Abstract
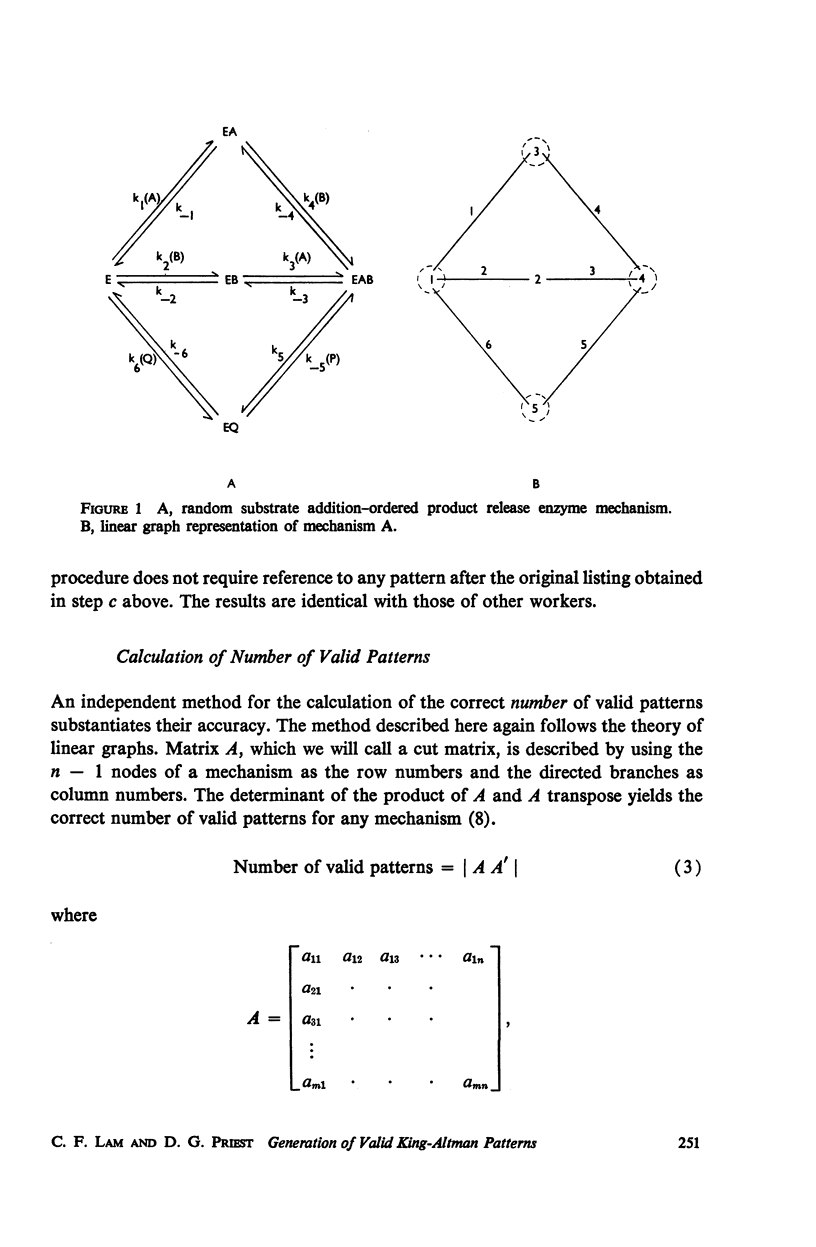
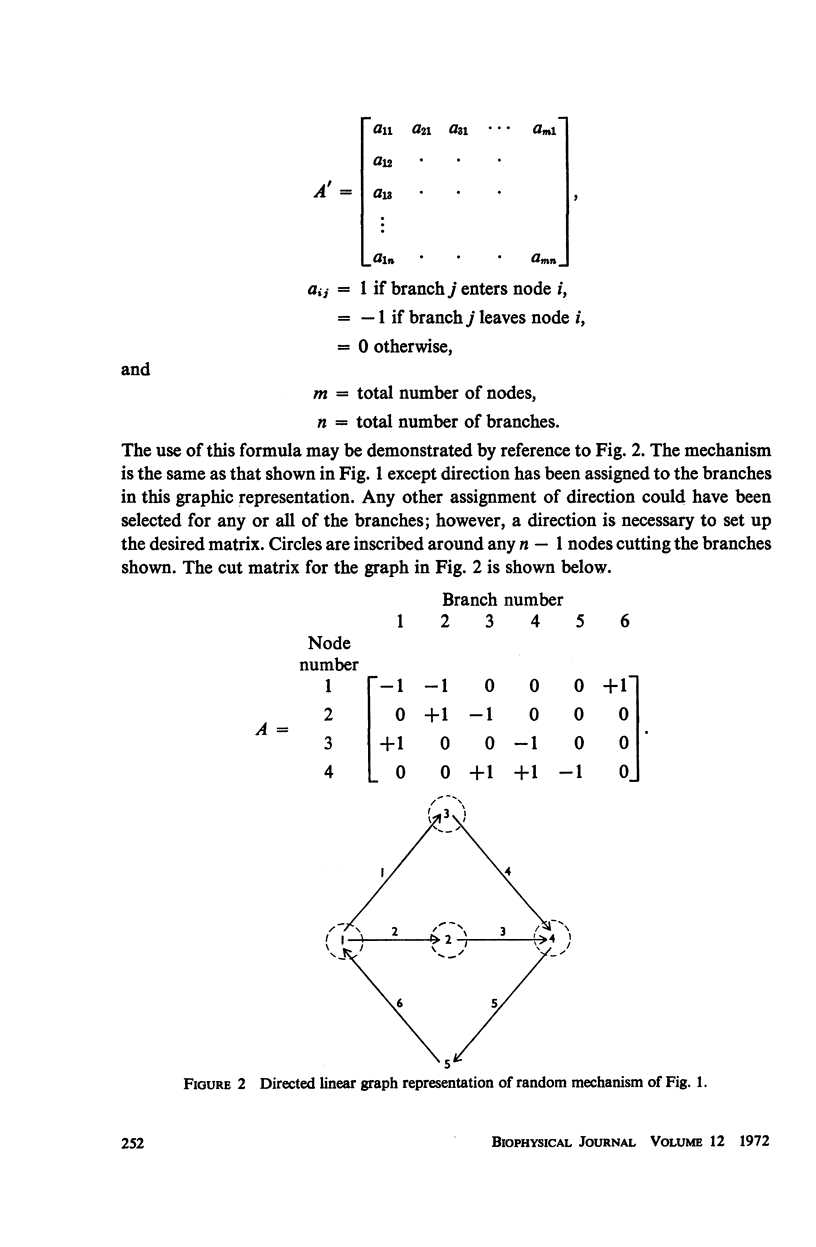
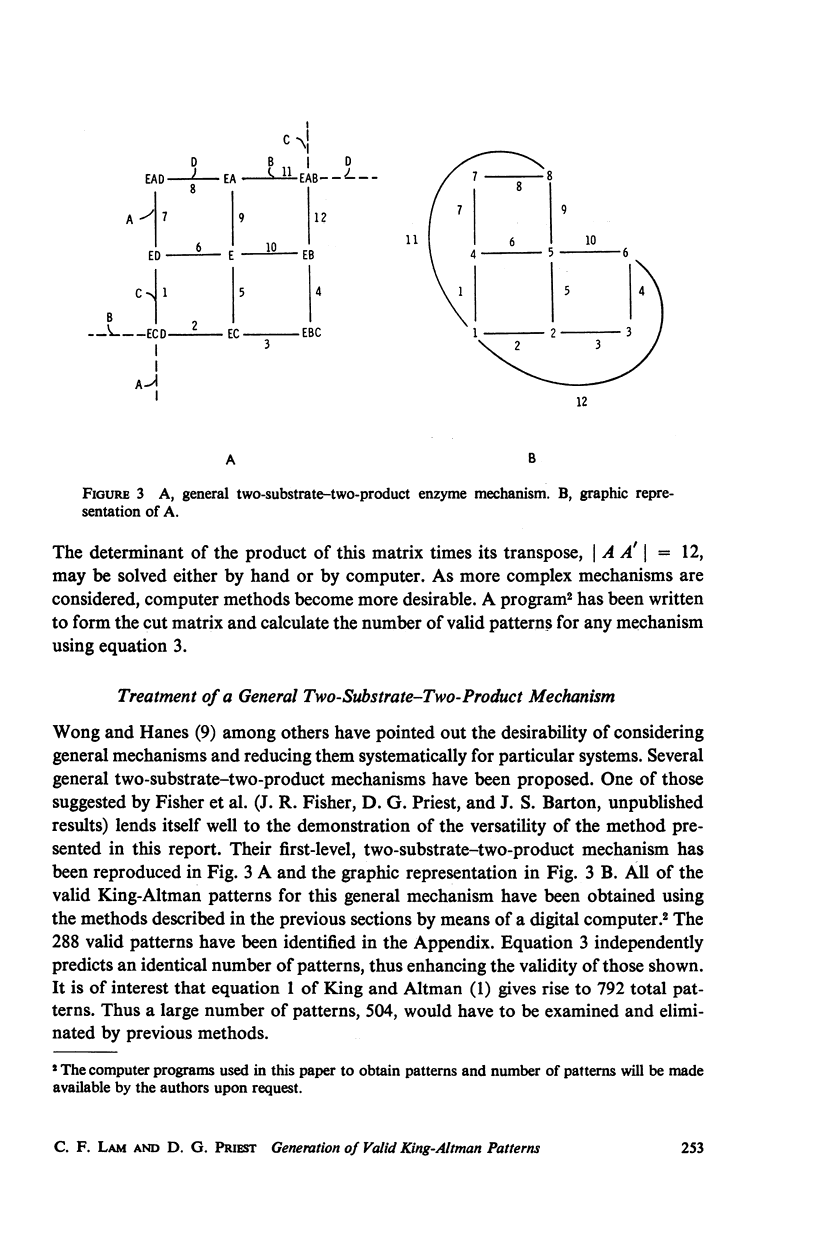
One of the most generally applicable algorithms for the derivation of steady-state rate equations for complex enzyme reaction mechanisms is that of King and Altman. Several modifications of this algorithm have been suggested; however, each requires the generation of numerous valid and invalid patterns and the subsequent elimination of those that are invalid. A method is presented, employing topological theory of linear graphs, for the systematic generation of only those patterns which are valid. This method is readily adaptable to use on a digital computer. An independent method for the calculation of the number of valid patterns is also presented. This calculation can be used to substantiate the accuracy of the patterns obtained. This calculation is also adaptable to computerization. Examples are included to demonstrate both the generation of patterns and the calculation of their number for specific enzyme mechanisms.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Fisher J. R., Hoagland V. D., Jr A systematic approach to kinetic studies of multisubstrate enzyme systems. Adv Biol Med Phys. 1968;12:163–211. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9928-3.50008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H. J. A simplified schematic method for deriving steady-state rate equations using a modification of the "theory of graphs" procedure. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1970 Aug 11;40(3):692–697. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(70)90959-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WONG J. T., HANES C. S. Kinetic formulations for enzymic reactions involving two substrates. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1962 Jun;40:763–804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


