Abstract
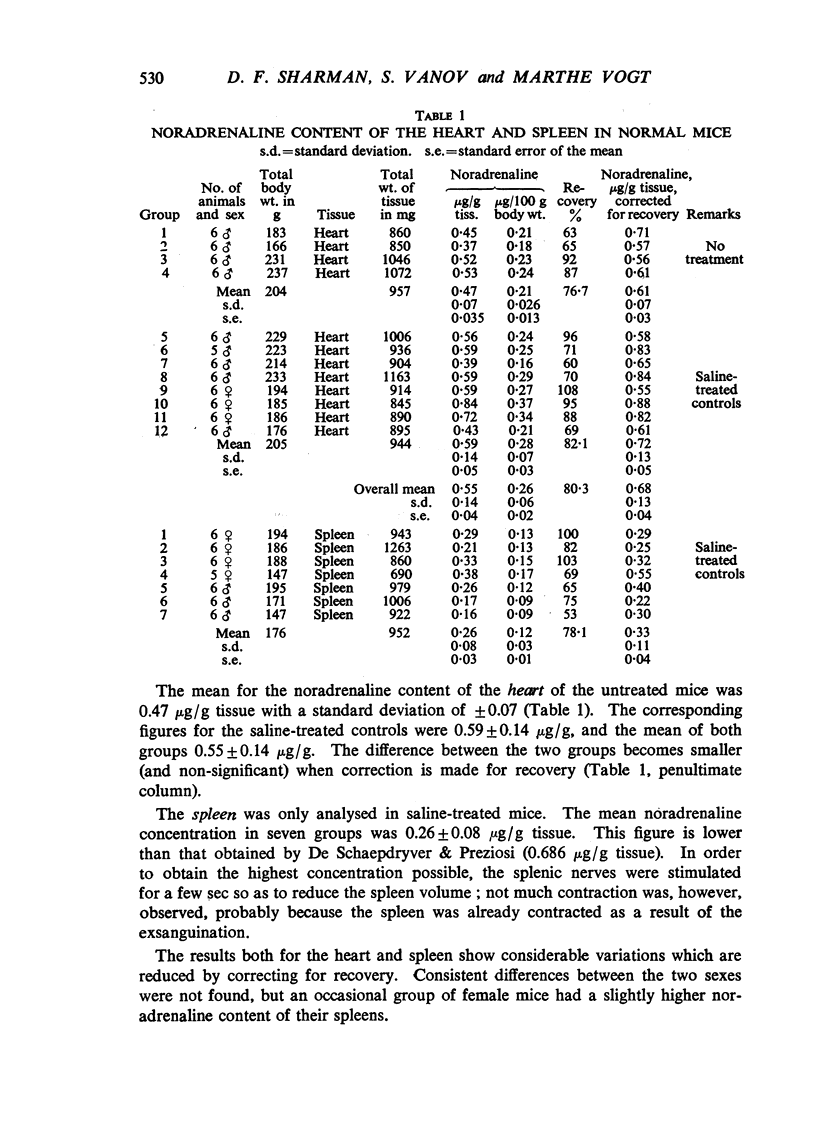
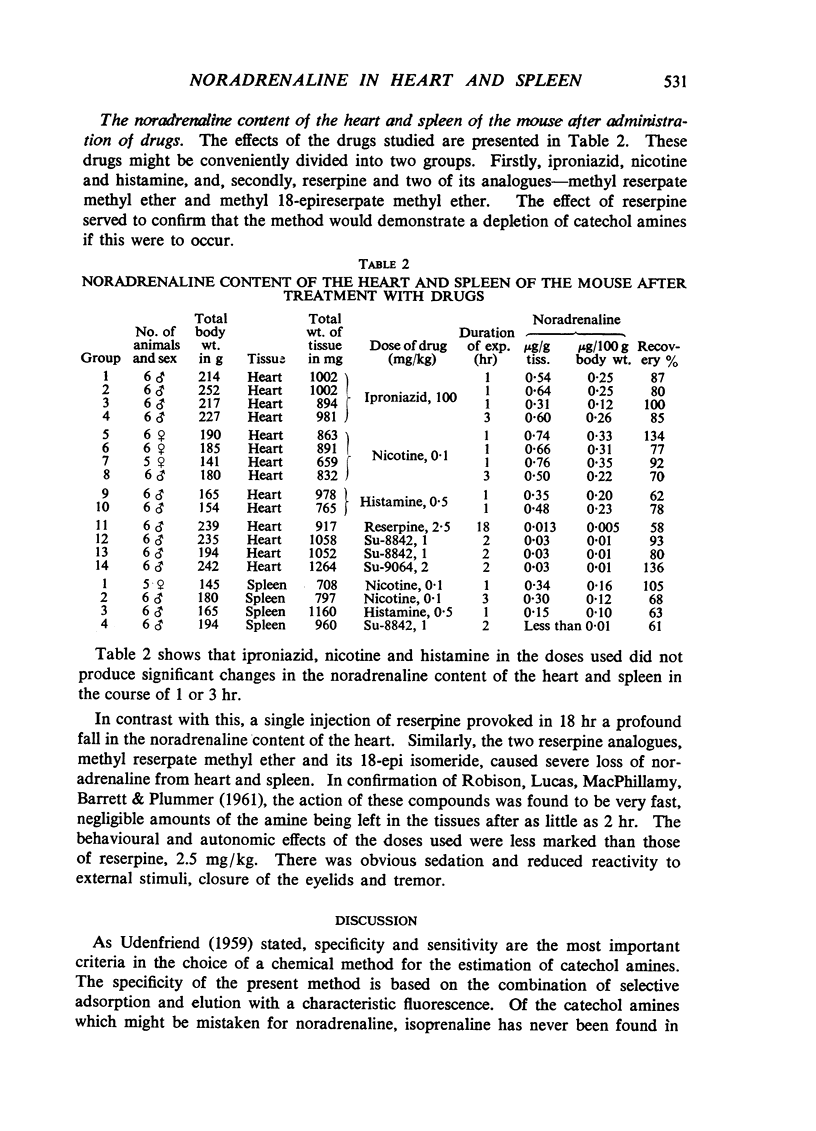
The noradrenaline content of the heart and spleen was investigated in normal mice and in mice treated with drugs. A modification of the methods of Bertler, Carlsson & Rosengren (1958) was used for extraction, and of v. Euler & Floding (1955) for fluorimetric estimation of the amine. In normal mice the mean noradrenaline content of the heart was 0.55 μg/g and that of the spleen 0.26 μg/g fresh tissue. Iproniazid (100 mg/kg), nicotine (0.1 mg/kg) and histamine (0.5 mg/kg), given 1 and 3 hr before killing the mice, did not significantly change the concentration of noradrenaline in the heart. Neither did nicotine and histamine, administered 1 hr before death, significantly alter the noradrenaline content of the spleen. The rapid changes in the catechol amine content of mouse tissues reported with these drugs by De Schaepdryver & Preziosi (1959) were not observed. In contrast, reserpine (2.5 mg/kg), methyl reserpate methyl ether (1 mg/kg), and methyl 18-epireserpate methyl ether (2 mg/kg) caused severe depletion of noradrenaline from the heart and spleen of the mice.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BERTLER A., CARLSSON A., ROSENGREN E. A method for the fluorimetric determination of adrenaline and noradrenaline in tissues. Acta Physiol Scand. 1958 Dec 15;44(3-4):273–292. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1958.tb01627.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAWFORD T. B., LAW W. A method for estimation of adrenaline and noradrenaline in urine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1958 Mar;10(3):179–188. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1958.tb10290.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SCHAEPDRYVER A. F., PREZIOSI P. Pharmacological depletion of adrenaline and noradrenaline in various organs of mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1959 Aug 1;121:177–221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUSCHOLL E., VOGT M. The action of reserpine on the peripheral sympathetic system. J Physiol. 1958 Apr 3;141(1):132–155. