Abstract
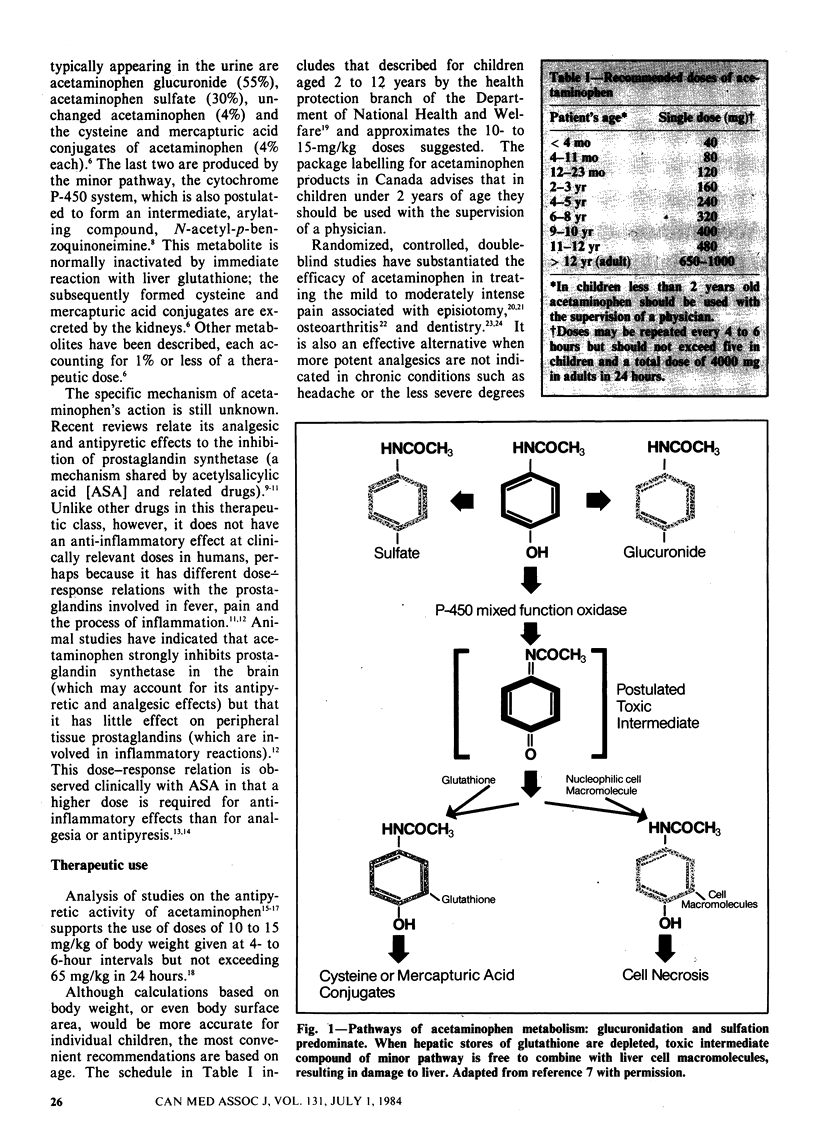
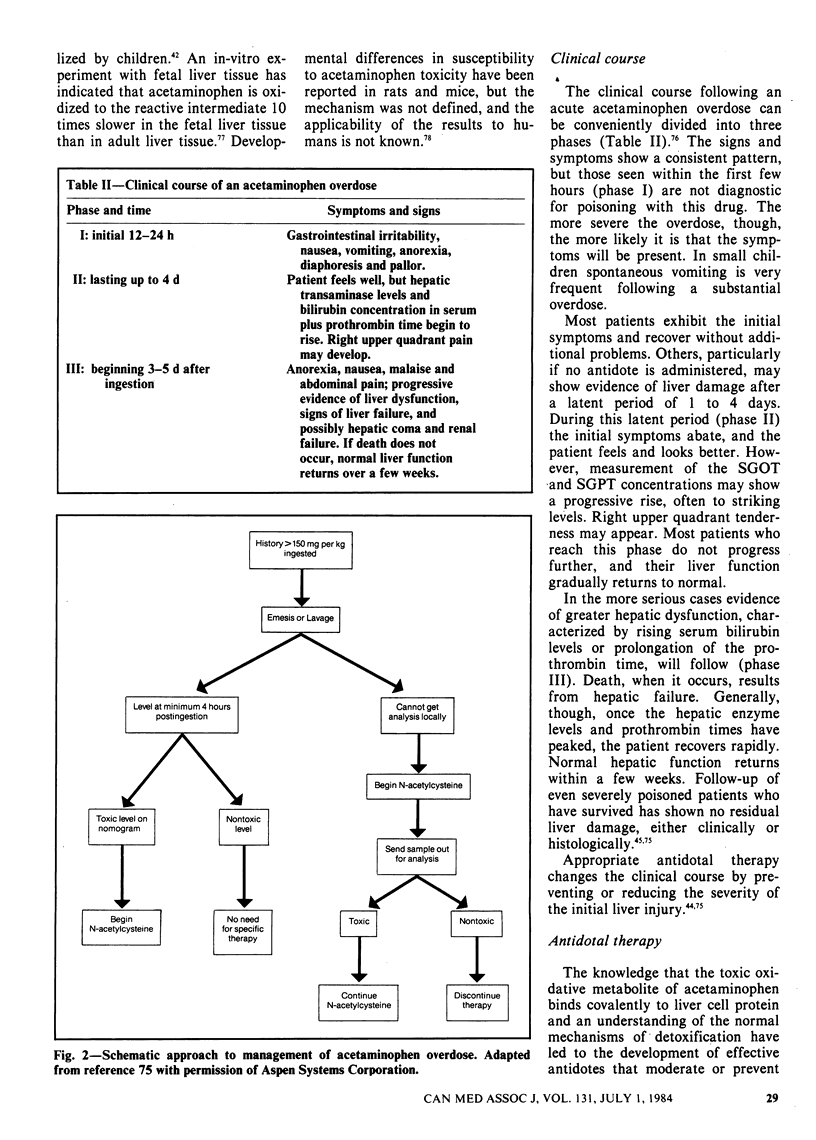
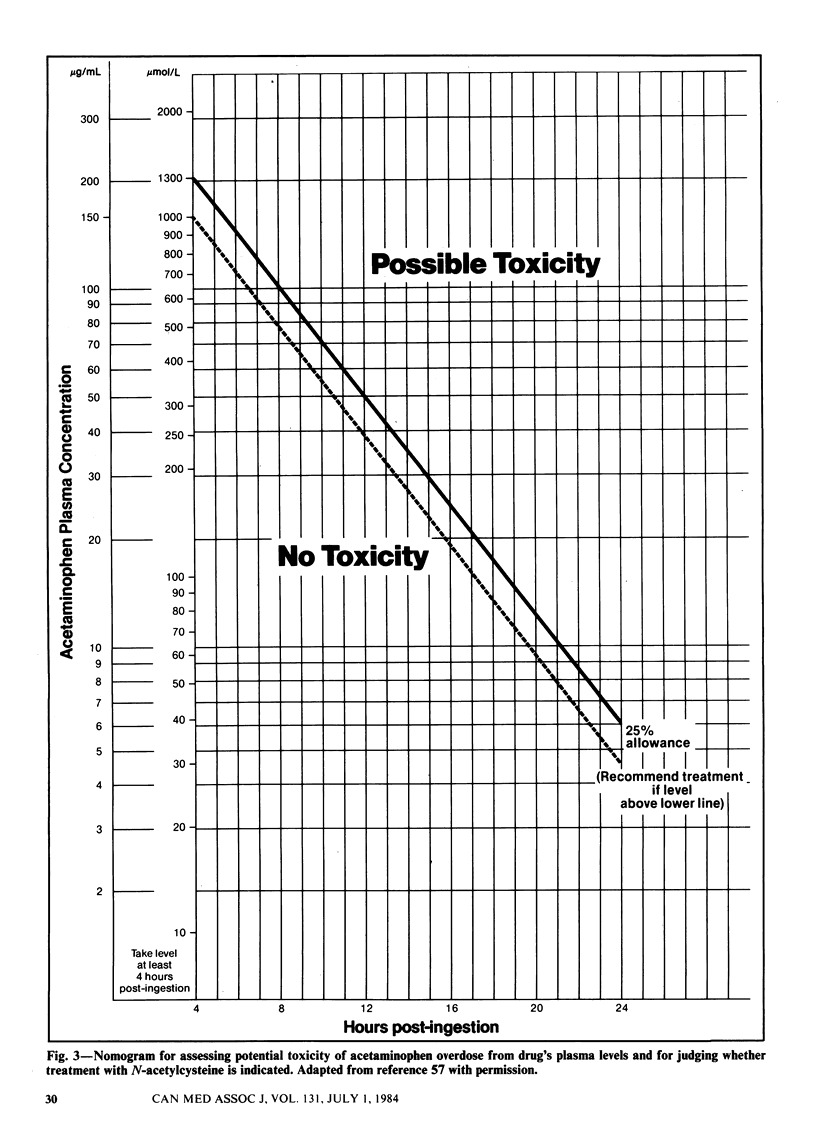
Acetaminophen is an effective analgesic and antipyretic agent with few adverse effects when used in recommended dosages. The drug is metabolized mainly in the liver, and the several end products have no harmful effects. An intermediate compound in a minor metabolic pathway, however, is toxic; it is normally inactivated by glutathione. In the case of an acetaminophen overdose the hepatic stores of glutathione seem to become depleted, leaving the toxic intermediate free to damage liver tissue. Such damage is unlikely to occur unless the plasma concentration of acetaminophen peaks above 150 micrograms/mL--a level far in excess of the 5 to 20 micrograms/mL achieved with therapeutic doses of the drug. Long-term therapeutic use of acetaminophen does not appear to be associated with liver damage, although some case reports suggest the possibility. Acetaminophen poisoning follows an acute overdose and, if untreated, is manifested clinically by an initial phase of nonspecific signs and symptoms, a latent period in which the liver transaminase levels rise and then, 3 to 5 days after the ingestion, signs of more serious hepatic dysfunction. Most patients do not progress beyond the first or second phase. They and those who survive the third phase recover with no residual injury to the liver. Appropriate antidotal therapy markedly reduces the severity of the initial damage.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abernethy D. R., Greenblatt D. J., Divoll M., Ameer B., Shader R. I. Differential effect of cimetidine on drug oxidation (antipyrine and diazepam) vs. conjugation (acetaminophen and lorazepam): prevention of acetaminophen toxicity by cimetidine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1983 Mar;224(3):508–513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambre J., Alexander M. Liver toxicity after acetaminophen ingestion. Inadequacy of the dose estimate as an index of risk. JAMA. 1977 Aug 8;238(6):500–501. doi: 10.1001/jama.238.6.500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ameer B., Greenblatt D. J. Acetaminophen. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Aug;87(2):202–209. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-2-202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barker J. D., Jr, de Carle D. J., Anuras S. Chronic excessive acetaminophen use and liver damage. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):299–301. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson G. D. Acetaminophen in chronic liver disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1983 Jan;33(1):95–101. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1983.14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonkowsky H. L., Mudge G. H., McMurtry R. J. Chronic hepatic inflammation and fibrosis due to low doses of paracetamol. Lancet. 