Abstract
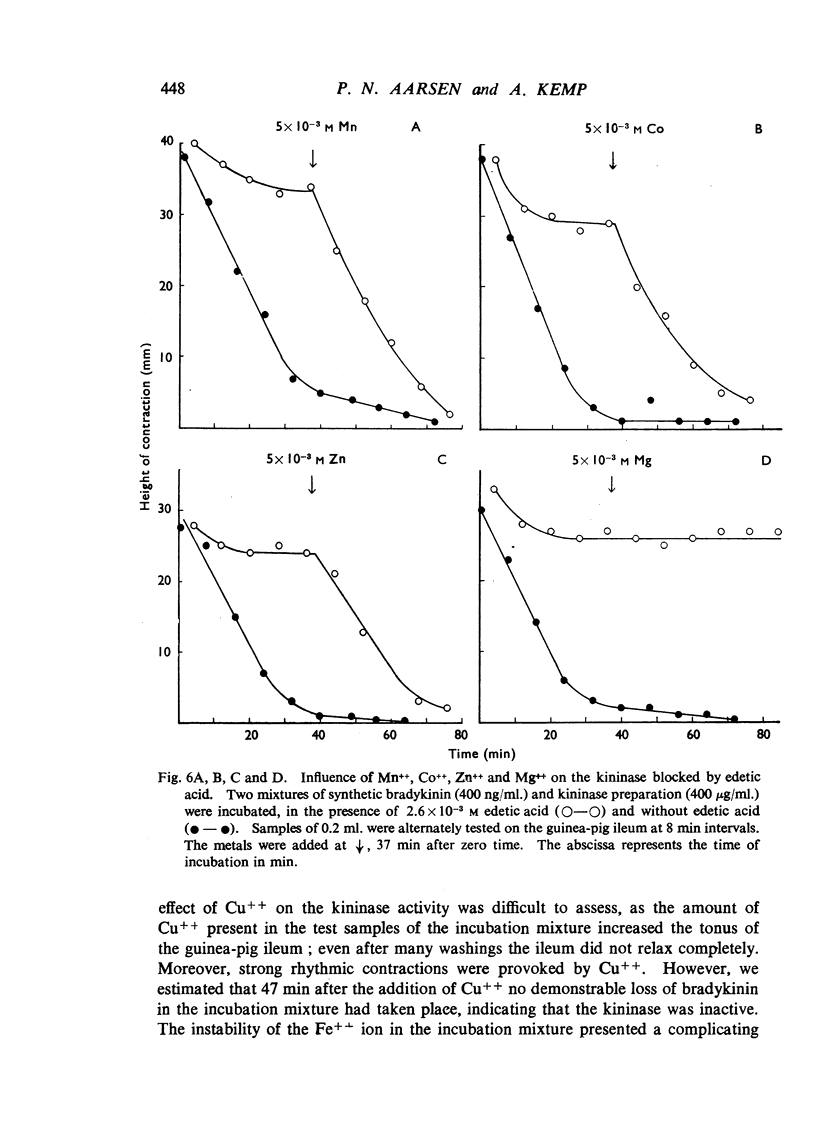
Kininase prepared from guinea-pig serum was inhibited by cysteine at pH 7.4 to 7.6. A similar effect was found with edetic acid. The enzyme blocked by edetic acid was reactivated immediately by addition of Mn++, Co++ and Zn++. These findings indicate that kininase is a metal-activated enzyme.
