Abstract
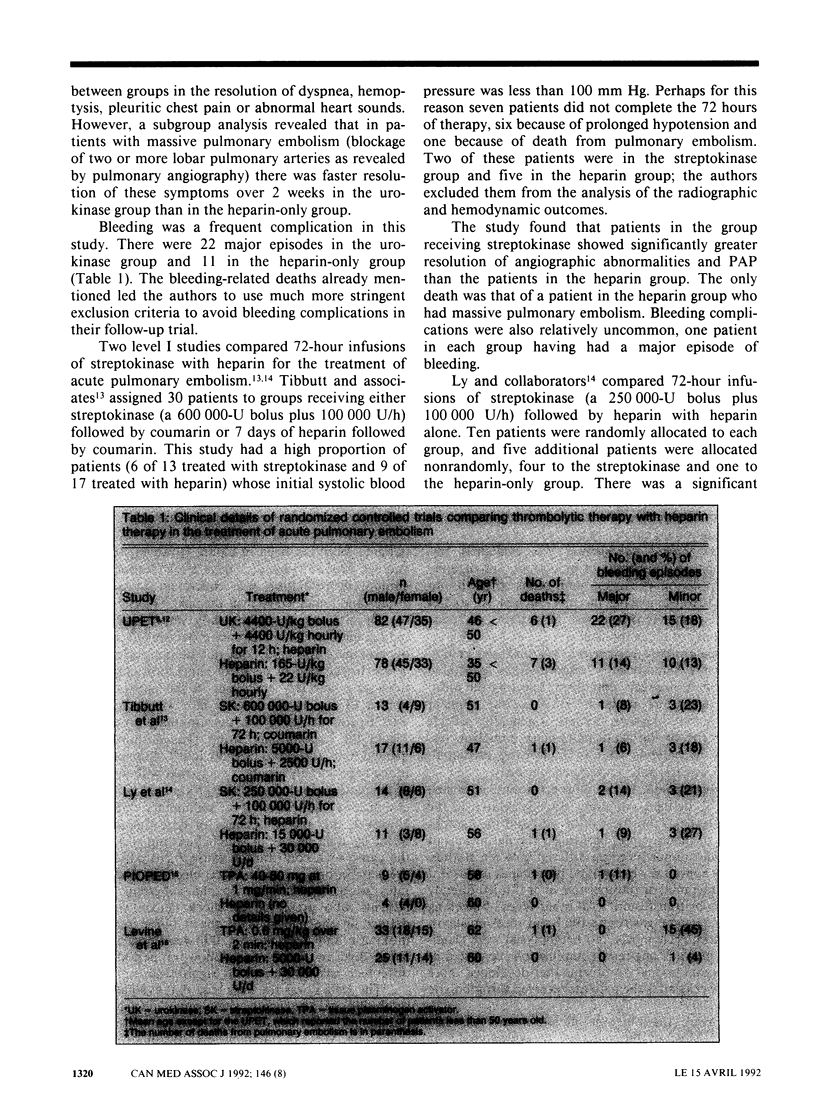
OBJECTIVES: To determine whether thrombolytic therapy reduces the rate of death or complications in patients with acute pulmonary embolism and whether a particular thrombolytic regimen is more effective than others. DATA SOURCES: The key words "fibrinolytic agents," "plasminogen activators," "streptokinase," "urokinase" and "pulmonary embolism" were used to search MEDLINE for relevant articles in English; the bibliographies of these articles were reviewed for additional publications. STUDY SELECTION: Articles were included if they were of a randomized controlled design; 10 such articles were found. DATA EXTRACTION: Ten trials were appraised with the use of the following methodologic criteria: a clear description of the study population; use of objective criteria to diagnose pulmonary embolism and to assess outcomes; use of clinically relevant outcomes; and blinded outcome assessments. RESULTS: In the nine trials that met the methodologic criteria thrombolytic therapy led to a more rapid resolution of the radiographic and hemodynamic abnormalities associated with acute pulmonary embolism than did anticoagulant therapy alone, although these benefits were short-lived. No difference was detected in the death rate or the resolution of symptoms between patients receiving thrombolytic therapy and those receiving anticoagulant therapy alone. In addition, bleeding complications were more frequent and serious in patients who received lytic therapy, although these events were related to the use of invasive procedures. CONCLUSION: There is a lack of evidence that thrombolytic therapy improves clinically relevant outcomes of patients with acute pulmonary embolism. This may be a reflection of the small sample size of the clinical trials. Further research is required to define the role of thrombolytic therapy in the management of patients with acute pulmonary embolism.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARRITT D. W., JORDAN S. C. Anticoagulant drugs in the treatment of pulmonary embolism. A controlled trial. Lancet. 1960 Jun 18;1(7138):1309–1312. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(60)92299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalen J. E., Alpert J. S. Natural history of pulmonary embolism. Prog Cardiovasc Dis. 1975 Jan-Feb;17(4):259–270. doi: 10.1016/s0033-0620(75)80017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillum R. F. Pulmonary embolism and thrombophlebitis in the United States, 1970-1985. Am Heart J. 1987 Nov;114(5):1262–1264. doi: 10.1016/0002-8703(87)90212-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giuntini C., Marini C., Di Ricco G., Palla R., Giacomelli V., Rindi M. A controlled clinical trial on the effect of heparin infusion and two regimens of urokinase in acute pulmonary embolism. G Ital Cardiol. 1984;14 (Suppl 1):26–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldhaber S. Z., Kessler C. M., Heit J., Markis J., Sharma G. V., Dawley D., Nagel J. S., Meyerovitz M., Kim D., Vaughan D. E. Randomised controlled trial of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator versus urokinase in the treatment of acute pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 1988 Aug 6;2(8606):293–298. