Abstract
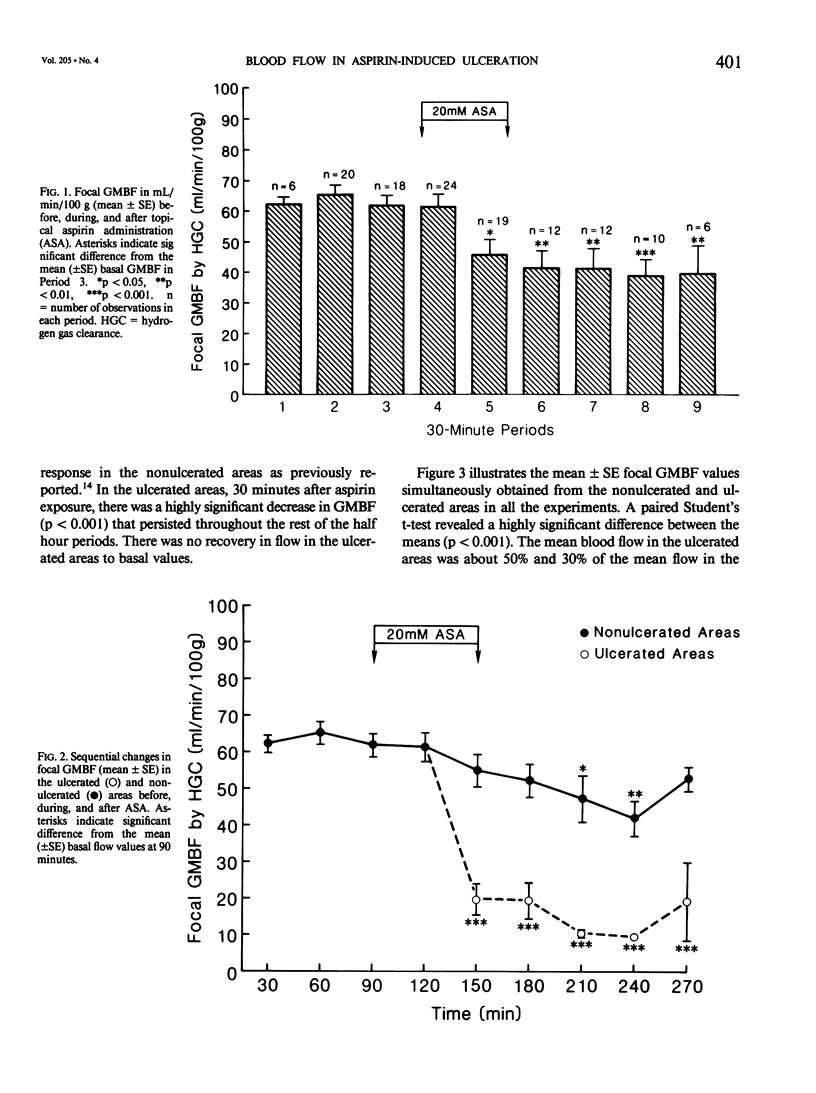
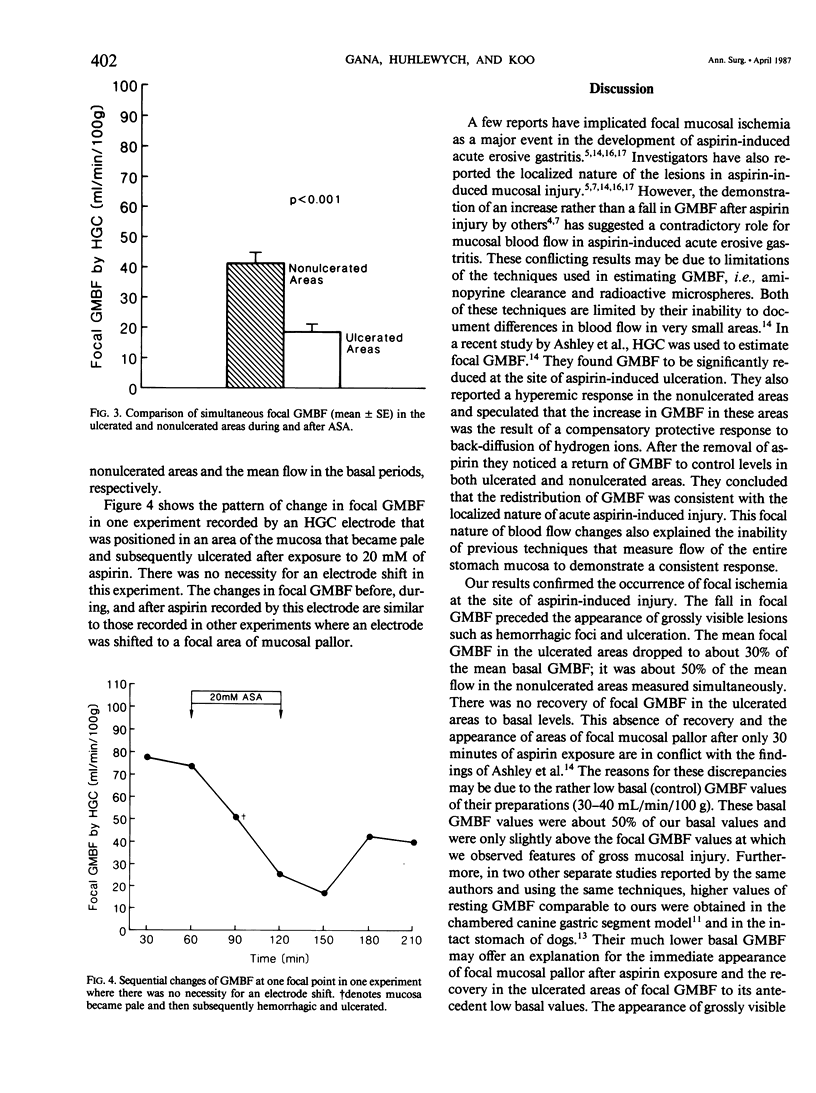
Focal gastric mucosal blood flow was studied during aspirin injury by hydrogen gas clearance in a chambered segment model of canine gastric corpus. Measurements were made simultaneously every 15 minutes at ulcerated and nonulcerated areas 1.5 hours before, during (20 mM of aspirin in 150 mM of HCl for 1 hour), and 2 hours after exposure of the mucosa to topical aspirin. There was a highly significant decrease (p less than 0.001) in flow at the ulcerated areas 30 minutes after exposure to aspirin, coinciding with the appearance of focal mucosal pallor followed by subsequent hemorrhagic foci and ulceration. This was not followed by recovery to basal flow values. Blood flow to the non-ulcerated areas was significantly but less severely reduced than in the ulcerated areas (p less than 0.05) 90 minutes after exposure to aspirin. This was followed by recovery to basal levels. It is proposed that aspirin induces reduction of focal mucosal blood flow of varying degrees and that mucosal areas with flow reduced to below a "critical value" develop gross damage.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashley S. W., Cheung L. Y. Measurements of gastric mucosal blood flow by hydrogen gas clearance. Am J Physiol. 1984 Oct;247(4 Pt 1):G339–G345. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1984.247.4.G339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashley S. W., Sonnenschein L. A., Cheung L. Y. Focal gastric mucosal blood flow at the site of aspirin-induced ulceration. Am J Surg. 1985 Jan;149(1):53–59. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(85)80009-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Augur N. A., Jr Gastric mucosal blood flow following damage by ethanol, acetic acid, or aspirin. Gastroenterology. 1970 Mar;58(3):311–320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung L. Y., Moody F. G., Reese R. S. Effect of aspirin, bile salt, and ethanol on canine gastric mucosal blood flow. Surgery. 