1978 May 13;1(8072):1016–1018. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(78)90740-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer T. D., Rouff S. L. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis and renal failure. JAMA. 1971 Oct 18;218(3):440–441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridges R. R., Kinniburgh D. W., Keehn B. J., Jennison T. A. An evaluation of common methods for acetaminophen quantitation for small hospitals. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1983 Mar;20(1):1–17. doi: 10.3109/15563658308990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLGAN M. T., MINTZ A. A. The comparative antipyretic effect of N-acetyl-p-aminophenol and acetylsalicylic acid. J Pediatr. 1957 May;50(5):552–555. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(57)80219-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. A., Heading R. C., Nimmo W. S., Prescott L. F. Kinetics of acetaminophen absorption and gastric emptying in man. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1978 Oct;24(4):420–431. doi: 10.1002/cpt1978244420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobden I., Record C. O., Ward M. K., Kerr D. N. Paracetamol-induced acute renal failure in the absence of fulminant liver damage. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1982 Jan 2;284(6308):21–22. doi: 10.1136/bmj.284.6308.21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. B., Burk R. F. Acetaminophen overdoses at a county hospital: a year's experience. South Med J. 1978 Nov;71(11):1359-63, 1365. doi: 10.1097/00007611-197811000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper S. A., Beaver W. T. A model to evaluate mild analgesics in oral surgery outpatients. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1976 Aug;20(2):241–250. doi: 10.1002/cpt1976202241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran G. B., Mitchell J. R., Vaishnav Y. N., Horning E. C. Evidence that acetaminophen and N-hydroxyacetaminophen form a common arylating intermediate, N-acetyl-p-benzoquinoneimine. Mol Pharmacol. 1980 Nov;18(3):536–542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosh J. A. Anti-inflammatory drugs in rheumatic diseases. Practitioner. 1974 Oct;213(1276 Spec No):519–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critchley J. A., Dyson E. H., Scott A. W., Jarvie D. R., Prescott L. F. Is there a place for cimetidine or ethanol in the treatment of paracetamol poisoning? Lancet. 1983 Jun 18;1(8338):1375–1376. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(83)92150-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curry R. W., Jr, Robinson J. D., Sughrue M. J. Acute renal failure after acetaminophen ingestion. JAMA. 1982 Feb 19;247(7):1012–1014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson D. G., Eastham W. N. Acute liver necrosis following overdose of paracetamol. Br Med J. 1966 Aug 27;2(5512):497–499. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5512.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flower R. J., Vane J. R. Inhibition of prostaglandin synthetase in brain explains the anti-pyretic activity of paracetamol (4-acetamidophenol). Nature. 1972 Dec 15;240(5381):410–411. doi: 10.1038/240410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest J. A., Adriaenssens P., Finlayson N. D., Prescott L. F. Paracetamol metabolism in chronic liver disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;15(6):427–431. doi: 10.1007/BF00561743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrest J. A., Clements J. A., Prescott L. F. Clinical pharmacokinetics of paracetamol. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1982 Mar-Apr;7(2):93–107. doi: 10.2165/00003088-198207020-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfinger R., Ahmed K. S., Pitchumoni C. S., Weseley S. A. Concomitant alcohol and drug abuse enhancing acetaminophen toxicity. Report of a case. Am J Gastroenterol. 1978 Oct;70(4):385–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamlyn A. N., Douglas A. P., James O. F., Lesna M., Watson A. J. Liver function and structure in survivors of acetaminophen poisoning. A follow-up study of serum bile acids and liver histology. Am J Dig Dis. 1977 Jul;22(7):605–610. doi: 10.1007/BF01073078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henriques C. C. Acetaminophen sensitivity and fixed dermatitis. JAMA. 1970 Dec 28;214(13):2336–2336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ho S. W., Beilin L. J. Asthma associated with N-acetylcysteine infusion and paracetamol poisoning: report of two cases. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1983 Sep 24;287(6396):876–877. doi: 10.1136/bmj.287.6396.876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkinson J. H., 3rd, Bartlett F. H., Jr, Steffens A. O., McGlumphy T. H., Macht E. L., Smith M. Acetaminophen versus propoxyphene hydrochloride for relief of pain in episiotomy patients. J Clin Pharmacol. 1973 Jul;13(7):251–263. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1973.tb00265.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter J. Study of antipyretic therapy in current use. Arch Dis Child. 1973 Apr;48(4):313–315. doi: 10.1136/adc.48.4.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. K., Tolman K. G. Chronic liver disease and acetaminophen. Ann Intern Med. 1977 Sep;87(3):302–304. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-87-3-302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleinman J. G., Breitenfield R. V., Roth D. A. Acute renal failure associated with acetaminophen ingestion: report of a case and review of the literature. Clin Nephrol. 