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(88)92354-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine M., Hirsh J., Weitz J., Cruickshank M., Neemeh J., Turpie A. G., Gent M. A randomized trial of a single bolus dosage regimen of recombinant tissue plasminogen activator in patients with acute pulmonary embolism. Chest. 1990 Dec;98(6):1473–1479. doi: 10.1378/chest.98.6.1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loscalzo J., Braunwald E. Tissue plasminogen activator. N Engl J Med. 1988 Oct 6;319(14):925–931. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198810063191407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ly B., Arnesen H., Eie H., Hol R. A controlled clinical trial of streptokinase and heparin in the treatment of major pulmonary embolism. Acta Med Scand. 1978;203(6):465–470. doi: 10.1111/j.0954-6820.1978.tb14909.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marder V. J., Sherry S. Thrombolytic therapy: current status (1). N Engl J Med. 1988 Jun 9;318(23):1512–1520. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198806093182306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G. A., Sutton G. C., Kerr I. H., Gibson R. V., Honey M. Comparison of streptokinase and heparin in treatment of isolated acute massive pulmonary embolism. Br Med J. 1971 Jun 19;2(5763):681–684. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5763.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sackett D. L. Rules of evidence and clinical recommendations on the use of antithrombotic agents. Chest. 1989 Feb;95(2 Suppl):2S–4S. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma G. V., Burleson V. A., Sasahara A. A. Effect of thrombolytic therapy on pulmonary-capillary blood volume in patients with pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 1980 Oct 9;303(15):842–845. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198010093031502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tibbutt D. A., Davies J. A., Anderson J. A., Fletcher E. W., Hamill J., Holt J. M., Thomas M. L., Lee G., Miller G. A., Sharp A. A. Comparison by controlled clinical trial of streptokinase and heparin in treatment of life-threatening pulmonay embolism. Br Med J. 1974 Mar 2;1(5904):343–347. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5904.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tognoni G., Fresco C., Franzosi M. G., Maggioni A. P. Thrombolysis in acute myocardial infarction. Chest. 1991 Apr;99(4 Suppl):121S–127S. doi: 10.1378/chest.99.4.121s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urokinase versus tissue plasminogen activator in pulmonary embolism. Lancet. 1988 Sep 17;2(8612):691–692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstraete M., Miller G. A., Bounameaux H., Charbonnier B., Colle J. P., Lecorf G., Marbet G. A., Mombaerts P., Olsson C. G. Intravenous and intrapulmonary recombinant tissue-type plasminogen activator in the treatment of acute massive pulmonary embolism. Circulation. 1988 Feb;77(2):353–360. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.77.2.353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


