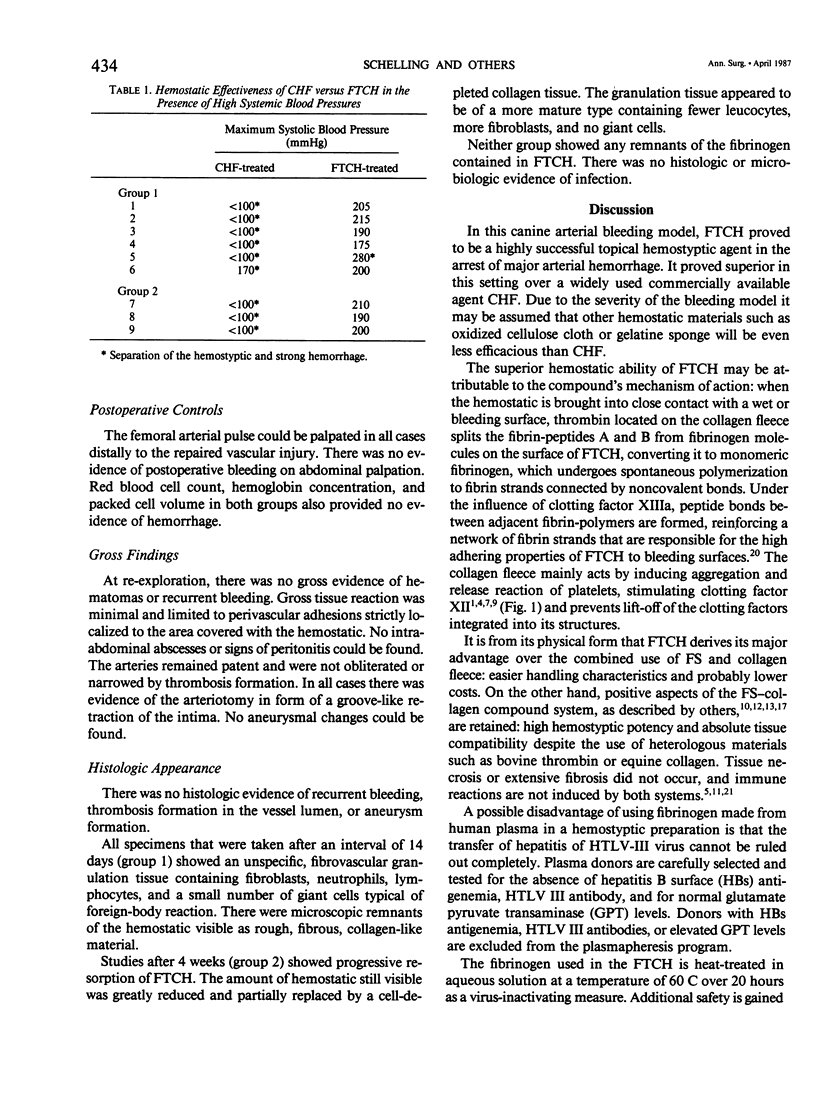
Abstract
The hemostyptic agent used in this study is a recently developed material that consists of a collagen fleece containing fibrinogen, thrombin, and aprotinin integrated into its surface (FTCH) with excellent topical hemostyptic properties. The potential use of this substance for cardiovascular surgery was evaluated in a canine arterial bleeding model, which allowed comparison of the new agent with previously used pure collagen (CHF) as well as study of the hemostyptic under elevated blood pressure conditions. The results revealed that FTCH induced reliable hemostasis in 10-mm injuries of the canine hypogastric artery up to a systolic blood pressure of 260 mmHg, whereas bleeding control by CHF alone was impossible. To assess the long-term reliability of FTCH, the dogs were re-explored at intervals of 14 and 31 days after operation. At relaparotomy, the arteries were patent and there was no evidence of recurrent bleeding, thrombosis formation, or aneurysmatic changes. Histologic examinations showed well-healed vascular lesions covered by cell-depleted collagen tissue and a partially resorped hemostyptic. FTCH will not replace adequate surgical techniques but could be useful as a quickly available and easily applicable hemostatic means in otherwise uncontrollable diffuse or acute bleeding in cardiovascular surgery.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott W. M., Austen W. G. The effectiveness and mechanism of collagen-induced topical hemostasis. Surgery. 1975 Dec;78(6):723–729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst H. G., Haverich A., Walterbusch G., Maatz W. Fibrin adhesive: an important hemostatic adjunct in cardiovascular operations. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1982 Oct;84(4):548–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun F., Holle J., Knapp W., Kovac W., Passl R., Spängler H. P. Immunologische und histologische Untersuchungen bei der Gewebeklebung mit heterologem hochkonzentriertem Fibrinogen. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 1975 Dec 26;87(24):815–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay S. The immunology of collagen. Monogr Pathol. 1983;24:120–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hait M. R., Battista O. A., Stark R. B., McCord C. W. Microcrystalline collagen as a biologic dressing, vascular prosthesis, and hemostatic agent. Surg Forum. 1969;20:51–53. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haussmann P., Mergard U. E., Köhnlein H. E. Zur Wirkung verschiedener Hämostyptika. Tierexperimentelle Untersuchungen. Fortschr Med. 1974 May 9;92(13):579–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haverich A., Walterbusch G., Borst H. G. The use of fibrin glue for sealing vascular prostheses of high porosity. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1981 Aug;29(4):252–254. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1023489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katthagen B. D., Hellstern P. In vitro-Untersuchungen über die Wirkung von gelöstem und ungelöstem heterologen Collagen-Vlies auf menschliche Thrombozyten. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb. 1984 Sep-Oct;122(5):677–681. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1045050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhnlein H. E., Mergard U. Experimentelle Testung likaler Hämostyptica. Chirurg. 1972 Aug;43(8):378–381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köveker G. Clinical application of fibrin glue in cardiovascular surgery. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1982 Aug;30(4):228–229. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1022392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgenstern L. Microcrystalline collagen used in experimental splenic injury. A new surface hemostatic agent. Arch Surg. 1974 Jul;109(1):44–47. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.1974.01360010030006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousou J. A., Engelman R. M., Breyer R. H. Fibrin glue: an effective hemostatic agent for nonsuturable intraoperative bleeding. Ann Thorac Surg. 1984 Oct;38(4):409–410. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(10)62297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheele J., Gentsch H. H., Matteson E. Splenic repair by fibrin tissue adhesive and collagen fleece. Surgery. 1984 Jan;95(1):6–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverstein M. E., Keown K., Owen J. A., Chvapil M. Collagen fibers as a fleece hemostatic agent. J Trauma. 1980 Aug;20(8):688–694. doi: 10.1097/00005373-198008000-00010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spängler H. P., Braun F., Holle J., Moritz E., Wolner E. Die lokale Anwendung von Fibrinogen und Kollagen zur Blutstillung in der Herzchirurgie. Wien Med Wochenschr. 1976 Feb 13;126(7):86–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stemberger A., Blümel G. Fibrinogen-fibrin conversion and inhibition of fibrinolysis. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1982 Aug;30(4):209–214. doi: 10.1055/s-2007-1022389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