1980 Oct;14(4):201–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korberly B. H., Schreiber G. F., Kilkuts A., Orkand R. K., Segal H. Evaluation of acetaminophen and aspirin in the relief of preoperative dental pain. J Am Dent Assoc. 1980 Jan;100(1):39–42. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.1980.0038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Licht H., Seeff L. B., Zimmerman H. J. Apparent potentiation of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity by alcohol. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Apr;92(4):511–511. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-4-511_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mancini R. E., Sonawane B. R., Yaffe S. J. Developmental susceptibility to acetaminophen toxicity. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1980 Mar;27(3):603–606. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matts S. G. Headache. Br J Clin Pract. 1972 Aug;26(8):361–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClain C. J., Kromhout J. P., Peterson F. J., Holtzman J. L. Potentiation of acetaminophen hepatotoxicity by alcohol. JAMA. 1980 Jul 18;244(3):251–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehlisch D. R. Review of the comparative analgesic efficacy of salicylates, acetaminophen, and pyrazolones. Am J Med. 1983 Nov 14;75(5A):47–52. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90232-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meredith T. J., Goulding R. Paracetamol. Postgrad Med J. 1980 Jul;56(657):459–473. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.56.657.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills J. A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1974 Apr 4;290(14):781–784. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197404042901406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milton A. S. Modern views on the pathogenesis of fever and the mode of action of antipyretic drugs. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1976 Apr;28(4 Suppl):393–399. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1976.tb04186.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. R., Thorgeirsson S. S., Potter W. Z., Jollow D. J., Keiser H. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic injury: protective role of glutathione in man and rationale for therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1974 Oct;16(4):676–684. doi: 10.1002/cpt1974164676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moertel C. G., Ahmann D. L., Taylor W. F., Schwartau N. A comparative evaluation of marketed analgesic drugs. N Engl J Med. 1972 Apr 13;286(15):813–815. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197204132861504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger J., Davis M., Williams R. Long-term ingestion of paracetamol and liver disease. J R Soc Med. 1980 Oct;73(10):701–707. doi: 10.1177/014107688007301004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter W. Z., Thorgeirsson S. S., Jollow D. J., Mitchell J. R. Acetaminophen-induced hepatic necrosis. V. Correlation of hepatic necrosis, covalent binding and glutathione depletion in hamsters. Pharmacology. 