Abstract
The proposition is made that the red cell membrane is a two-dimensional, incompressible material and a general stress-strain law is developed for finite deformations. In the linear form, the character of such a material is analogous to a two-dimensional Mooney material (e.g., rubber), indicating that the molecular structure in the plane of the membrane would consist of long chains, randomly kinked and cross-linked in the natural state. The loose network could be provided by the protein component and the lipid phase could exist interstitially as a liquid bilayer, giving the membrane its two-dimensional incompressibility. The material provides the capability of large deformations exhibited by the discocyte and yet the rigidity associated with the osmotic spherocyte state. It is demonstrated that a membrane of this type can form a sphere at constant area. An illustrative example of the application to single cell discocyte-to-osmotic spherocyte transformations is presented.
Full text
PDF









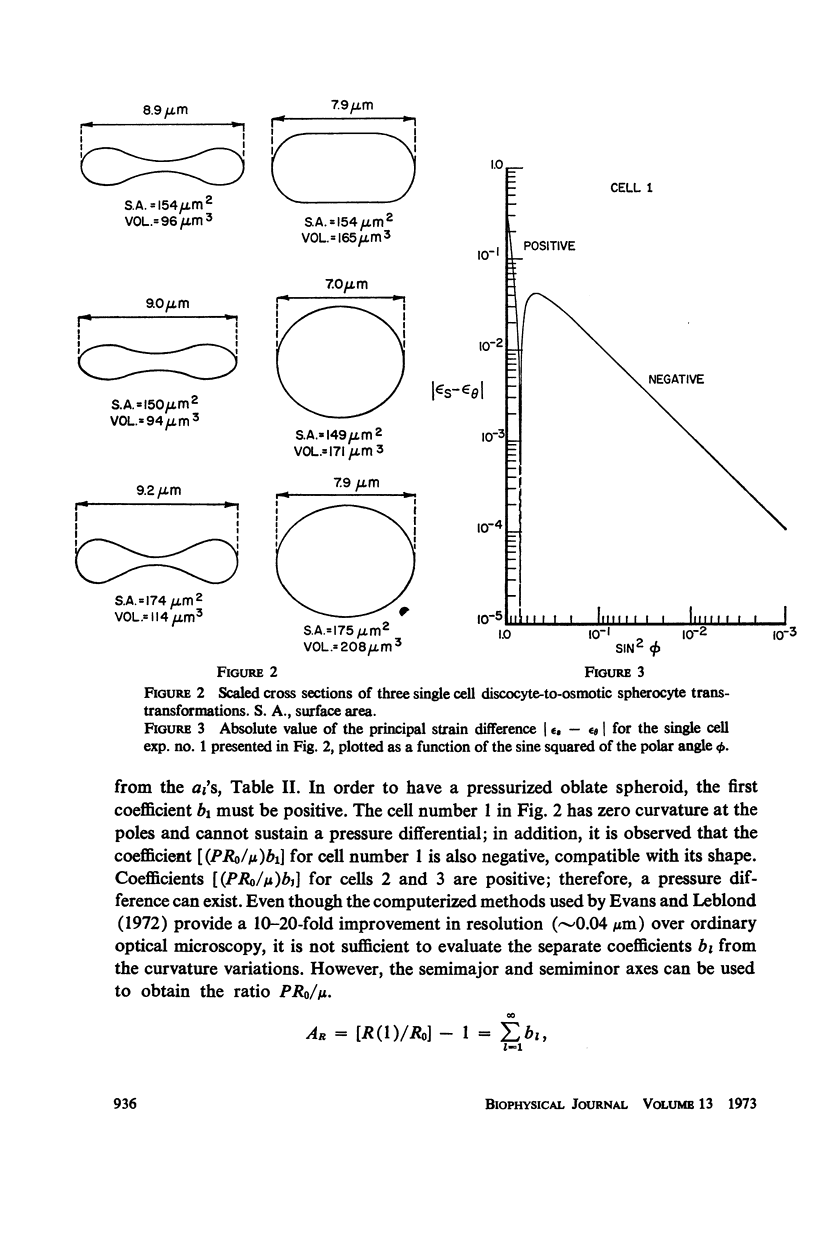




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bessis M., Lessin L. S. The discocyte-echinocyte equilibrium of the normal and pathologic red cell. Blood. 1970 Sep;36(3):399–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canham P. B. The minimum energy of bending as a possible explanation of the biconcave shape of the human red blood cell. J Theor Biol. 1970 Jan;26(1):61–81. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(70)80032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E., Fung Y. C. Improved measurements of the erythrocyte geometry. Microvasc Res. 1972 Oct;4(4):335–347. doi: 10.1016/0026-2862(72)90069-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C. Theoretical considerations of the elasticity of red cells and small blood vessels. Fed Proc. 1966 Nov-Dec;25(6):1761–1772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fung Y. C., Tong P. Theory of the sphering of red blood cells. Biophys J. 1968 Feb;8(2):175–198. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86484-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldsmith H. L. Deformation of human red cells in tube flow. Biorheology. 1971 May;7(4):235–242. doi: 10.3233/bir-1971-7407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochmuth R. M., Mohandas N. Uniaxial loading of the red-cell membrane. J Biomech. 1972 Sep;5(5):501–509. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(72)90007-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lew H. S. Electro-tension and torque in biological membranes modeled as a dipole sheet in fluid conductors. J Biomech. 1972 Jul;5(4):399–408. doi: 10.1016/0021-9290(72)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez L., Duck I. M., Hunt W. A. On the shape of the erythrocyte. Biophys J. 1968 Nov;8(11):1228–1235. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(68)86552-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P., BURTON A. C. Area and volume changes in hemolysis of single erythrocytes. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1963 Jun;61:245–253. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030610306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P., BURTON A. C. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. I. MEMBRANE STIFFNESS AND INTRACELLULAR PRESSURE. Biophys J. 1964 Mar;4:115–135. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86773-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAND R. P. MECHANICAL PROPERTIES OF THE RED CELL MEMBRANE. II. VISCOELASTIC BREAKDOWN OF THE MEMBRANE. Biophys J. 1964 Jul;4:303–316. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3495(64)86784-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer S. J., Nicolson G. L. The fluid mosaic model of the structure of cell membranes. Science. 1972 Feb 18;175(4023):720–731. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4023.720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalak R., Branemark P. I. Deformation of red blood cells in capillaries. Science. 1969 May 9;164(3880):717–719. doi: 10.1126/science.164.3880.717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skalak R., Tozeren A., Zarda R. P., Chien S. Strain energy function of red blood cell membranes. Biophys J. 1973 Mar;13(3):245–264. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85983-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