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1958.sp005961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAASONEN M. K., KRAYER O. The release of norepinephrine from the mammalian heart by reserpine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1958 Jun;123(2):153–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PORTER C. C., TOTARO J. A., LEIBY C. M. Some biochemical effects of alpha-methyl-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and related compounds in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1961 Nov;134:139–145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROBISON M. M., LUCAS R. A., MACPHILLAMY H. B., BARRETT W., PLUMMER A. J. Rauwolfia alkaloids XXXV. Potent, fast-acting sedatives derived from methyl reserpate. Experientia. 1961 Jan 15;17:14–15. doi: 10.1007/BF02157923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SANAN S., VOGT M. Effect of drugs on the noradrenaline content of brain and peripheral tissues and its significance. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1962 Feb;18:109–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1962.tb01155.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- UDENFRIEND S. Survey of chemical and physical methods for measuring catecholamines. Pharmacol Rev. 1959 Jun;11(2 Pt 2):252–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VOGT M. The concentration of sympathin in different parts of the central nervous system under normal conditions and after the administration of drugs. J Physiol. 1954 Mar 29;123(3):451–481. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1954.sp005064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VON EULER U. S., FLODING I. A fluorimetric micromethod for differential estimation of adrenaline and noradrenaline. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1955;33(118):45–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von EULER U., LISHAJKO F. Improved technique for the fluorimetric estimation of catecholamines. Acta Physiol Scand. 1961 Apr;51:348–355. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1961.tb02128.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