1974;12(3):129–143. doi: 10.1159/000136531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F. Analgesic nephropathy: a reassessment of the role of phenacetin and other analgesics. Drugs. 1982 Jan-Feb;23(1-2):75–149. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198223010-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Critchley J. A., Balali-Mood M., Pentland B. Effects of microsomal enzyme induction on paracetamol metabolism in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1981 Aug;12(2):149–153. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1981.tb01193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F., Illingworth R. N., Critchley J. A., Stewart M. J., Adam R. D., Proudfoot A. T. Intravenous N-acetylcystine: the treatment of choice for paracetamol poisoning. Br Med J. 1979 Nov 3;2(6198):1097–1100. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.6198.1097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prescott L. F. Paracetamol overdosage. Pharmacological considerations and clinical management. Drugs. 1983 Mar;25(3):290–314. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198325030-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins M. D., Henderson D. B., Hijab A. R. Pharmacokinetics of paracetamol (acetaminophen) after intravenous and oral administration. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1977 Apr 20;11(4):283–286. doi: 10.1007/BF00607678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rollins D. E., von Bahr C., Glaumann H., Moldéus P., Rane A. Acetaminophen: potentially toxic metabolite formed by human fetal and adult liver microsomes and isolated fetal liver cells. Science. 1979 Sep 28;205(4413):1414–1416. doi: 10.1126/science.38505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin T. N., Tomosada W. P. The pain cocktail as an adjunctive agent in the treatment of spine pain patients. Drug Intell Clin Pharm. 1981 Dec;15(12):958–963. doi: 10.1177/106002808101501207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruffalo R. L., Thompson J. F. Cimetidine and acetylcysteine as antidote for acetaminophen overdose. South Med J. 1982 Aug;75(8):954–958. doi: 10.1097/00007611-198208000-00013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumack B. H. Acetaminophen overdose. Am J Med. 1983 Nov 14;75(5A):104–112. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(83)90240-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumack B. H., Matthew H. Acetaminophen poisoning and toxicity. Pediatrics. 1975 Jun;55(6):871–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumack B. H., Peterson R. C., Koch G. G., Amara I. A. Acetaminophen overdose. 