Full text
PDF

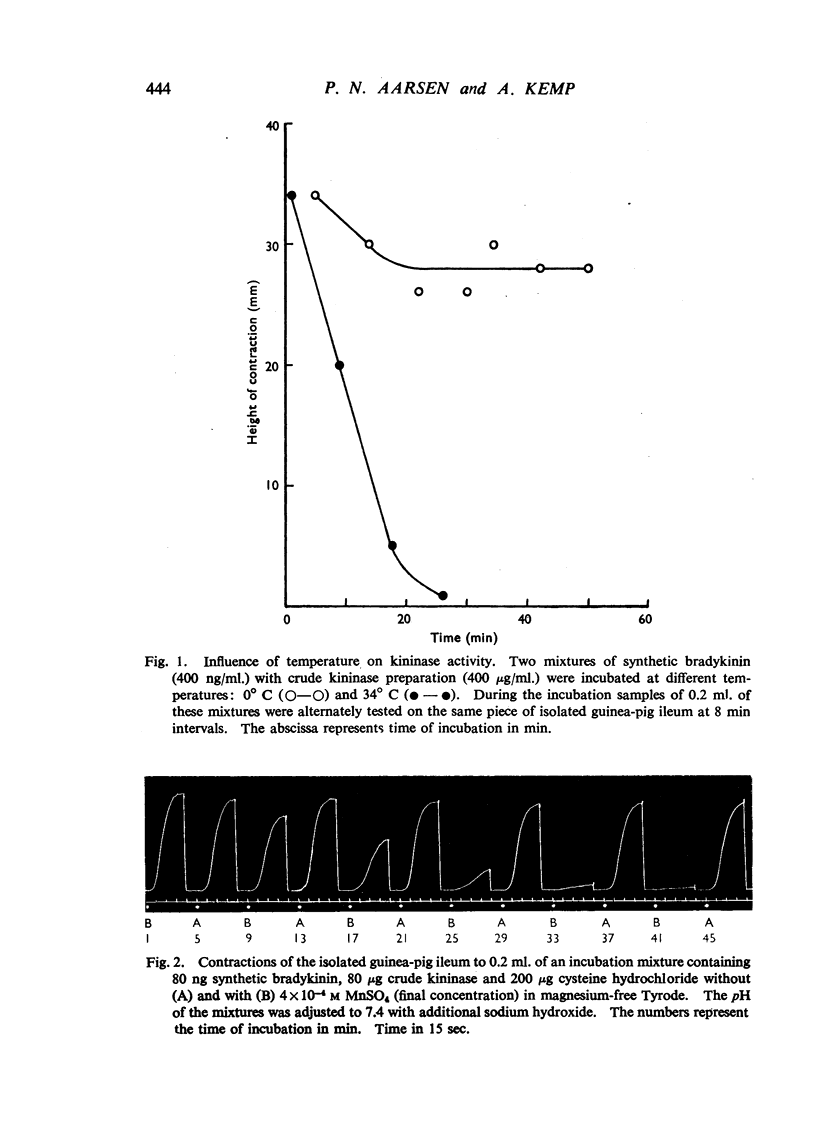
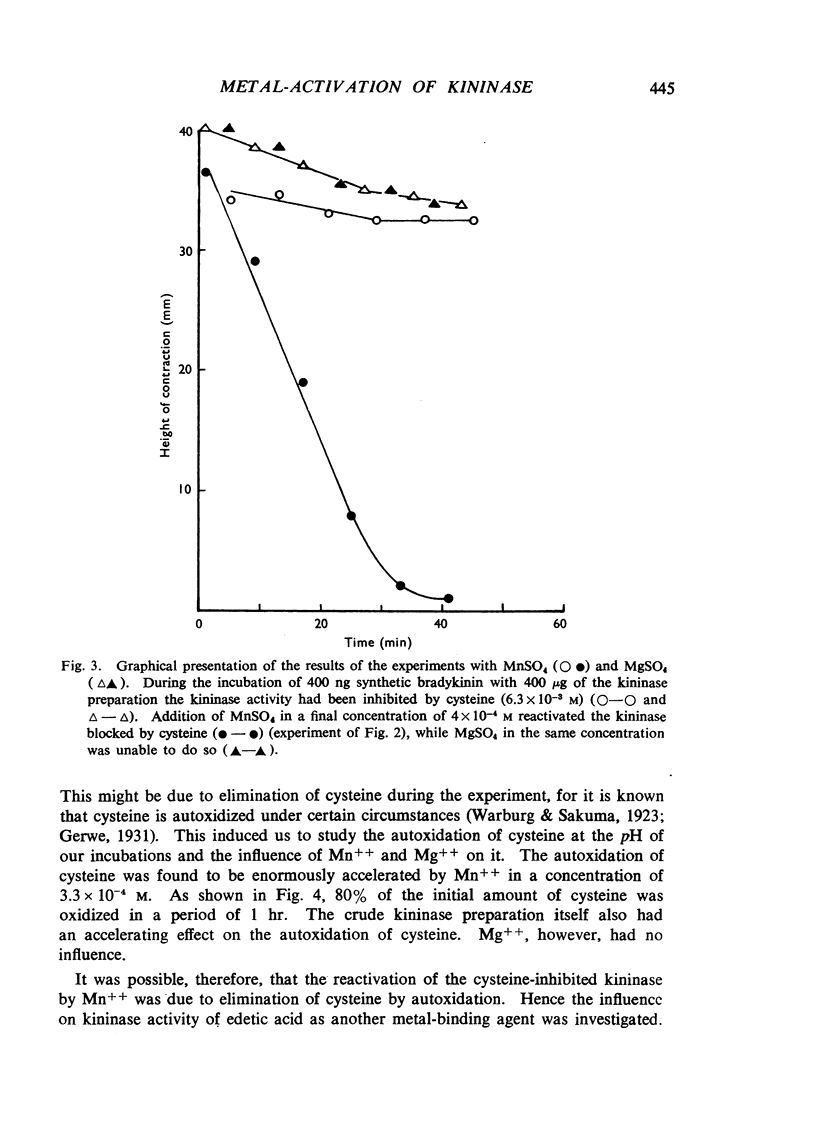
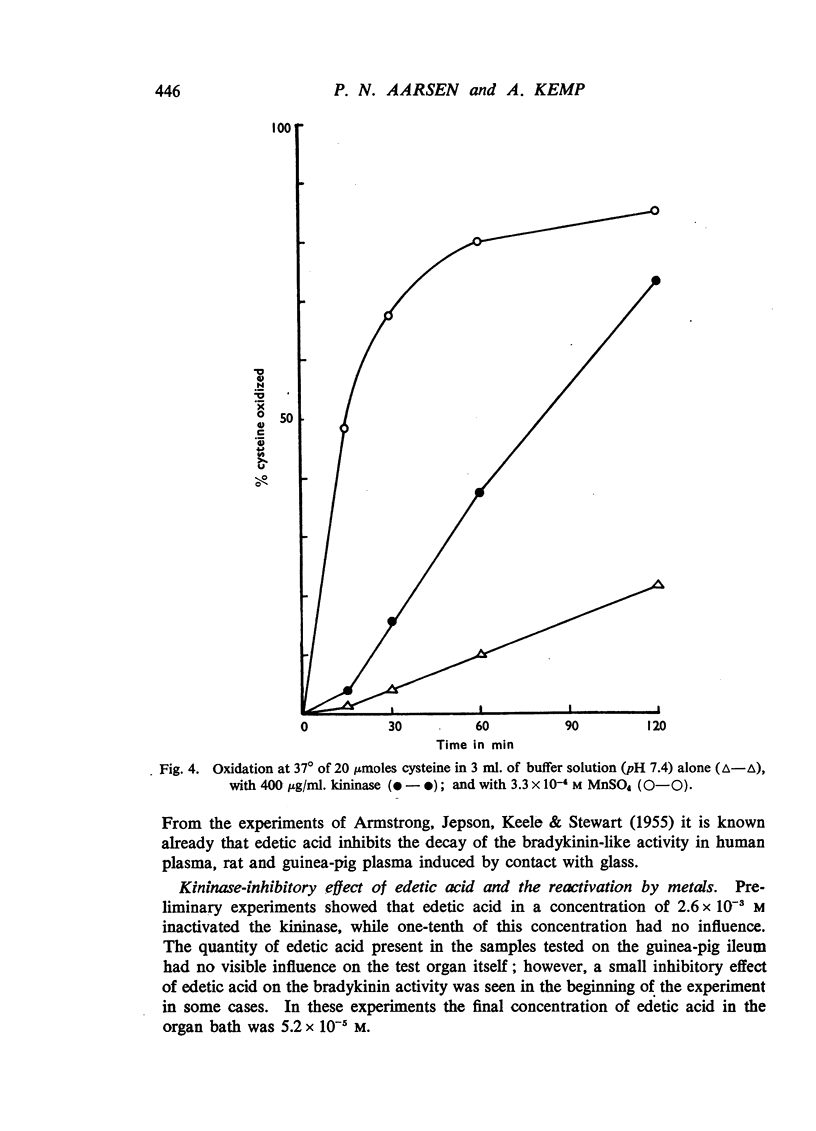
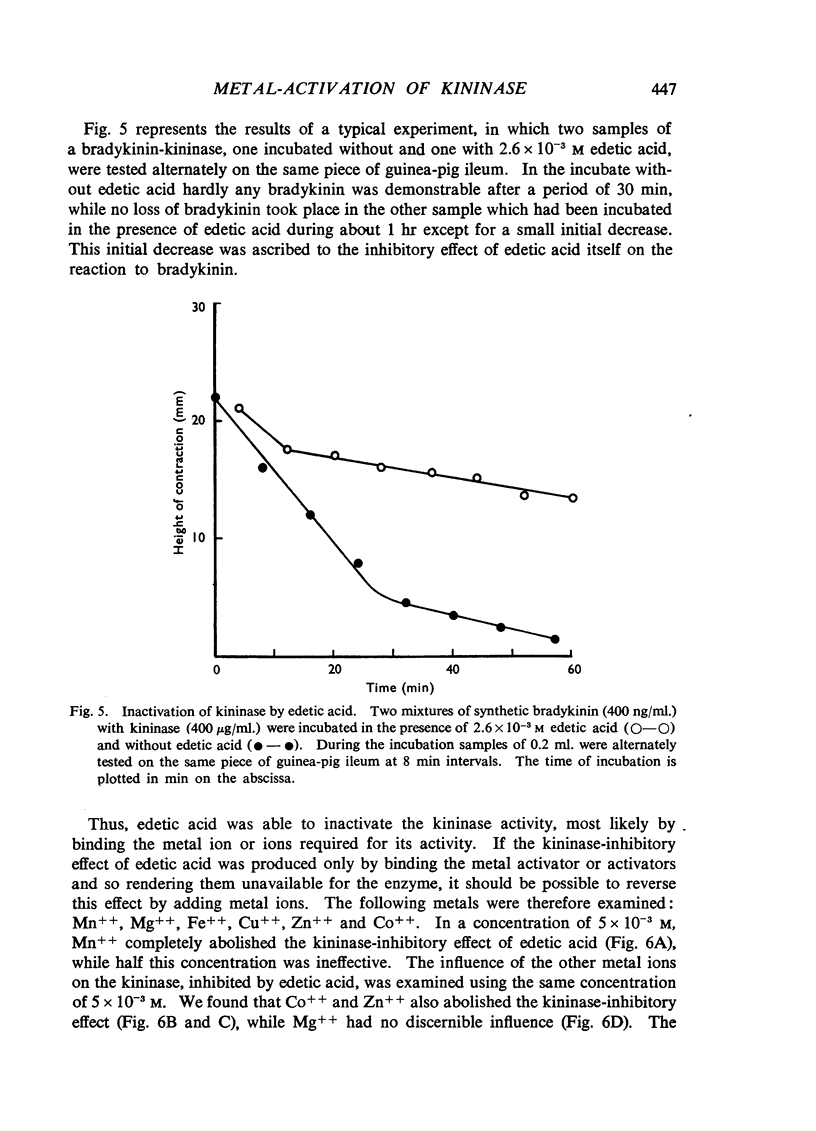


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARMSTRONG D., JEPSON J. B., KEELE C. A., STEWART J. W. Activation by glass of pharmacologically active agents in blood of various species. J Physiol. 1955 Sep 28;129(3):80–1P. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1955.sp005387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERDOS E. G., SLOANE E. M. An enzyme in human blood plasma that inactivates bradykinin and kallidins. Biochem Pharmacol. 1962 Jul;11:585–592. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(62)90119-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HORTON E. W. The estimation of urinary kallkrein. J Physiol. 1959 Oct;148:267–282. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIS G. P. Active polypeptides derived from plasma proteins. Physiol Rev. 1960 Oct;40:647–676. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1960.40.4.647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT W. Naturally occurring lipidsoluble acids of pharmacological interest. Pharmacol Rev. 1958 Sep;10(3):407–435. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


