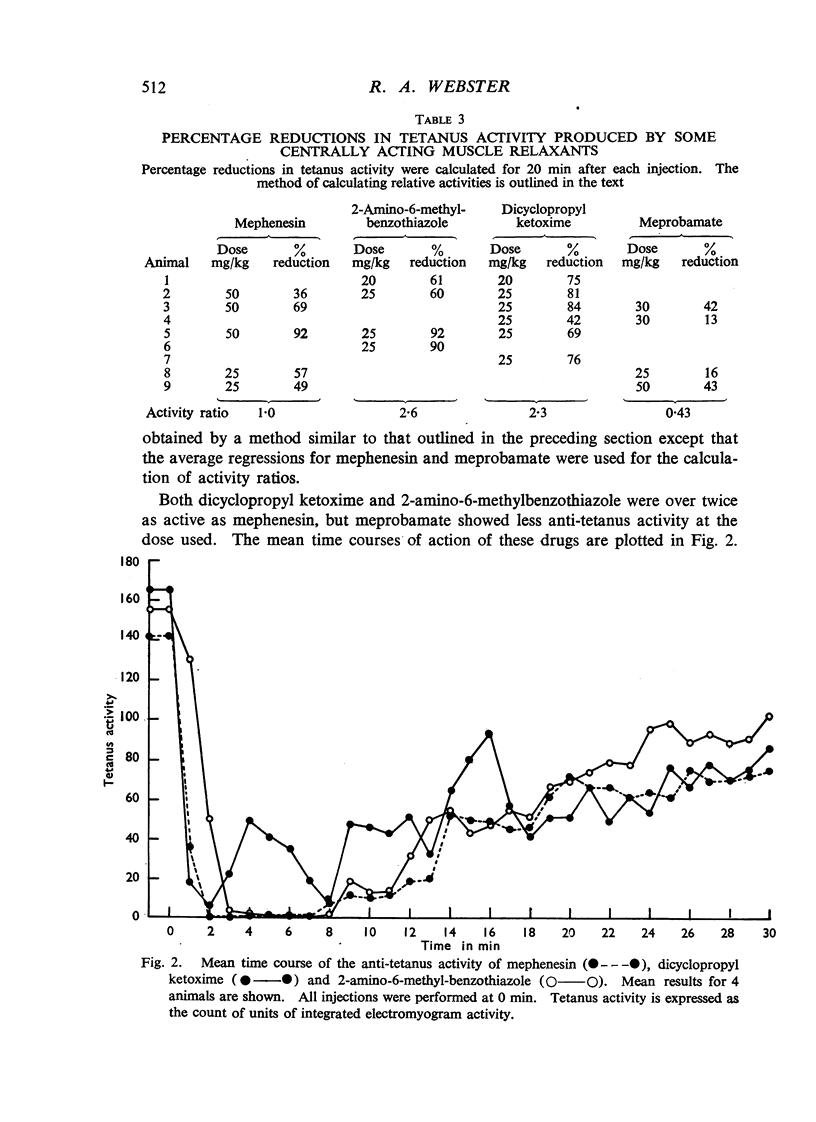
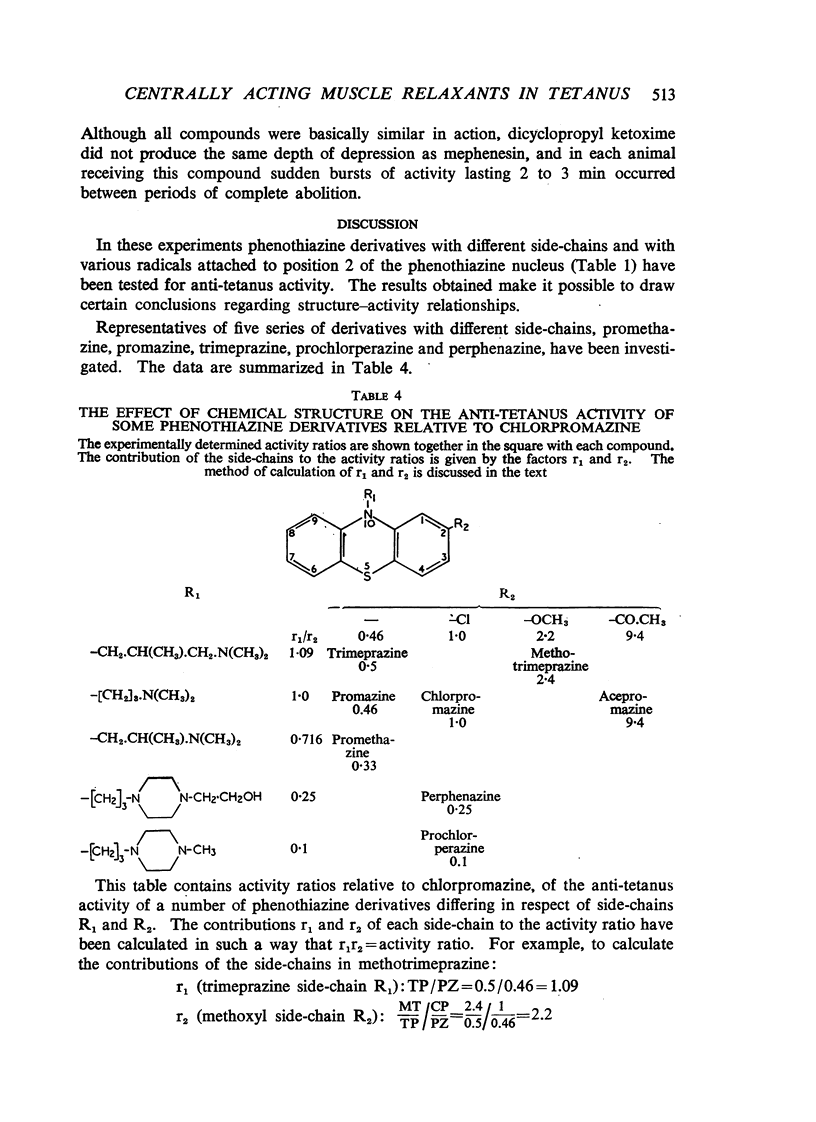
The anti-tetanus activity of a number of phenothiazine derivatives and other centrally acting muscle relaxants, such as mephenesin, dicyclopropyl ketoxime, 2-amino-6-methylbenzothiazole and meprobamate, has been determined in rabbits with experimental local tetanus. Structure-activity relationships were obtained for the phenothiazine derivatives and their anti-tetanus activity correlated with other central and peripheral properties. Both dicyclopropyl ketoxime and 2-amino-6-methyl-benzothiazole were twice as active as mephenesin. Meprobamate does not appear to be primarily a muscle relaxant of the mephenesin type.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARRIGONI-MARTELLI E., KRAMER M. Studio farmacologico di un nuovo derivato fenotiazinico: la perfenazina. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Apr 1;119(3-4):311–333. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER F. M., CAMPBELL G. L., HENDLEY C. D., LUDWIG B. J., LYNES T. E. The action of tranquilizers on brain potentials and serotonin. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Mar 14;66(3):686–694. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb40758.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER F. M. The anticonvulsant activity of carbamate esters of certain 2,2-disubstituted-1,3-propanediols. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Feb;104(2):229–233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER F. M. The pharmacological properties of 2-methyl-2-n-propyl-1,3-propanediol dicarbamate (miltown), a new interneuronal blocking agent. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Dec;112(4):413–423. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONVALLET M., DELL P., HIEBEL G. Tonus sympathique et activité électrique corticale. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1954 Feb;6(1):119–144. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(54)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRADLEY P. B., HANCE A. J. The effect of chlorpromazine and methopromazine on the electrical activity of the brain in the cat. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1957 May;9(2):191–215. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(57)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNAUD M., SCHMITT J., AUROUSSEAU M., NAVARRO J. Activité adrenolytique de quelques dérivés de la phénothiazine. J Physiol (Paris) 1957 Jan-Mar;49(1):67–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRUNAUD M., SCHMITT J., NAVARRO J., AUROUSSEAU M. Action dépressive sur le système nerveux central de quelques dérivés de la phénothiazine. J Physiol (Paris) 1957 Jan-Mar;49(1):70–72. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURVOISIER S., DUCROT R., FOURNEL J., JULOU L. Propriétés pharmacodvnamiques générales de la lévomépromazine (7.044 R.P.). C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1957;151(7):1378–1382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURVOISIER S., DUCROT R., FOURNEL J., JULOU L. Propriétés pharmacodynamiques générales de la prochlorpémazine (6. 