662 cases with evaluation of oral acetylcysteine treatment. Arch Intern Med. 1981 Feb 23;141(3 Spec No):380–385. doi: 10.1001/archinte.141.3.380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rumack B. H., Peterson R. G. Acetaminophen overdose: incidence, diagnosis, and management in 416 patients. Pediatrics. 1978 Nov;62(5 Pt 2 Suppl):898–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sellers E. M., Freedman F. Treatment of acetaminophen poisoning. Can Med Assoc J. 1981 Oct 15;125(8):827–829. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seymour R. A. Analgesic efficacy and plasma concentration of three analgesics in pain after lower third molar removal. SAAD Dig. 1983 Jul;5(7):172–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shnaps Y., Halkin H., Dany S., Tirosh M. Inadequacy of reported intake in assessing the potential hepatotoxicity of acetaminophen overdose. Isr J Med Sci. 1980 Nov;16(11):752–755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarlin L., Landrigan P., Babineau R., Alpert J. J. A comparison of the antipyretic effect of acetaminophen and aspirin. Another approach to poison prevention. Am J Dis Child. 1972 Dec;124(6):880–882. doi: 10.1001/archpedi.1972.02110180082011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vale J. A., Wheeler D. C. Anaphylactoid reaction to acetylcysteine. Lancet. 1982 Oct 30;2(8305):988–988. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)90188-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton N. G., Mann T. A., Shaw K. M. Anaphylactoid reaction to N-acetylcysteine. Lancet. 1979 Dec 15;2(8155):1298–1298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)92306-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ware A. J., Upchurch K. S., Eigenbrodt E. H., Norman D. A. Acetaminophen and the liver. Ann Intern Med. 1978 Feb;88(2):267–268. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-88-2-267. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. R., Gault M. H. Declining incidence of analgesic nephropathy in Canada. Can Med Assoc J. 1982 Sep 15;127(6):500–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson H. T. A fixed drug eruption due to paracetamol. Br J Dermatol. 1975 Feb;92(2):213–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1975.tb03061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson J. T., Brown R. D., Bocchini J. A., Jr, Kearns G. L. Efficacy, disposition and pharmacodynamics of aspirin, acetaminophen and choline salicylate in young febrile children. Ther Drug Monit. 1982;4(2):147–180. doi: 10.1097/00007691-198206000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrights N., Prescott L. F. Potentiation by previous drug therapy of hepatotoxicity following paracetamol overdosage. Scott Med J. 1973 Mar;18(2):56–58. doi: 10.1177/003693307301800205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