1975 Jun;77(6):786–792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung L. Y., Sonnenschein L. A. Measurement of regional gastric mucosal blood flow by hydrogen gas clearance. Am J Surg. 1984 Jan;147(1):32–37. doi: 10.1016/0002-9610(84)90030-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm D. Drug-induced gastric mucosal injury. World J Surg. 1981 Mar;5(2):199–208. doi: 10.1007/BF01658289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung F. W., Guth P. H., Scremin O. U., Golanska E. M., Kauffman G. L., Jr Regional gastric mucosal blood flow measurements by hydrogen gas clearance in the anesthetized rat and rabbit. Gastroenterology. 1984 Jul;87(1):28–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOODY F. G., DURBIN R. P. EFFECTS OF GLYCINE AND OTHER INSTILLATES ON CONCENTRATION OF GASTRIC ACID. Am J Physiol. 1965 Jul;209:122–126. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1965.209.1.122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGreevy J. M., Moody F. G. Focal microcirculatory changes during the production of aspirin-induced gastric mucosal erosions. Surgery. 1981 Mar;89(3):337–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami M., Moriga M., Miyake T., Uchino H. Contact electrode method in hydrogen gas clearance technique: a new method for determination of regional gastric mucosal blood flow in animals and humans. Gastroenterology. 1982 Mar;82(3):457–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P., Silen W. Effect of bile salts and aspirin on the gastric mucosal blood flow. Gastroenterology. 1973 Feb;64(2):246–253. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie W. P., Jr Acute gastric mucosal damage induced by bile salts, acid, and ischemia. Gastroenterology. 1975 Apr;68(4 Pt 1):699–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie W. P., Jr Stress ulcer and erosive gastritis--introduction. World J Surg. 1981 Mar;5(2):135–137. doi: 10.1007/BF01658274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robins P. G. Ultrastructural observations on the pathogenesis of aspirin-induced gastric erosions. Br J Exp Pathol. 1980 Oct;61(5):497–504. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Semb B. K. Gastric flow measured with hydrogen clearance technique. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1979;14(6):641–646. doi: 10.3109/00365527909181930. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silen W., Merhav A., Simson J. N. The pathophysiology of stress ulcer disease. World J Surg. 1981 Mar;5(2):165–174. doi: 10.1007/BF01658279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