140 R.P.). C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1957;151(6):1144–1148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURVOISIER S., DUCROT R., FOURNEL J., JULOU L. Propriétés pharmacologiques générales d'un nouveau dérivé de la phénothiazine, neuroleptique puissant a action neurovégétative discrète, le chlorhydrate de (méthyl-2' diméthyl-amino-3' propyl-1')-10 phénothiazine (6.549 R.P.). Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1958 May 1;115(1-2):90–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COURVOISIER S., FOURNEL J., DUCROT R., KOLSKY M., KOETSCHET P. Propriétés pharmacodynamiques du chlorhydrate de chloro-3-(diméthylamino-3'-propyl)-10-phénothiazine (4,560 R.P.); étude expérimentale d'un nouveau corps utilisé dans l'anesthésie potentialisée et dans l'hibernation artificielle. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1953 Jan;92(3-4):305–361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DASGUPTA S. R., WERNER G. Inhibitory actions of chlorpormazine on motor activity. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1955 Jan 1;100(3-4):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELL P., BONVALLET M., HUGELIN A. Tonus sympathique, adrénaline et contróle réticulaire de la motricité spinale. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1954 Nov;6(4):599–618. doi: 10.1016/0013-4694(54)90087-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DOMINO E. F., UNNA K. R., KERWIN J. Pharmacological properties of benzazoles. I. Relationship between structure and paralyzing action. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1952 Aug;105(4):486–497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FUNDERBURK W. H., KING E. E., DOMINO E. F., UNNA K. R. Pharmacological properties of benzazoles. II. Sites of action in the central nervous system. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1953 Mar;107(3):356–367. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENATSCH H. D., INGVAR D. H. Chlorpromazin und Spastizität; eine experimentelle elektrophysiologische Untersuchung. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1956;195(1):77–93. doi: 10.1007/BF00342008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIEBEL G., BONVALLET M., DELL P. Action de la chlorpromazine (Largactil 45 60 RP) au niveau du système nerveux central. Sem Hop. 1954 Jun 6;30(37):2346–2353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. V., UNNA K. R. The action of mephenesin and other interneuron depressants on the brain stem. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Jul;111(3):293–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPERA J., ARMITAGE A. K. Comparison of some pharmacological properties of chlorpromazine, promethazine, and pethidine. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1954 Dec;9(4):392–401. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1954.tb00851.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENCE D. R., WEBSTER R. A. A method of assaying the anti-tetanus potency of drugs on experimental local tetanus in the rabbit. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Sep;13(3):330–333. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAURENCE D. R., WEBSTER R. A. The activity of a variety of chemical compounds against experimental tetanus. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1958 Sep;13(3):334–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1958.tb00914.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONGO V. G., VON BERGER G. P., BOVET D. Action of nicotine and of the "ganglioplegiques centraux" on the electrical activity of the brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1954 Jul;111(3):349–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MEIDINGER F. Action comparée des produits nos 3.277 R.P., 4.560 R.P., 4.909 R.P. et du phénobarbital sur les convulsions provoquées par la strychnine, la picrotoxine, la cocaïne, la caféine et l'amphétamine. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1956;150(7):1340–1343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLSTEIN M. A. Control of tetanus spasms by administration of meprobamate. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Aug 15;170(16):1902–1908. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.03010160018006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLSTEIN M. A., STEIN M. D., ELAM H. Routine treatment of tetanus. JAMA. 1960 Aug 6;173:1536–1541. doi: 10.1001/jama.1960.03020320016005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PERLSTEIN M. A. Use of meprobamate (Miltown) in convulsive and related disorders. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Jul 14;161(11):1040–1044. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02970110006003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PFEIFFER C. C., RIOPELLE A. J., SMITH R. P., JENNEY E. H., WILLIAMS H. L. Comparative study of the effect of meprobamate on the conditioned response on strychnine and pentylenetetrazol thresholds, on the normal electroencephalogram, and on polysynaptic reflexes. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 May 9;67(10):734–745. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb46010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RINALDI F., HIMWICH H. E. Drugs affecting psychotic behavior and the function of the mesodiencephalic activating system. Dis Nerv Syst. 1955 May;16(5):133–141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSENKILDE H., GOVIER W. M. A comparison of some phenothiazine derivatives in inhibiting apomorphine-induced emesis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1957 Jul;120(3):375–378. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHMITT J., MERCIER J., AUROUSSEAU M., HALLOT A., COMOY P. Sur une nouvelle série de composés neuroplégiques dérivés de la phénothiazine. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1957 Jan 7;244(2):255–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAINO ANDERSEN E., KJAER K. Tetanus behandlet med meprobamat (restenil). Nord Med. 1958 Jul 24;60(30):1049–1051. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRTH W., GOSSWALD R., HORLEIN U., RISSE K. H., KREISKOTT H. Zur Pharmakologie acylierter Phenothiazin-Derivate. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1958 May 1;115(1-2):1–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRTH W. Zur pharmakologischen Wirkung von Promazin. Arzneimittelforschung. 1958 Aug;8(8):507–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


